Bias circuits
A bias circuit and circuit technology, applied in the direction of adjusting electrical variables, instruments, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve the problems of bandgap reference and temperature sensor initial accuracy degradation, influence propagation and temperature dependence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
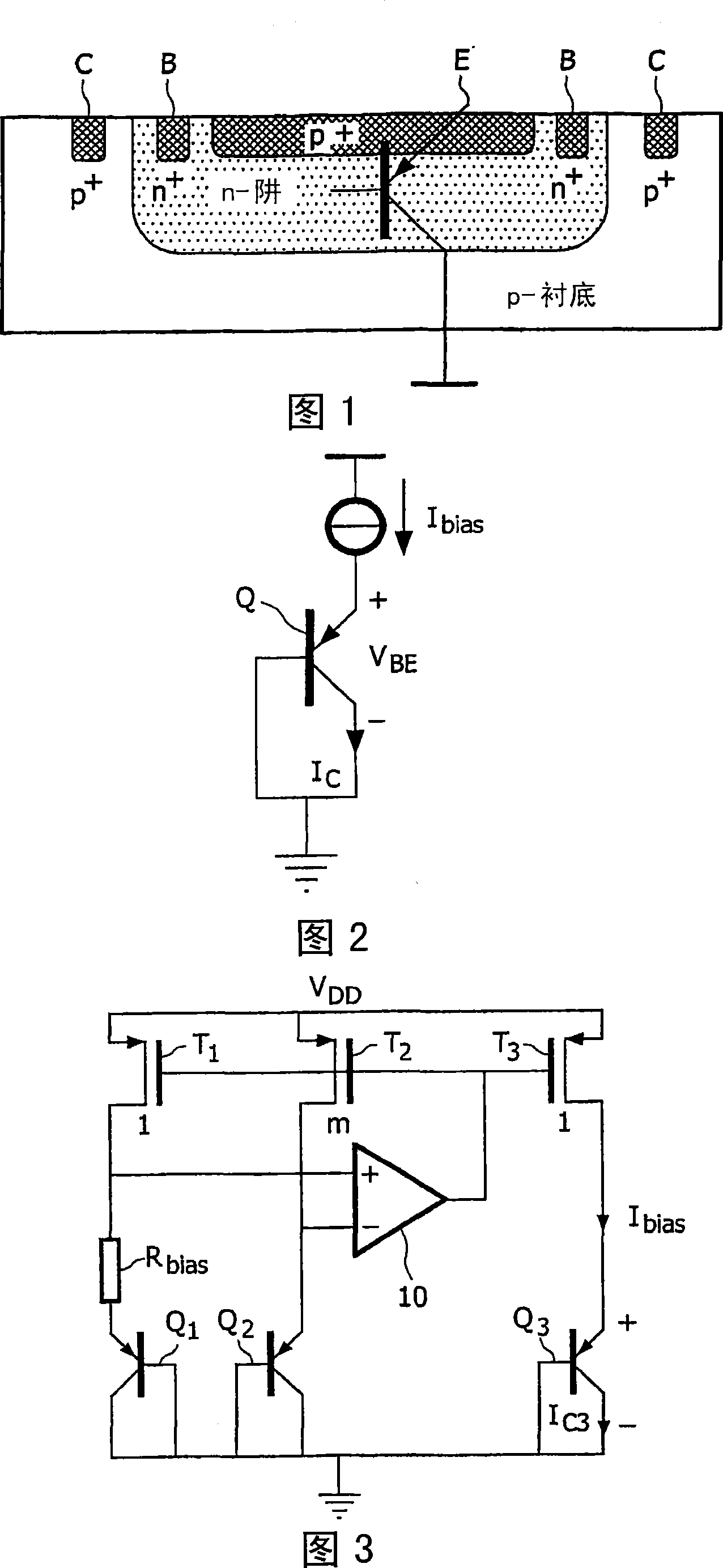
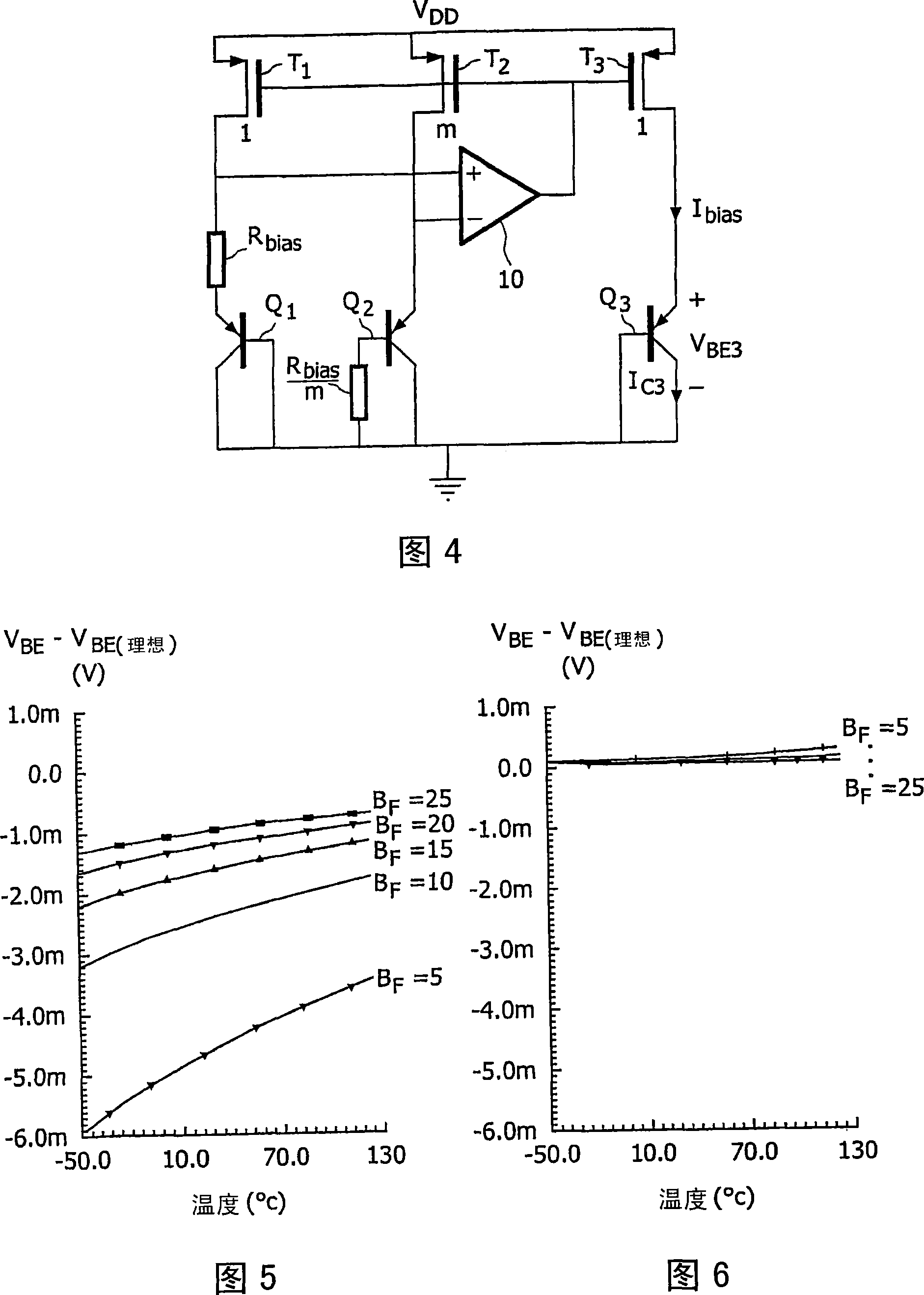
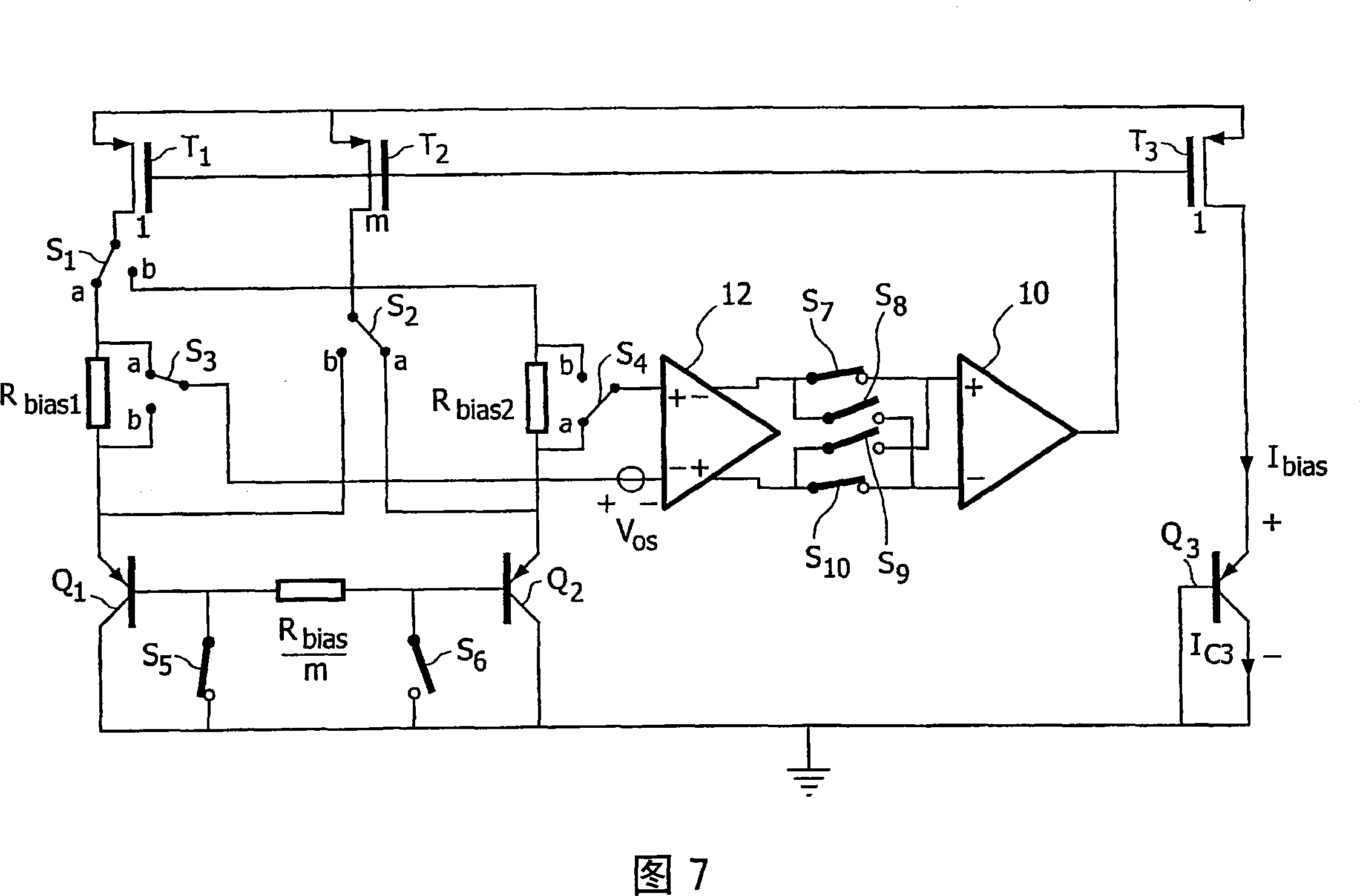
[0033] A circuit diagram of a bias circuit embodying the present invention is shown in FIG. 4 . Utilizing an additional resistor R connected in series with the base of Q2 bias / m, given by the equation for bias current I bias expression for:
[0034] V BE 1 + I bias R bias = m I bias 1 I + B F R bias m + V BE 2
[0035] ⇒ I bias = 1 + B F B ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com