Endoscope
A technology for endoscopes and bending parts, applied in the field of endoscopes, can solve the problems of changing flexibility, increasing costs, and not having, and achieve the effect of suppressing bending
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
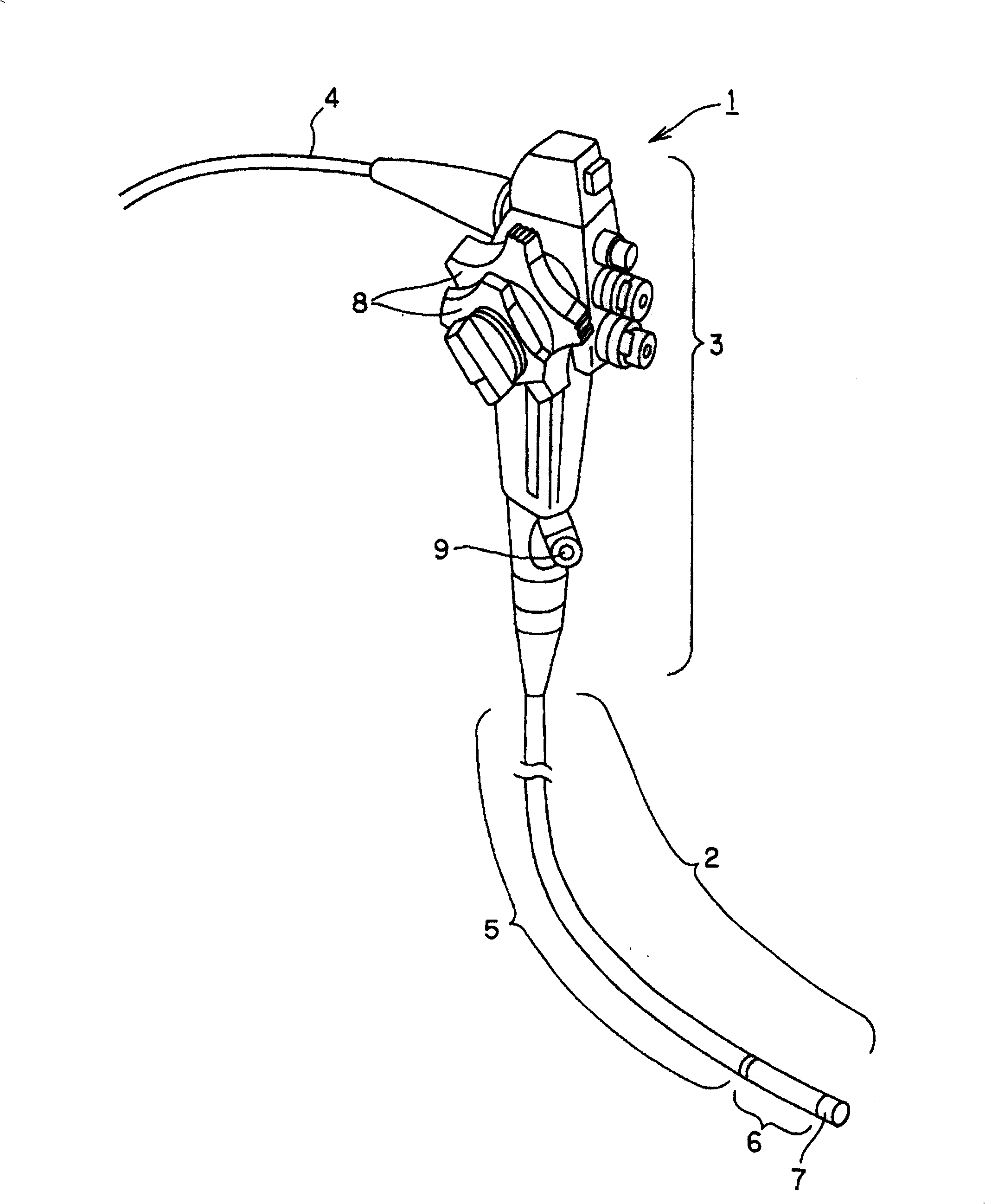
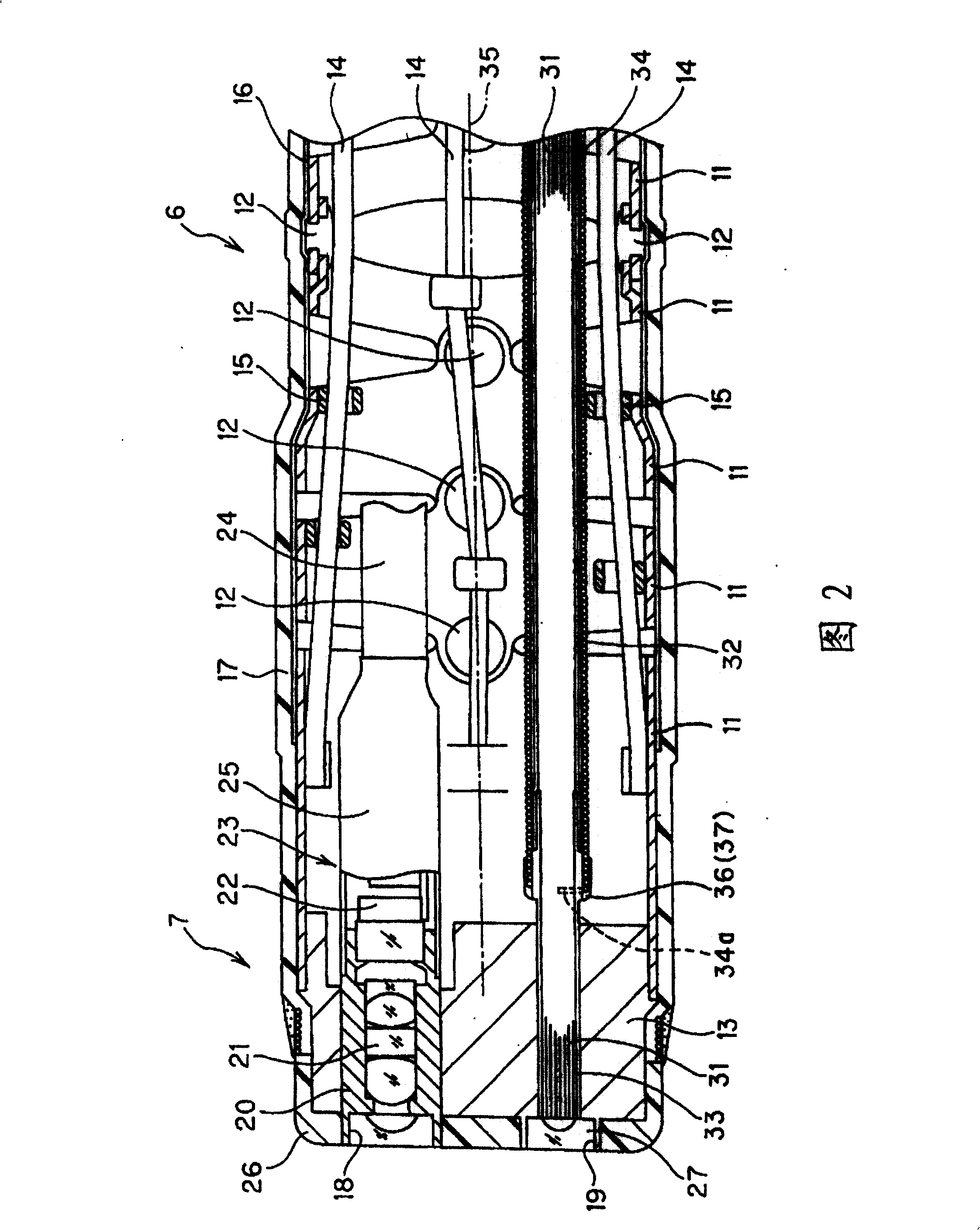
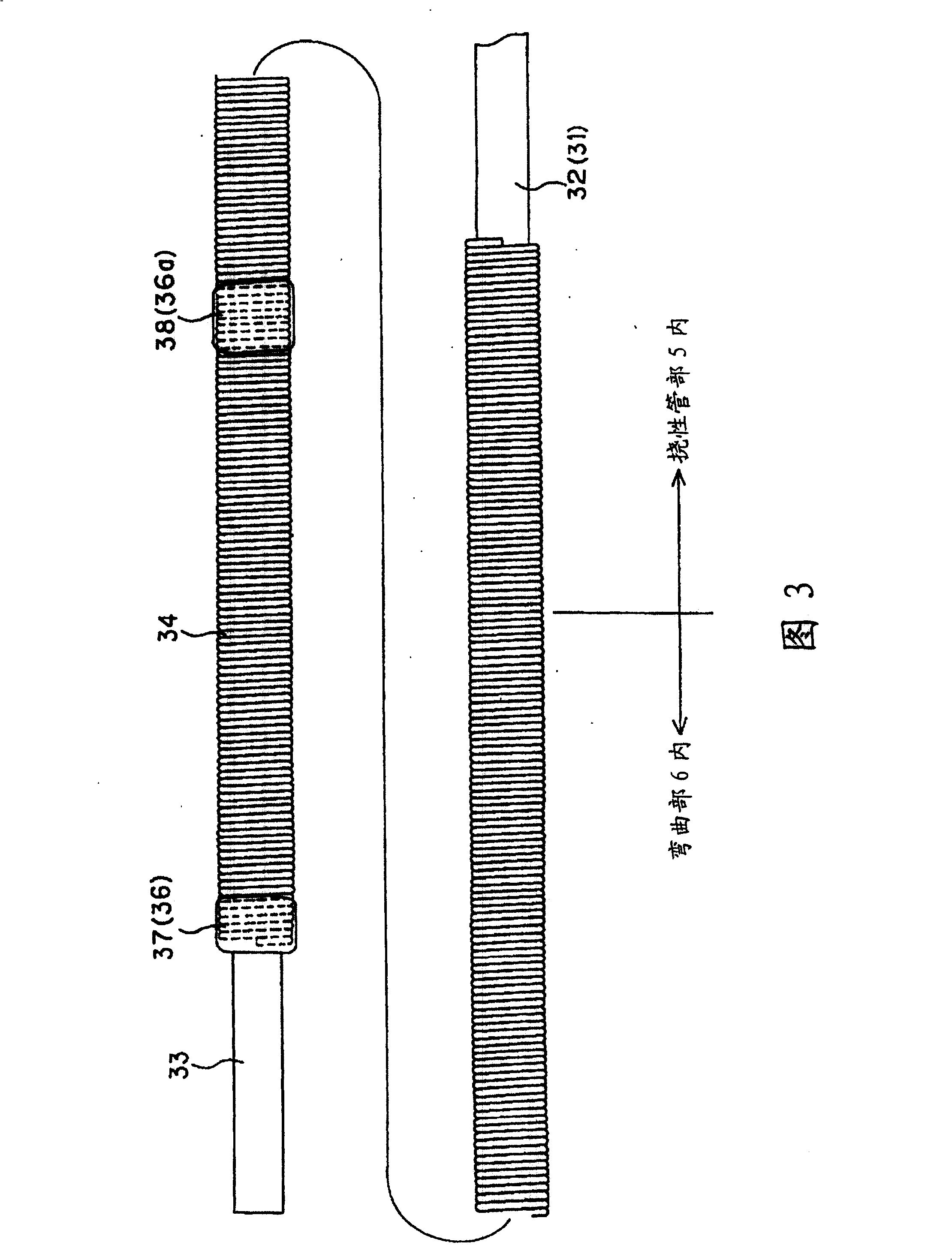
[0040] Figure 1 to Figure 13 Representing Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 1 The appearance of the endoscope according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is shown. FIG. 2 shows the internal structure of the distal end side of the insertion part. FIG. 3 shows the structure in which the optical fiber bundle is protected by a protective coil member. FIG. The position of the adhesive fixed between the wires of the protective coil component is located near the center of the bent portion in the longitudinal direction, Figure 5 Indicates that the adhesive is fixed at a position where the radius of curvature is the smallest in a state where the curved portion is bent the most.
