Method of determining a spatial distribution of magnetic particles
A technology of magnetic particles, spatial distribution, applied in the field of computer programs, which can solve problems such as not being good enough
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
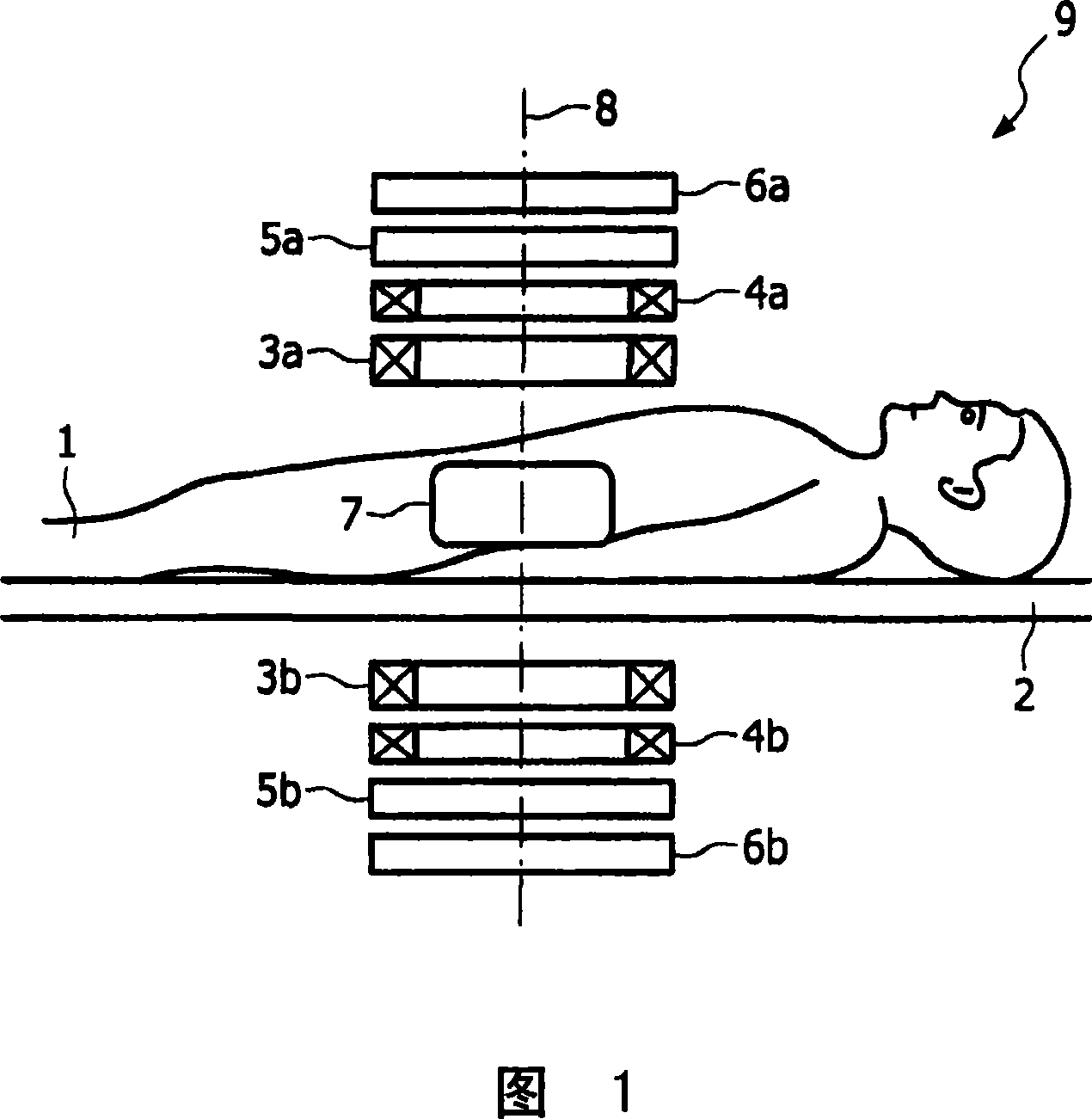
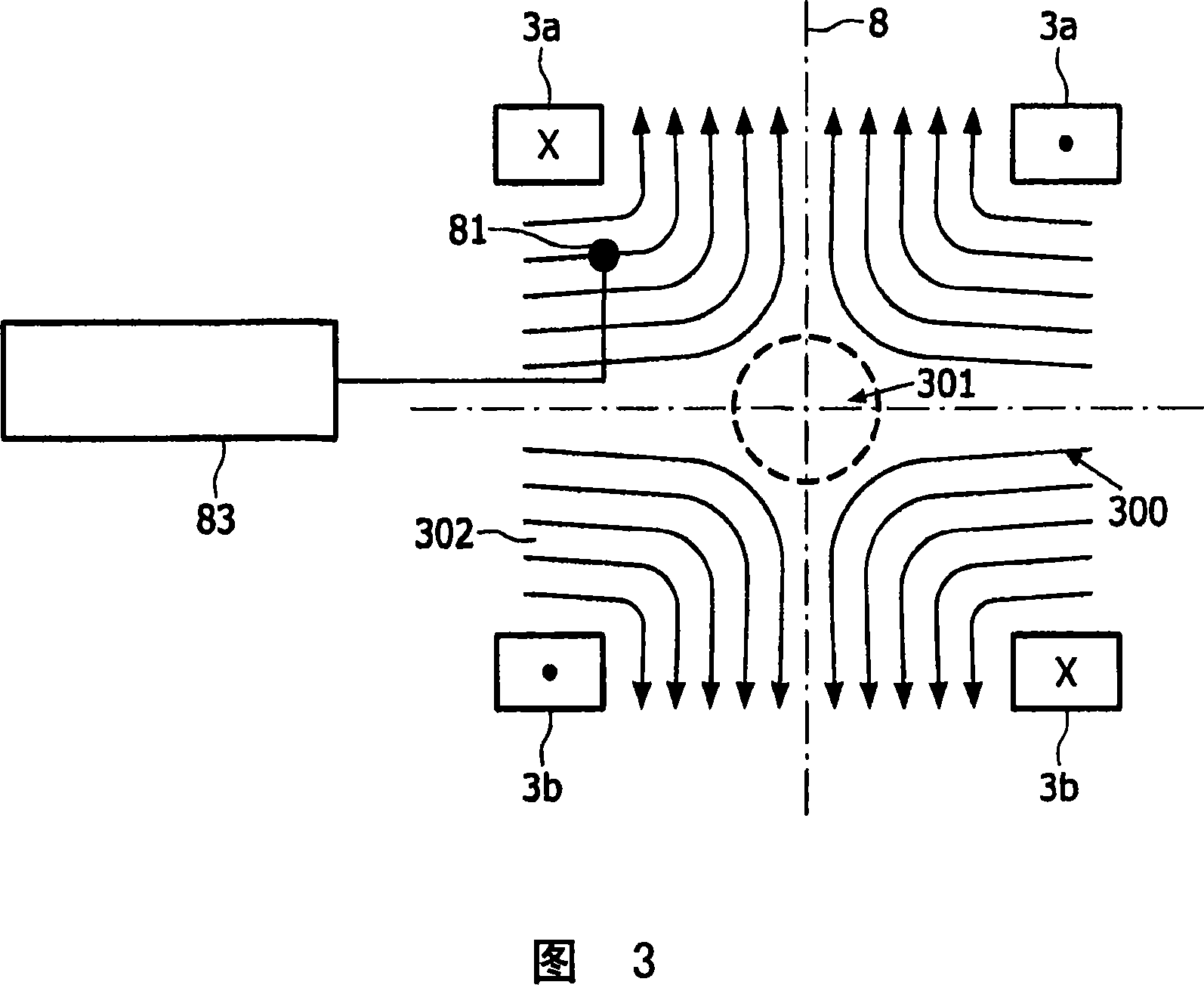
[0032] Figure 1 shows an embodiment of a device 9 according to the invention. Located on the patient display table 2 is an object, which is the patient 1 in the present invention. Located in the patient 1 , for example in the gastrointestinal tract, and in the examination area of the device 9 are magnetic particles for the patient in liquid or granular form. As described below, the size of the examination zone depends inter alia on the magnetic field and magnetic particles used.
