Method for IPv6 repeating vector IPv4/6 through inverse path
A technology of reverse path forwarding and vectoring, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., to achieve the effects of improving transmission quality, optimizing multicast functions, and wide applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
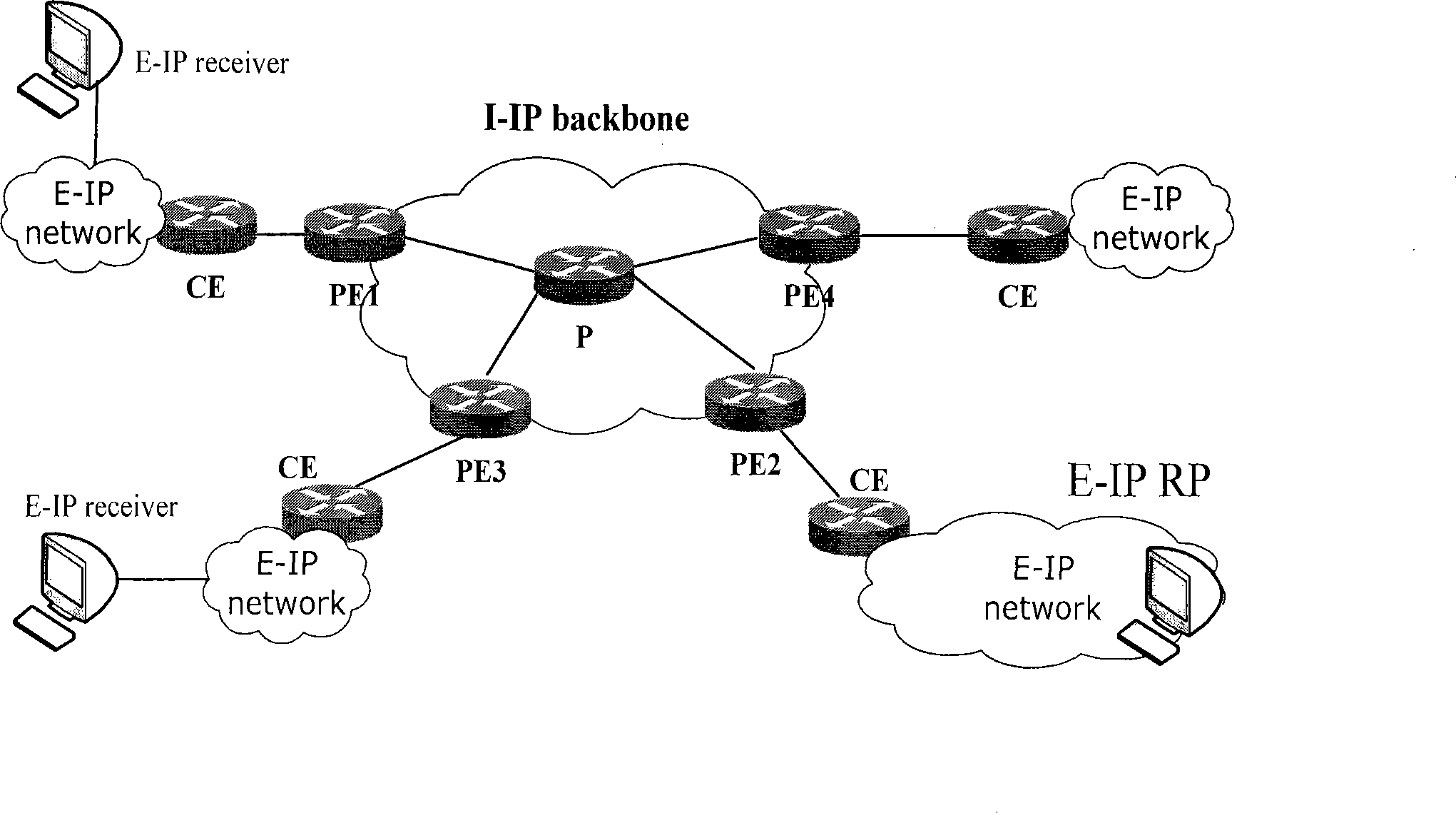
[0032] In softwire, the most basic components are several E-IP networks and an I-IP core network. This solution is suitable for IPv4 over IPv6, that is, E-IP and I-IP can use IPv4 and IPv6 respectively. The network connection mode is described in Figure 1.
[0033] From the perspective of the establishment of the multicast tree, when a host receiver in an E-IP network wants to join a multicast group with a host in another E-IP network as the source (RP address is 11.1.1.2, group The broadcast group address is 216.0.0.1), the Join message Join(11.1.1.2; 216.0.0.1) sent by the host first arrives at the PE1 router of the I-IP network, and the edge router PE1 router first transfers the message to the IPv4 / 6 address RPF Vector is added after conversion, and the Vector attribute value is the address EA::22 of the egress PE2, that is, Join(EF::11.1.1.2; FF::2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com