[0041] Fig. 6 and Fig. 7 show the example of the fixing position different from the fixing position of the adhesive shown in Fig. 3, Figure 8 to Figure 10 Shows the structure of the fixing portion in the circumferential direction when fixing the wires of the protective coil component, ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Next, Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 14 and 15 . This embodiment is basically the same as the embodiment 1 except that two bending parts are provided.
[0098] FIG. 14 schematically shows the bending member 11 constituting two independent first bending parts 51 and second bending parts 52 that can be bent.
[0099] FIG. 15 shows, as an example, a state where the first bending portion 51 is bent 90° toward the DOWN side, and the second bending portion 52 is bent 90° toward the UP side. Even if the bending value is the same at 90°, the total of the bending gaps 54 on the side of the second bending part 52 formed between adjacent bending parts 11 is designed to be equal to the total of the bending gaps 53 on the side of the first bending part 51. The amount (surplus) is small. In FIG. 15 , portions of the bending member 11 forming the bending gaps 53 , 54 are shown.
[0100] Although not shown in this embodiment, the prox...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. First, its background will be explained. In Japanese Utility Model Publication No. 54-90086, an endoscope insertion aid of such a sliding tube type is disclosed. An insertion portion of a mirror and the like are inserted and penetrated therethrough, the slide tube assists insertion into a body cavity, etc., and an inflatable and contractible balloon is provided on the outer periphery of the tip portion of the slide tube.
[0108] In this sliding tube type endoscope insertion aid, in order to improve the sliding properties, it is necessary to increase the gap between the endoscope and the sliding tube. As a result, the diameter of the sliding tube cannot be avoided.
[0109] When the sliding tube is thicker, the radius of curvature of the tube itself becomes larger, which not only makes it difficult to bend at a small bending part in the body cavity, but also becomes less slidable with the intestinal tube du...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com