Printing apparatus
A technology of printing equipment and platen rollers, applied in printing devices, printing, typewriters, etc., can solve the problems of damage or wear of each component, increase of paper conveying resistance, and troublesome conveying.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
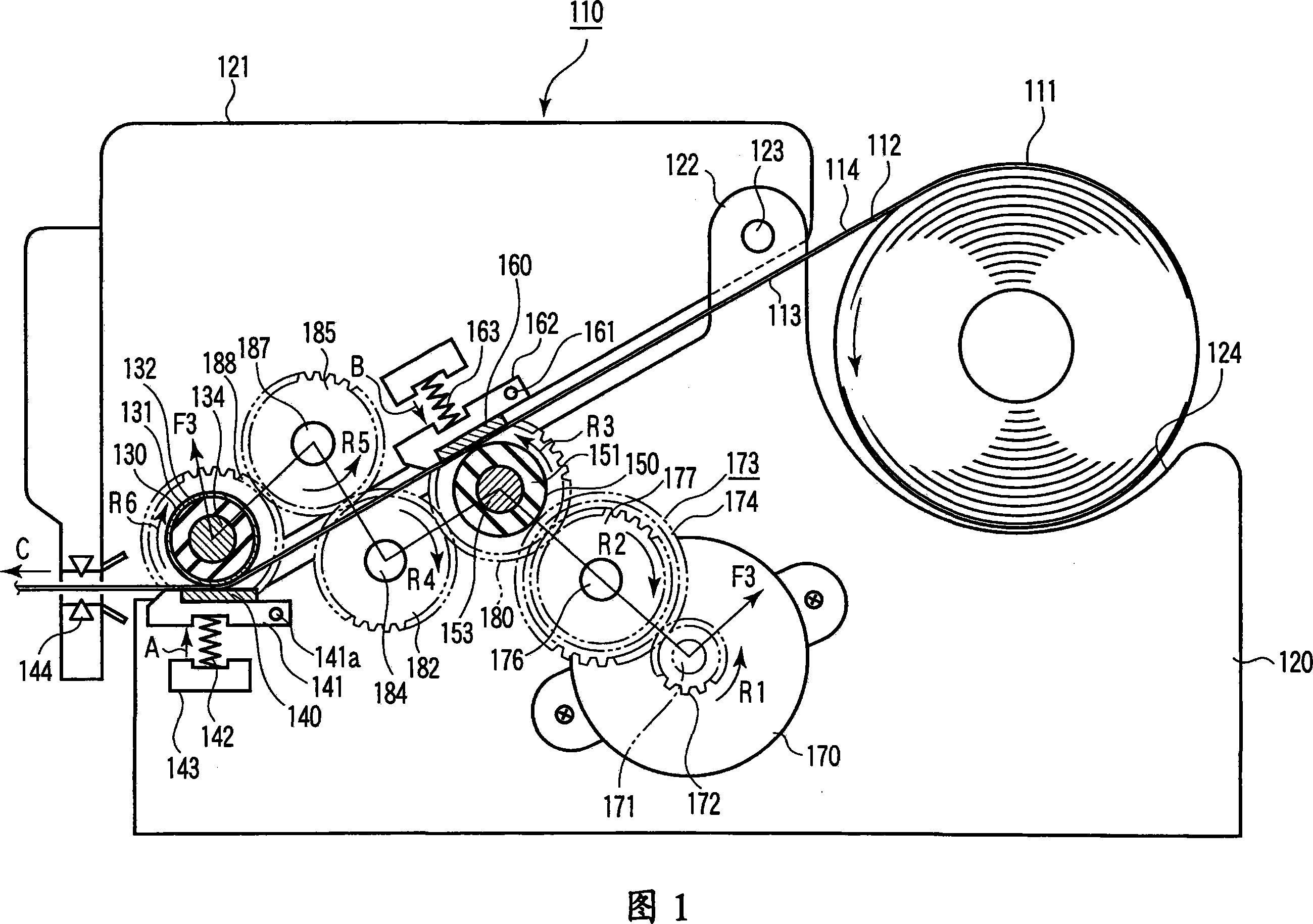
