Optical fiber having low and uniform optical loss along the entire length and method for fabricating the same
An optical fiber preform and optical fiber technology, which is used in manufacturing tools, optical waveguides, glass manufacturing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of heat capacity loss, inability to determine the number of insertions, and the capillary can not be completely closed, and achieve low optical attenuation loss. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
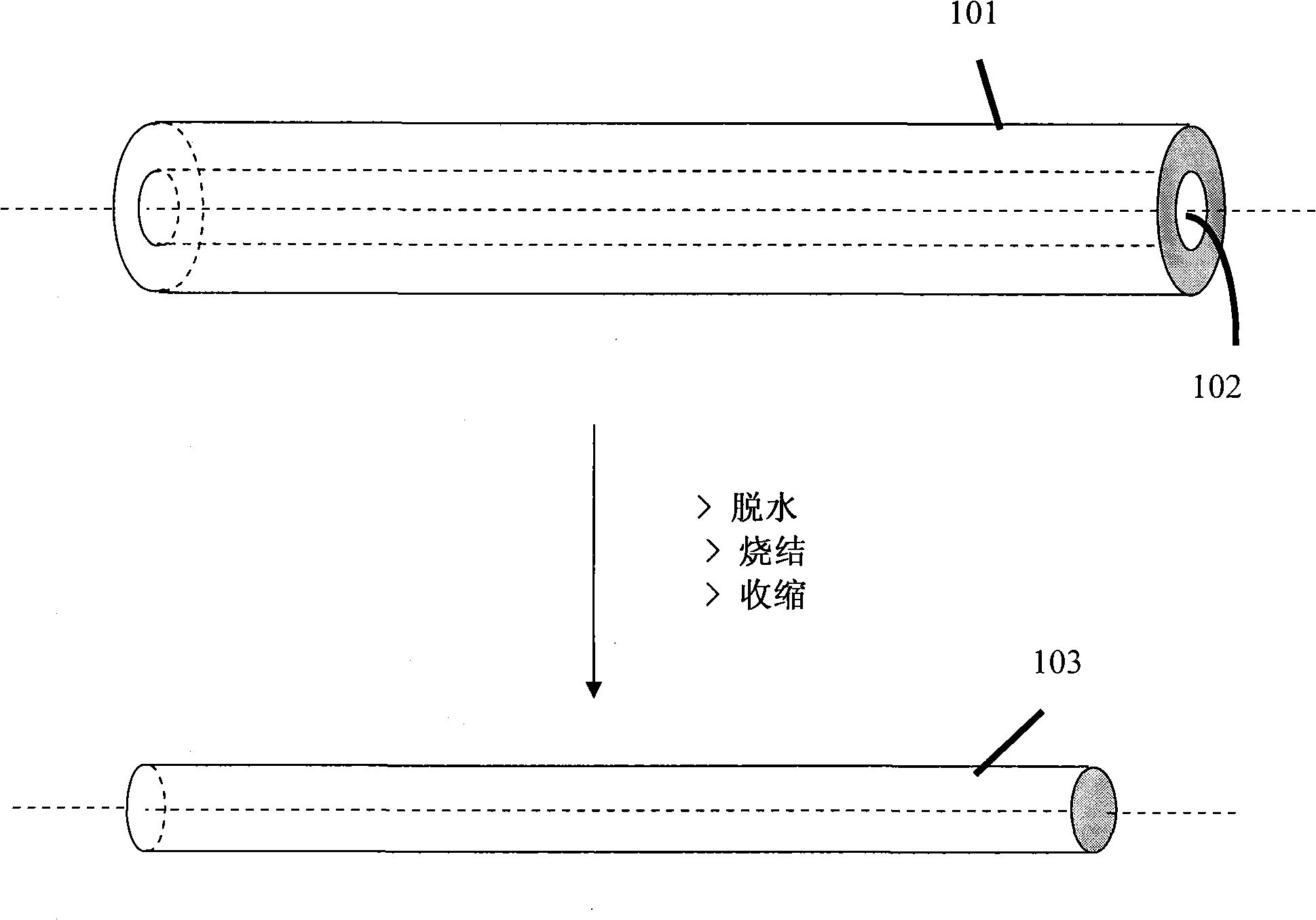
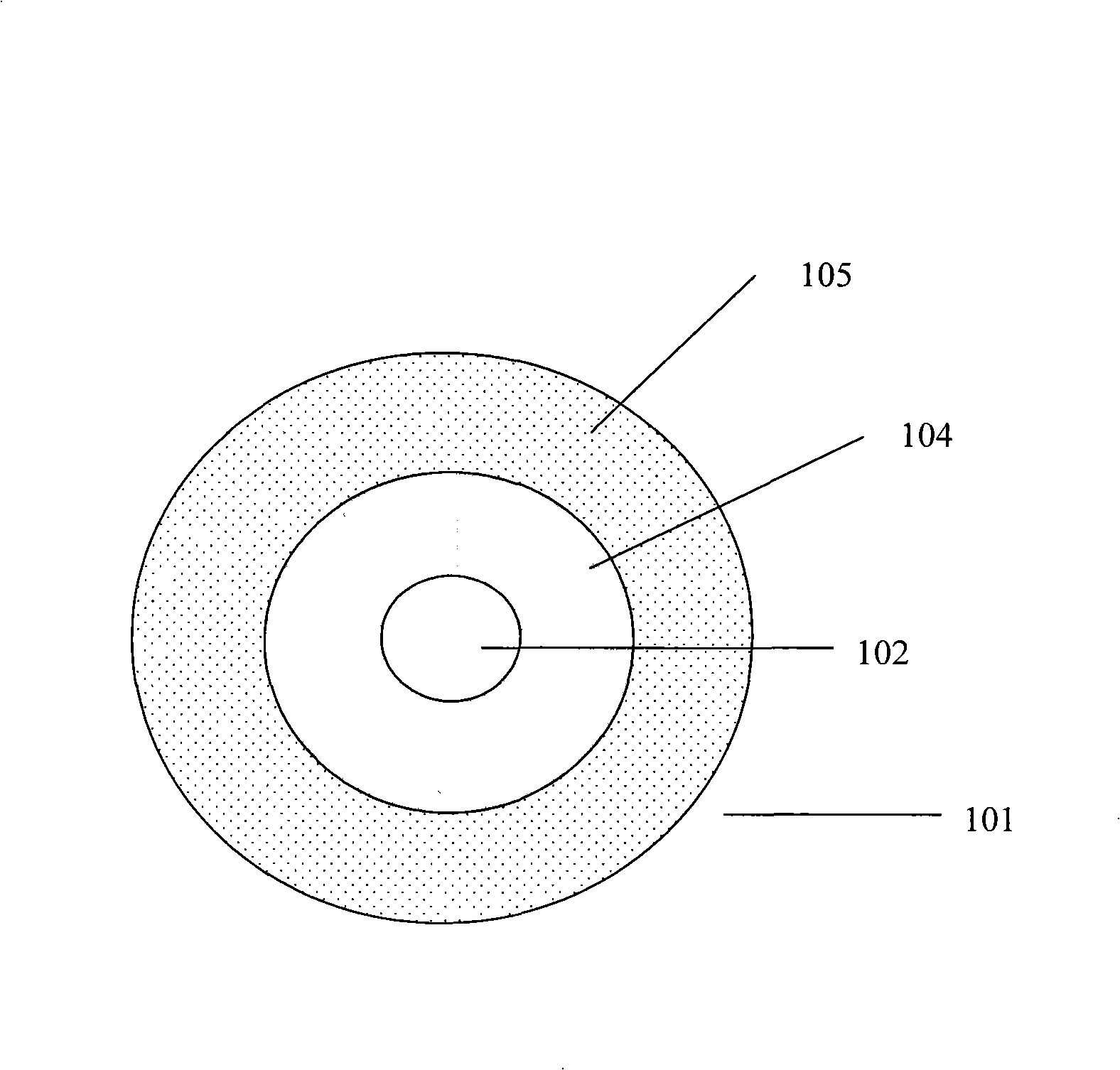
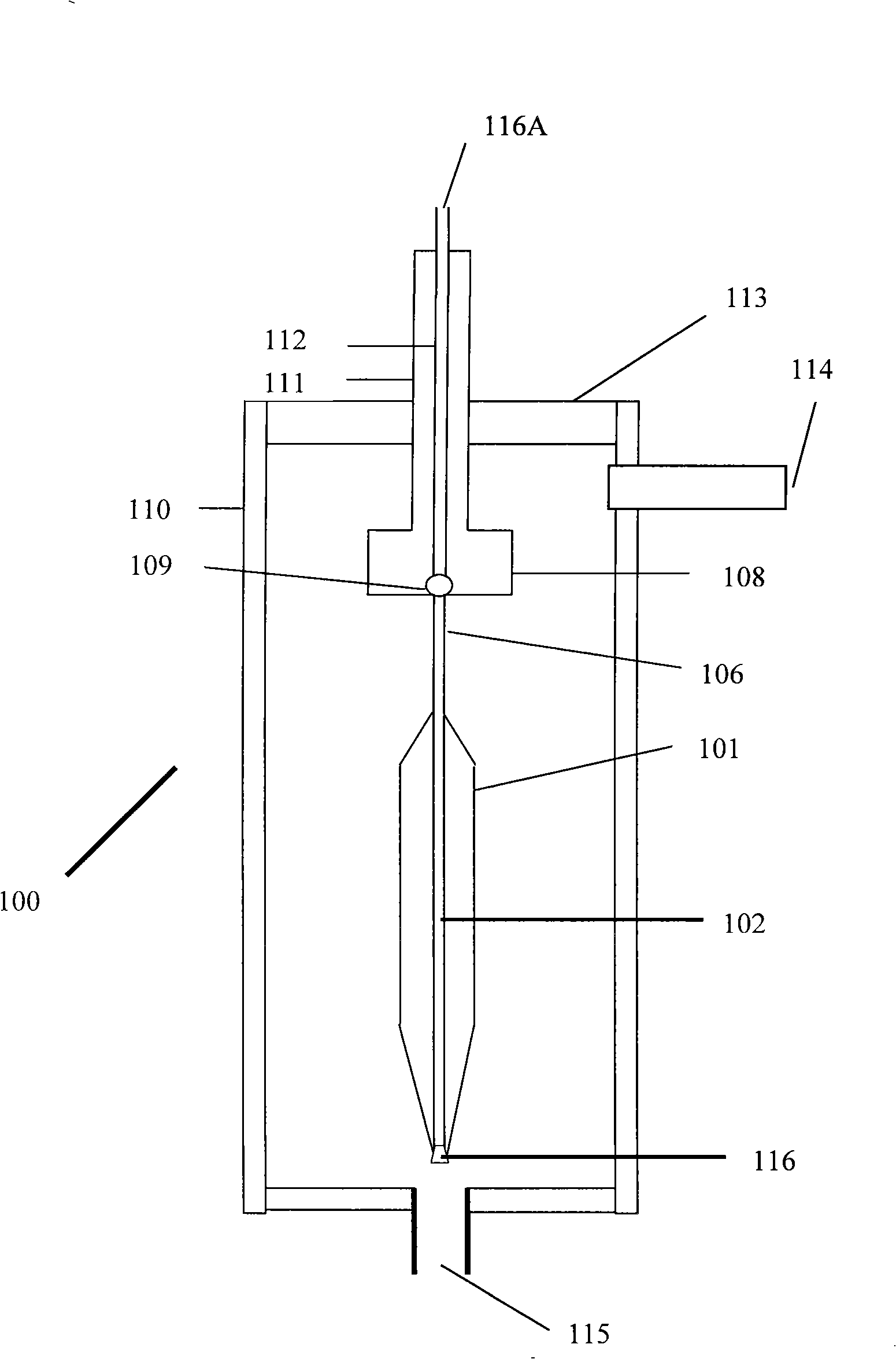
[0091] The processing of the present invention starts in the manner described above. Dehydration treatment step with gas such as Cl 2 , CCl 4 、SiCl 4 、GeCl 4 or any combination thereof and inert gases such as He, Ar, N that also act as heat carriers 2 To promote the effective dehydration and sintering of the hollow soot porous body 101. These gases are fed into the furnace 100 through an inlet 115 suitably located on the furnace, preferably near the bottom of the closed tube 110 . The top end of the closed tube 110 is closed with a cover 113 to achieve the optimum temperature profile inside the closed tube 110, for example, the