Organic ER affinity quick screening and forecast method based on receptor binding mode
A technology of receptor binding and prediction methods, applied in biological testing, material inspection products, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Adopt the method of the present invention to process a group of ER ligands and non-ER ligands (Matthews J., Celius T., Halgren R., et al.Differential estrogen receptor binding of estrogenic substances:aspecies comparison.Journal of Steroid Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 2000, 74:223-234.) A total of 34 compounds.
[0039] Classification principle: according to the logRBA value, the compounds are divided into 4 categories: 1~logRBA1, corresponding to extremely weak ER affinity There are four types of ER affinity, weak ER affinity, medium-strength ER affinity, and high ER affinity. Compared with the receptor affinity of estradiol, the three interval cut-off points of -3, 0, and 1 correspond to the affinity multiples of estradiol respectively. One hundred thousandth, one hundredth and one tenth of diol. 30 compounds were selected from it as a training group to build a model, and the remaining 4 compounds were used as a test group (corresponding to 4 types) for verifica...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Adopt the method of the present invention to process the ER affinity database (Estrogen receptor bindingdataset, www.fda.gov / nctr / science / centers / toxicoinformatics / edkb / index.htm) of U.S. FDA National Center for Toxicology Research (national center fortoxicological research, NCTR) 232 compounds in it.
