Girder bridge protection device using sacrifice mems
A technology for protection devices and bridges, applied in bridges, bridge parts, bridge construction, etc., can solve problems such as structural asymmetry, impossibility to resist earthquake loads, economic losses, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] Reference will now be made in detail to the preferred embodiments of the invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Wherever possible, the same reference numbers will be used throughout the drawings to refer to the same elements and to describe with reference to the same or like elements.
[0044] In the various figures, the same reference numerals, in particular reference numerals with the same first and second numerals or the same first and second numerals and the same reference letters, designate elements with the same function. Accordingly, elements denoted by respective reference numerals comply with this convention unless otherwise specified.
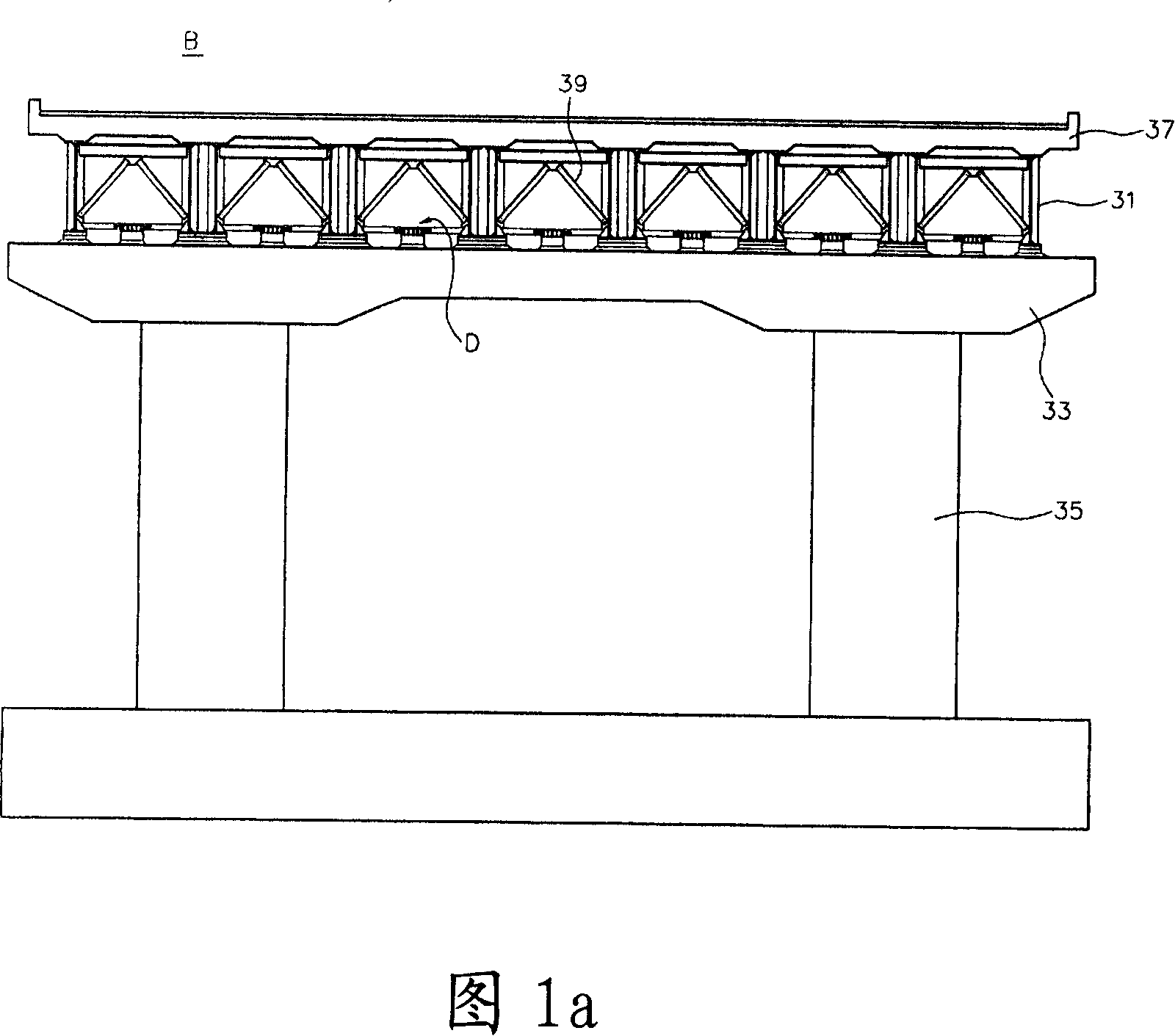
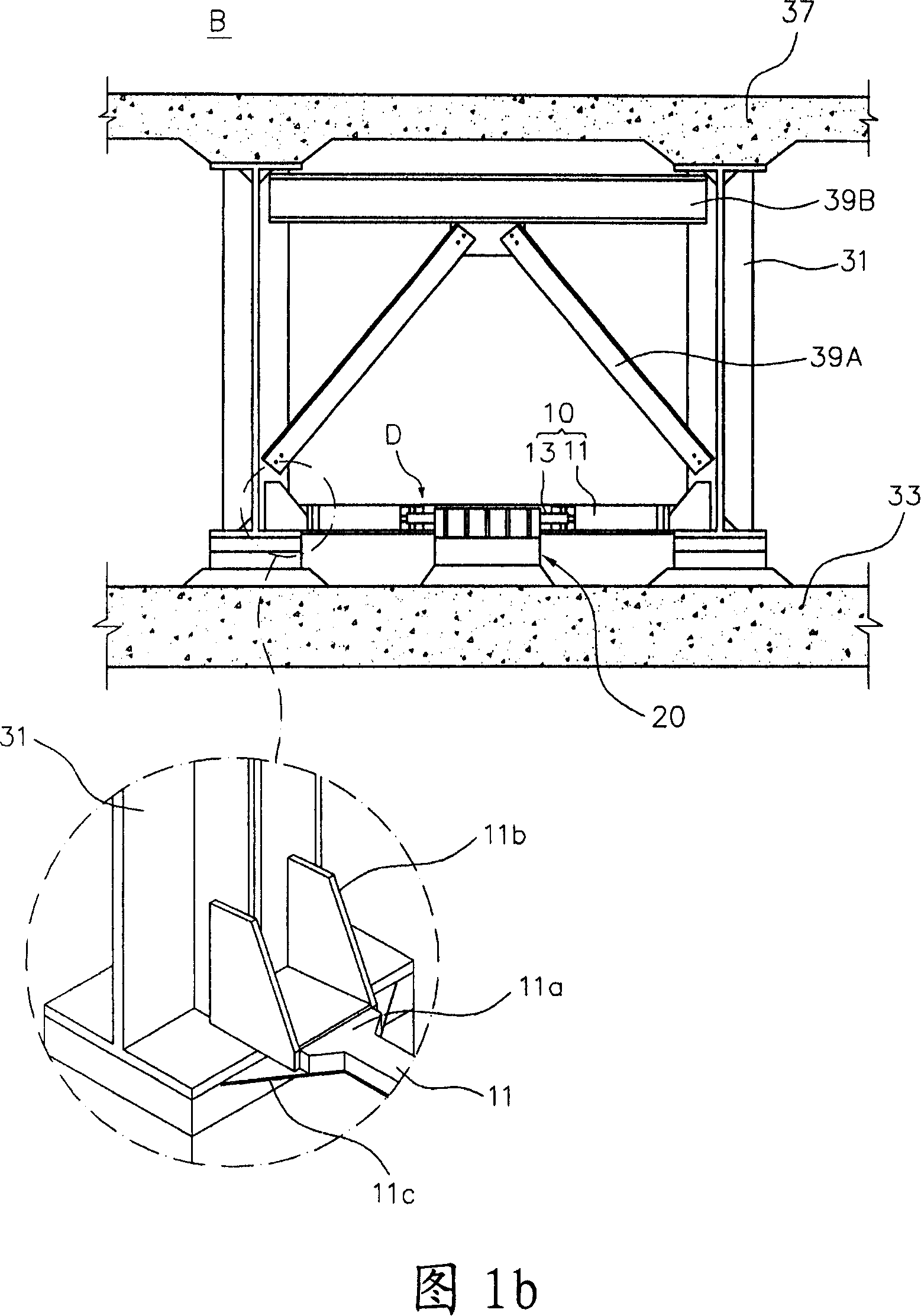
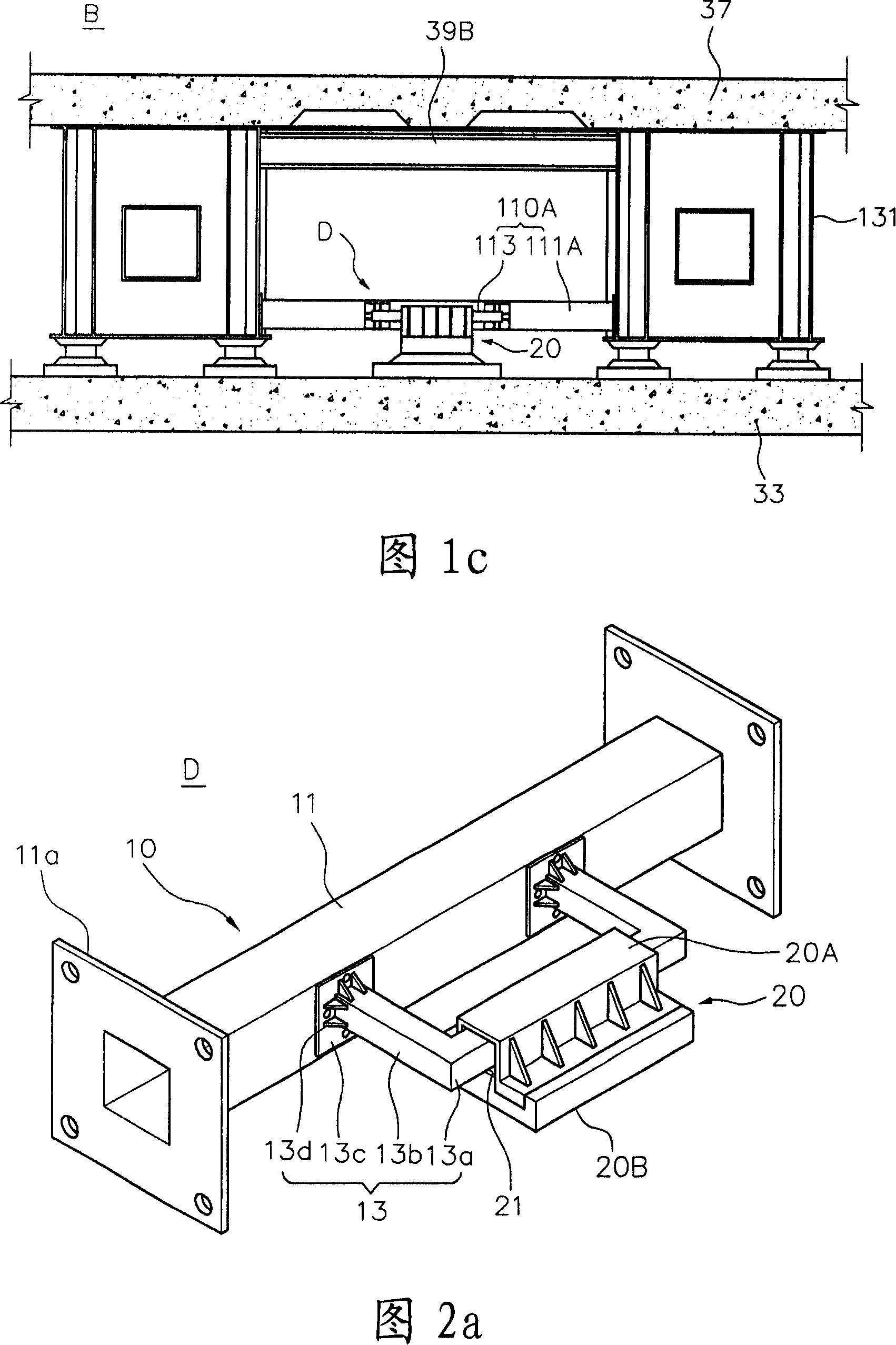
[0045] Before explaining the bridge protection device according to the present invention, the direction is set according to the following procedure with reference to FIGS. 1a and 1b. The longitudinal direction of the superstructure connecting the piers positioned at both ends of the bridge B...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com