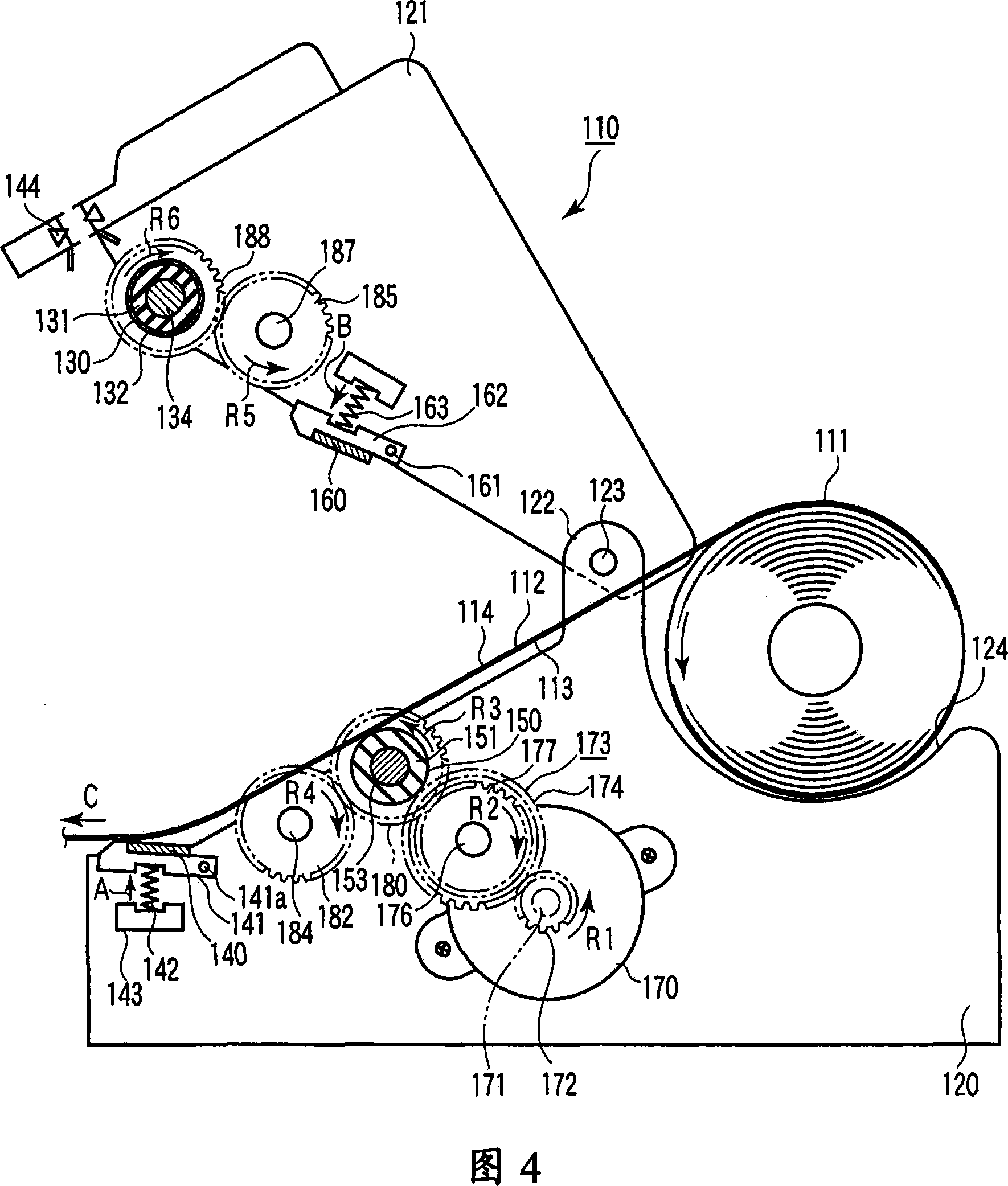
[0054] FIG. 1 schematically shows the interior of a thermal printer 110 according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The thermal printer 110 can print on both surfaces of the thermal recording paper 111 . For example, thermal printer 110 may be used in a cash register at a store.