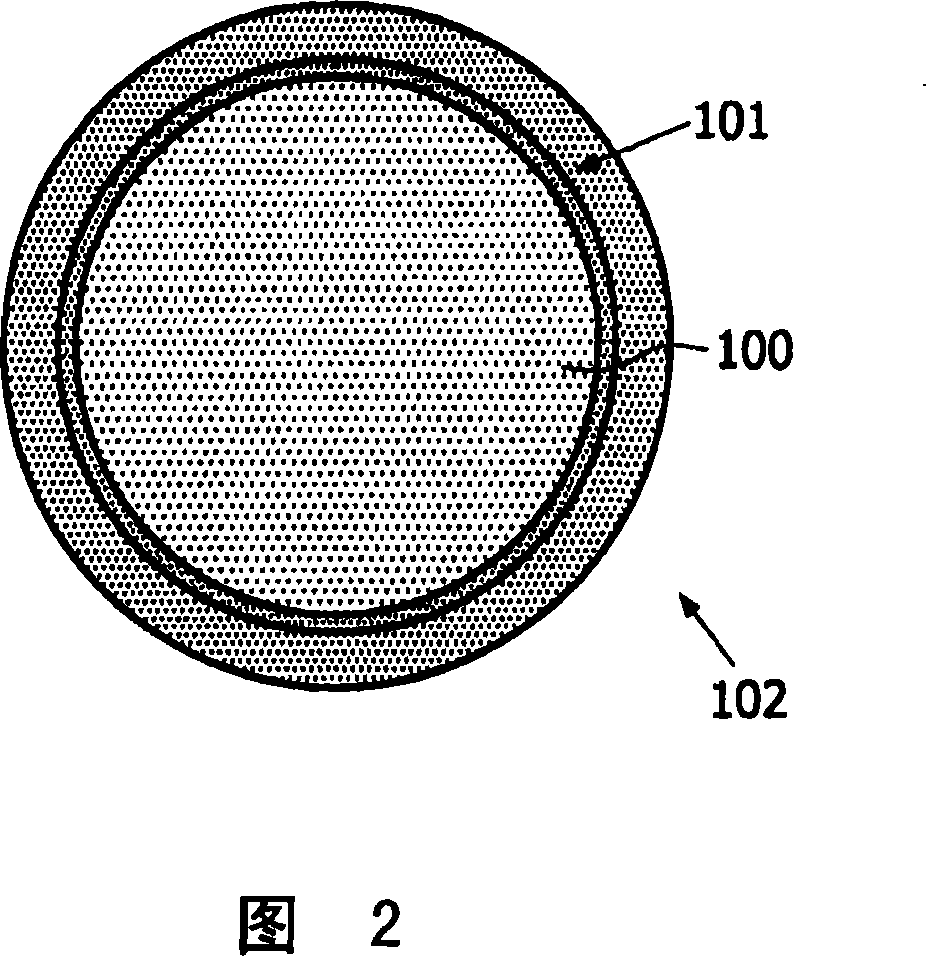
[0033] Figure 2 shows a magnetic particle. It comprises a spherical substrate 100 of eg glass covered with a soft magnetic layer 101 eg 5 mm thick and eg composed of an iron-nickel alloy (eg permalloy). This layer is covered, for example, with a cover layer 102 to protect the particles against acids. The magnetic field strength required to saturate such a particle depends on the particle's diameter. For a diameter of 10 μm, a magnetic field of 1 mT is required for this purpose, whereas for a di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com