curve 117( Figure 5 ), and maintain the same temperature profile during the dehydration, and simultaneous sintering and shrinking process steps, and avoid gas leakage from the closed tube 110 to the external environment. A suction port 114 is suitably located near the top of the closed tube 110 so that gas is evacuated from the closed tube 110 wh...
example 1
[0111] Example 1 (Prior Art Method)
[0112] Soot deposition is accomplished on a tapered cylindrical member by known methods to produce a soot porous body having the desired soot mandrel diameter and soot cladding diameter. The tapered cylindrical member is separated from the soot porous body to have a capillary diameter ranging from about 6 mm to about 8 mm from the bottom end to the top end of the hollow soot porous body. Before inserting the hollow soot porous body into the sintering furnace, the capillary of the hollow soot porous body was cleaned with N 2 Purge for approximately 5 minutes at a flow rate of approximately 20 SLPM to ensure that no loose soot particles are present in the capillary. For dehydration, the hollow soot porous body is inserted into the first heating zone of the sintering furnace, which is maintained at a temperature in the range of about 1050°C to about 1150°C. During the dehydration process, from the bottom end of the sintering furnace, the He...
example 2
[0113] Example 2 (this method)
[0114] Soot deposition is accomplished on a tapered cylindrical member by known methods to produce a soot porous body having the desired soot mandrel diameter and soot cladding diameter. The tapered cylindrical member is separated from the soot porous body such that the hollow soot porous body has a capillary diameter ranging from about 6 mm to about 8 mm from the bottom end to the top end. Before inserting the hollow soot porous body into the sintering furnace, the capillary of the hollow soot porous body was cleaned with N 2 Purge for approximately 5 minutes at a flow rate of approximately 20 SLPM to ensure that no loose soot particles are present in the capillary. For dehydration, the hollow soot porous body is inserted into the first heating zone of the sintering furnace, which is maintained at a temperature in the range of about 1050°C to about 1150°C. During the dehydration process, from the bottom end of the sintering furnace, the He f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dispersion value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dispersion value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com