[0055] Classification principle: The affinity index between compounds and ER can be divided into 3 categories: 1~logRBA<-3 is a compound with very weak ER affinity, 2~-3≤logRBA<0 is a compound with weak ER affinity, 3~logRBA≥ 0 is a compound with strong affinity for ER. 180 compounds were extracted from 188 non-phytoestrogens as a training group to build a model, including 111, 45, and 24 compounds of types 1, 2, and 3, and 40 compounds were extracted from 44 types of phytoestrogens as a training group. The training group model includes 16, 22, and 2 compounds of types 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The remaining 12 compounds were used as test groups to validate the model. ...
Embodiment 3
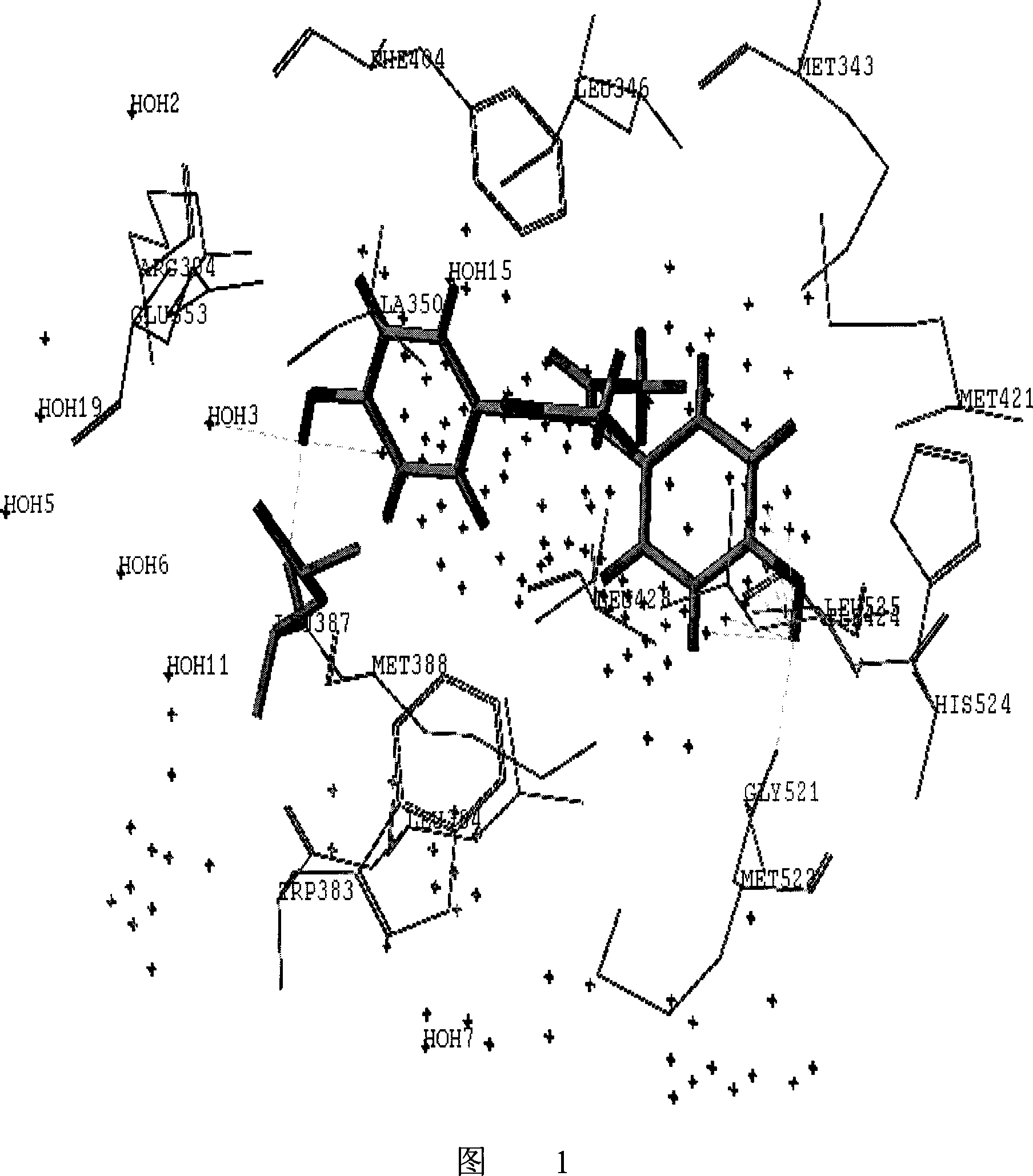
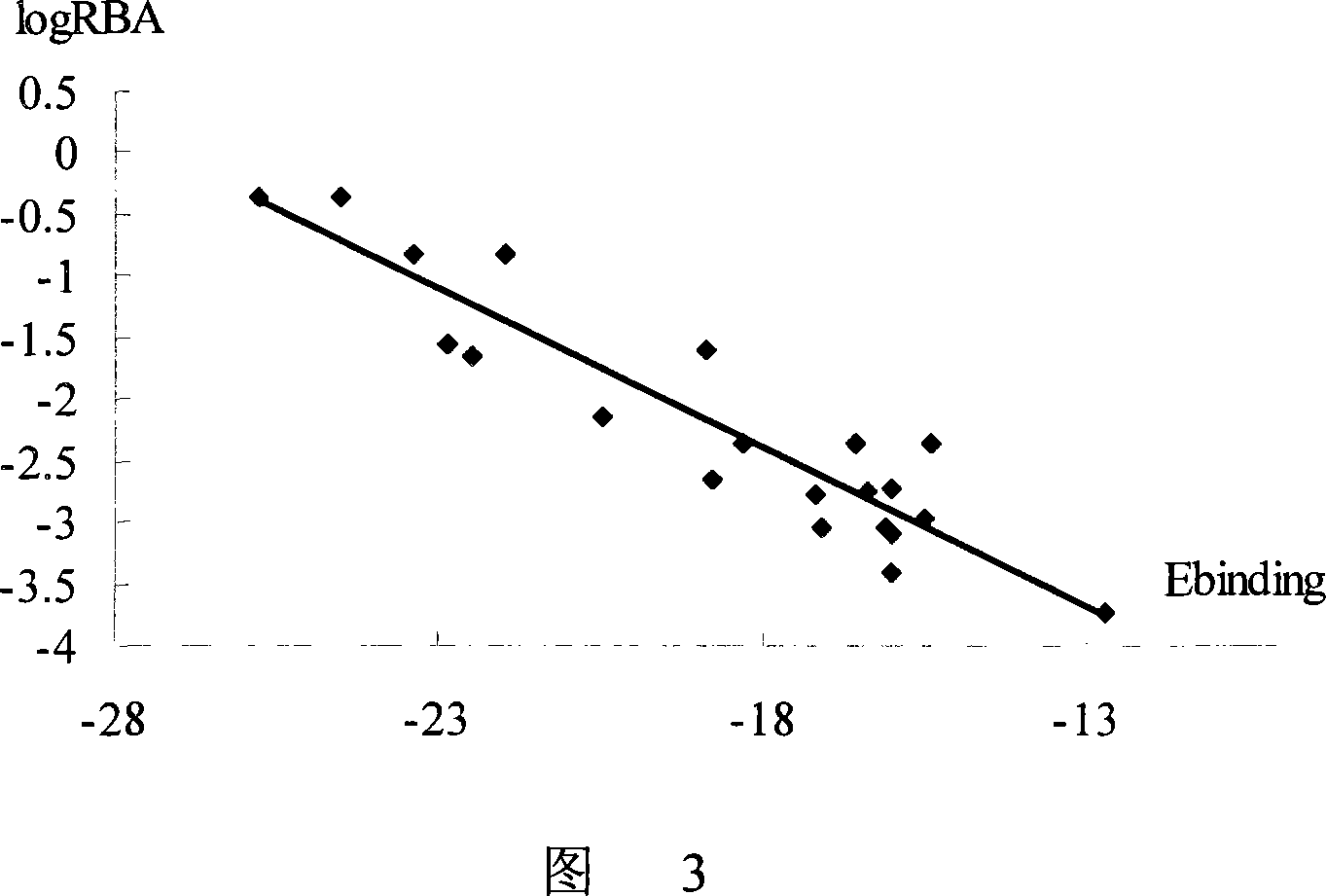
[0068] The method of the invention is used to analyze the mode of action between the compound and the active pocket of the receptor. Select dienestrol in the NCTR database to dock with the active pocket of hERα (PDB number 1ERE), and display the schematic diagram of the interaction between the compound and the receptor pocket (attached to Figure 1) (hydrogen bond interaction is represented by a dotted line), and determine the compound Whether there are hydrogen bonds with residues Glu353, Leu387, Gly521, His524, Leu346, crystal water (water) and other sites (other) in the pocket, and the number of hydrogen bonds is calculated. Compound and pocket binding free energy E binding It is -25.1kcal / mol. The figure shows the skeleton structure of the key residues and crystal water that make up the pocket. The main action area of the active pocket is represented by a purple dot matrix. The residue name and sequence number are marked on the α carbon atom of the residue. And the non-h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com