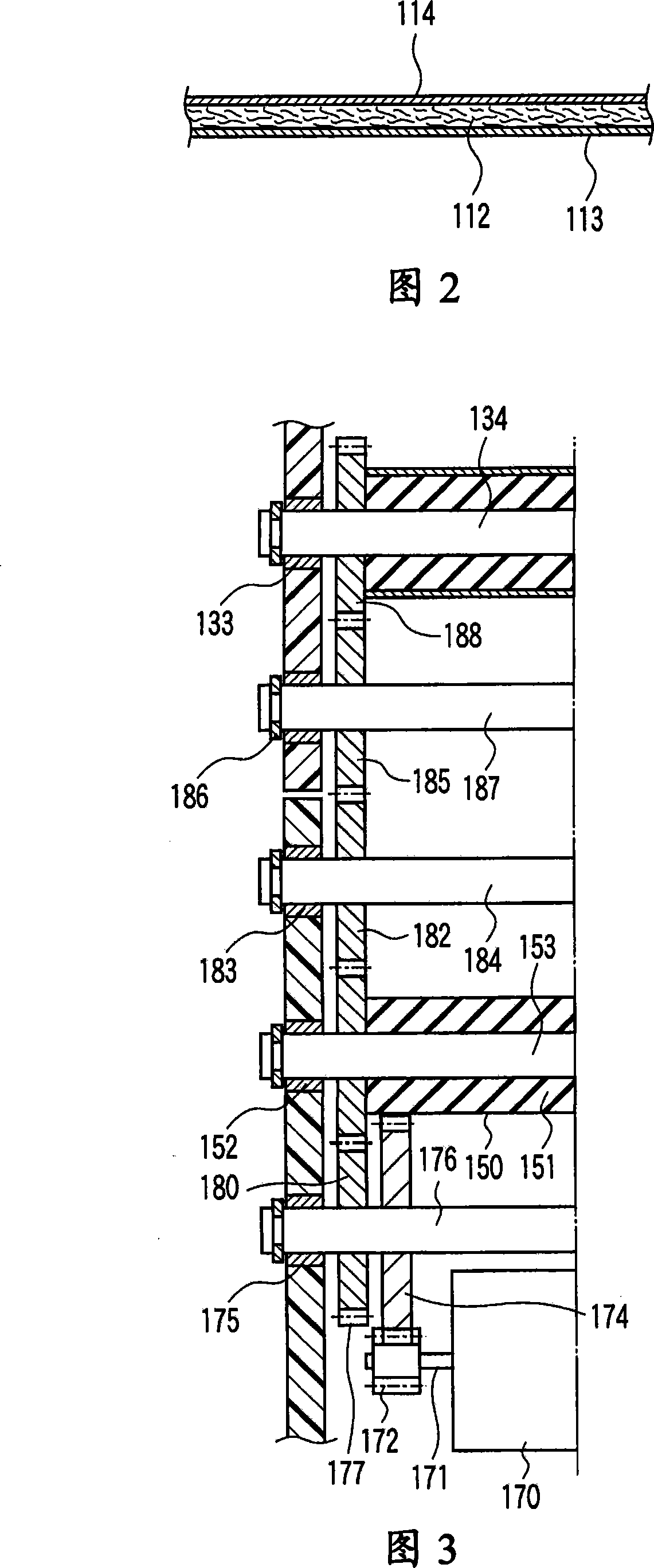
[0055] As shown in FIG. 2 , the thermosensitive recording paper 111 includes a base paper 112 and thermosensitive layers 113 and 114 formed on both surfaces of the base paper 112 . The first thermosensitive layer 113 is formed on one side (eg, the surface) of the base paper 112 , and the second thermosensitive layer 114 is formed on the other side (eg, the back side) of the base paper 112 . Each heat-sensitive layer 113 and 114 is made of a material that develops a desired color, such as black and red, when heated to a predetermined temperature or higher. As shown in FIG. 1 , the thermosensitive recording paper 111 is wound in a roll shape such that the first thermosensitive layer 113...
no. 2 example
[0087] A thermal printer 190 according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described below. The second embodiment differs from the first embodiment only in first and second platen rollers 130 and 150 and first and second biasing devices 191 and 192 . Therefore, the same components are denoted by the same reference numerals, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0088] In the second embodiment, the first platen roller 130a and the second platen roller 150a are composed of roller bodies 131a and 151a made of NBR, respectively. The first platen roller 130a is slightly larger in diameter than the second platen roller 150a.
[0089] The first biasing device 191 is smaller in spring constant than the second biasing device 192 . For example, the spring wire diameter of the first biasing device 191 is smaller than the spring wire diameter of the second biasing device 192 . Therefore, the force with which the first thermal head 140 presses against the first pla...
no. 3 example
[0096] FIG. 6 schematically shows the interior of the thermal printer 210 . The thermal printer 210 can print on both surfaces of the thermal recording paper 211 . For example, thermal printer 210 may be used in a cash register at a store.
[0097] As shown in FIG. 7 , the heat-sensitive recording paper 211 includes a base paper 212 and heat-sensitive layers 213 and 214 formed on both surfaces of the base paper 212 . The first thermosensitive layer 213 is formed on one side (eg, the surface) of the base paper 212 , and the second thermosensitive layer 214 is formed on the other side (eg, the back side) of the base paper 212 . Each heat-sensitive layer 213 and 214 is made of a material that develops a desired color, such as black and red, when heated to a predetermined temperature or higher. As shown in FIG. 6, the heat-sensitive recording paper 211 is wound in a roll shape such that the first heat-sensitive layer 213 faces inside.
[0098] The thermal printer 210 includes a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com