Low switching frequency power factor correction circuit
A circuit and frequency technology, applied in the direction of irreversible AC power input conversion to DC power output, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, climate sustainability, etc., can solve the problems of increased cost and dissipation in the power conversion chain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
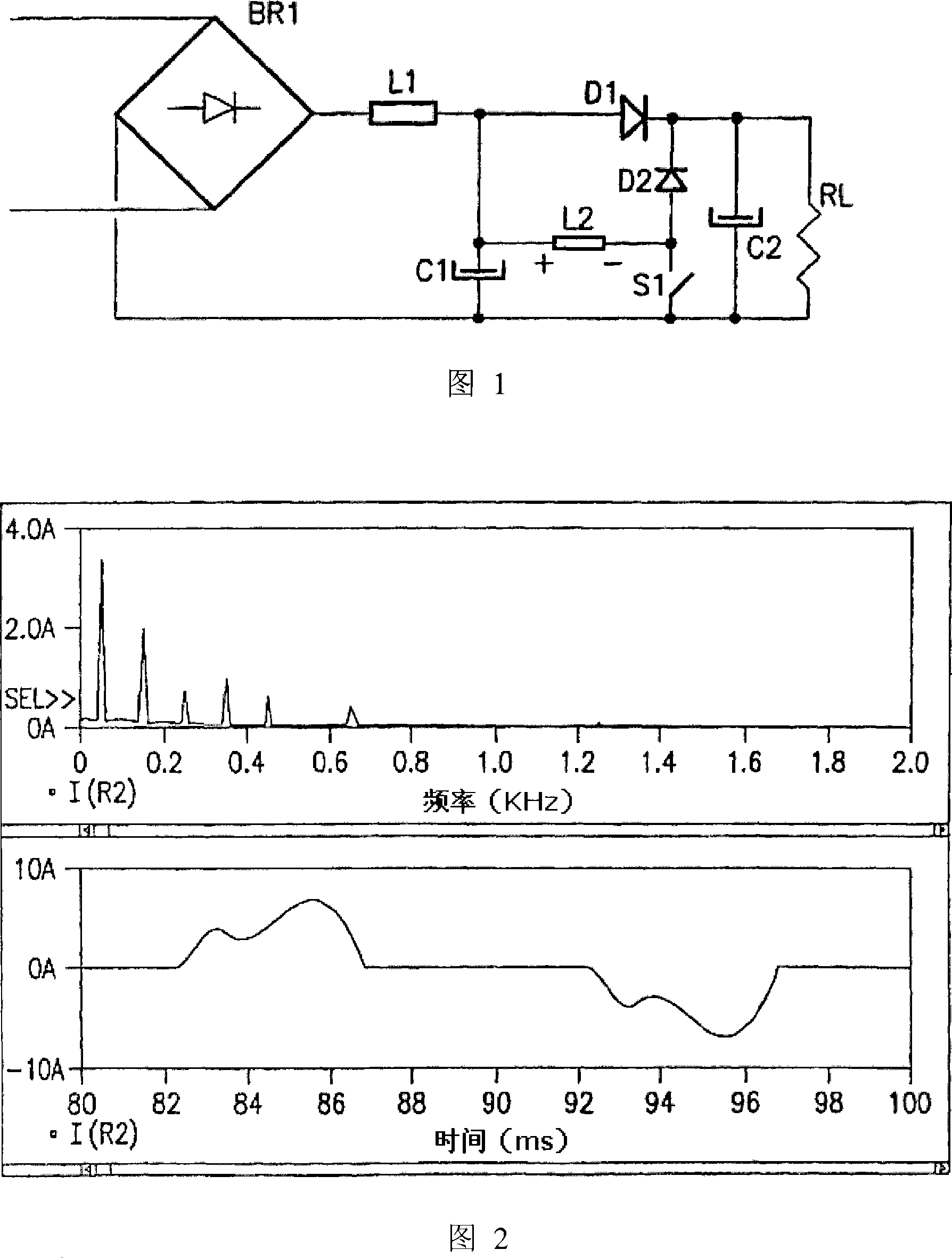
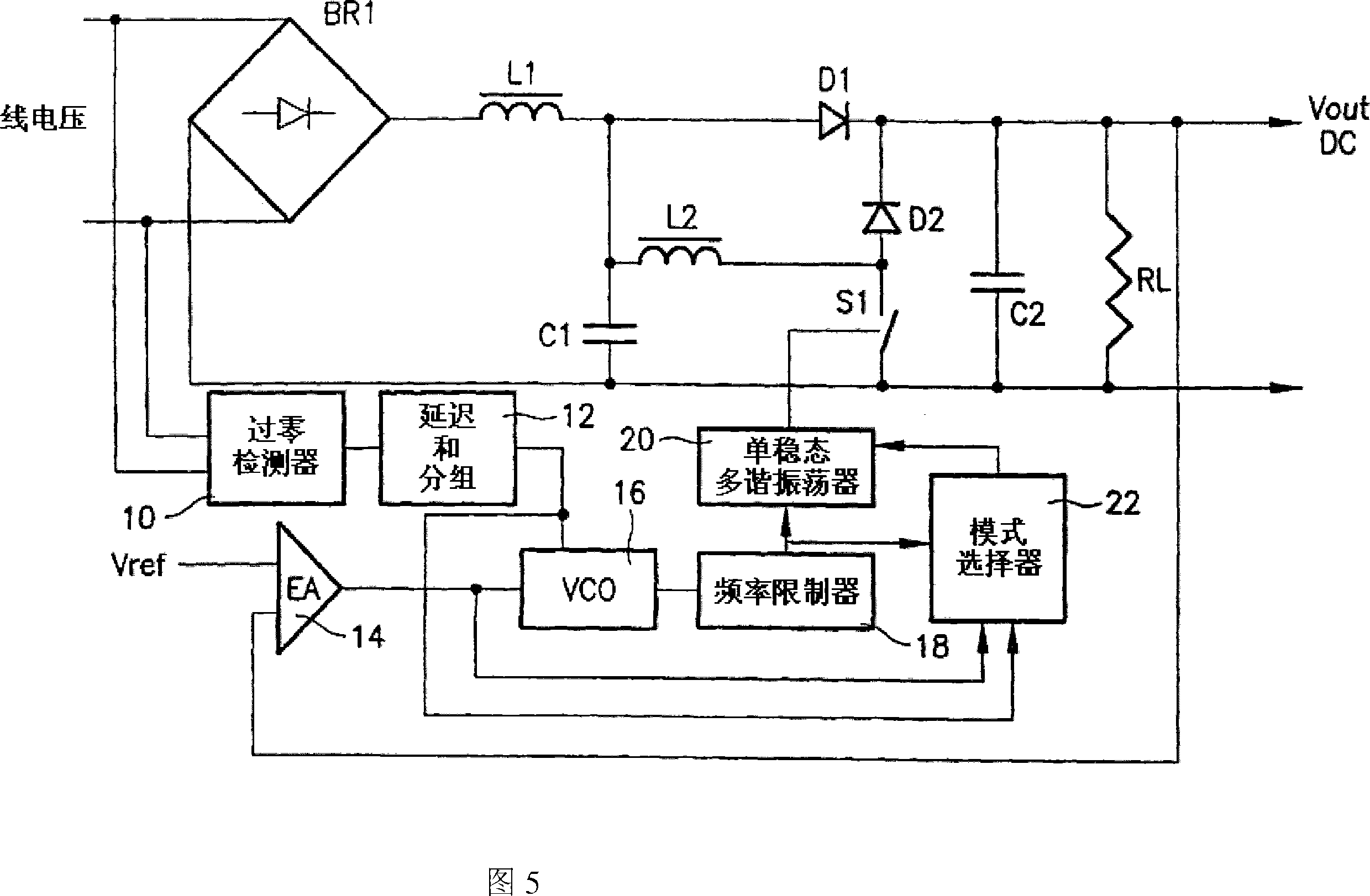
[0038] In the prior art circuit shown in Fig. 1, RL acts as an "equivalent" load of the harmonic correction (or power factor correction) circuit, representing the equipment to be fed (typically a further power conversion stage). The harmonic correction circuit consists of L1, C1, L2, S1, D1 and D2, while C2 together with BR1 represents the standard rectification and filtering stages which, when used alone, produce significant distortion of the line current. In Figure 1, the internal management power supply is not shown.
[0039] Referring to Figure 1, it is evident that the circuit in Figure 1 has several "degrees of freedom" as to how switch S1 is driven on and off in each line half-cycle.
[0040] First, the modulation of switch S1 must be the same for subsequent line half-cycles. In fact, if the modulation is different between two consecutive line half-cycles, the line current will contain a large number of even harmonics for which the specified limits are stricter than th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com