Focus-fixed lens
A fixed-focus lens and negative lens technology, applied in the field of fixed-focus lenses, can solve problems such as difficult to achieve balance, achieve good image quality, low cost, and avoid excessive system length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
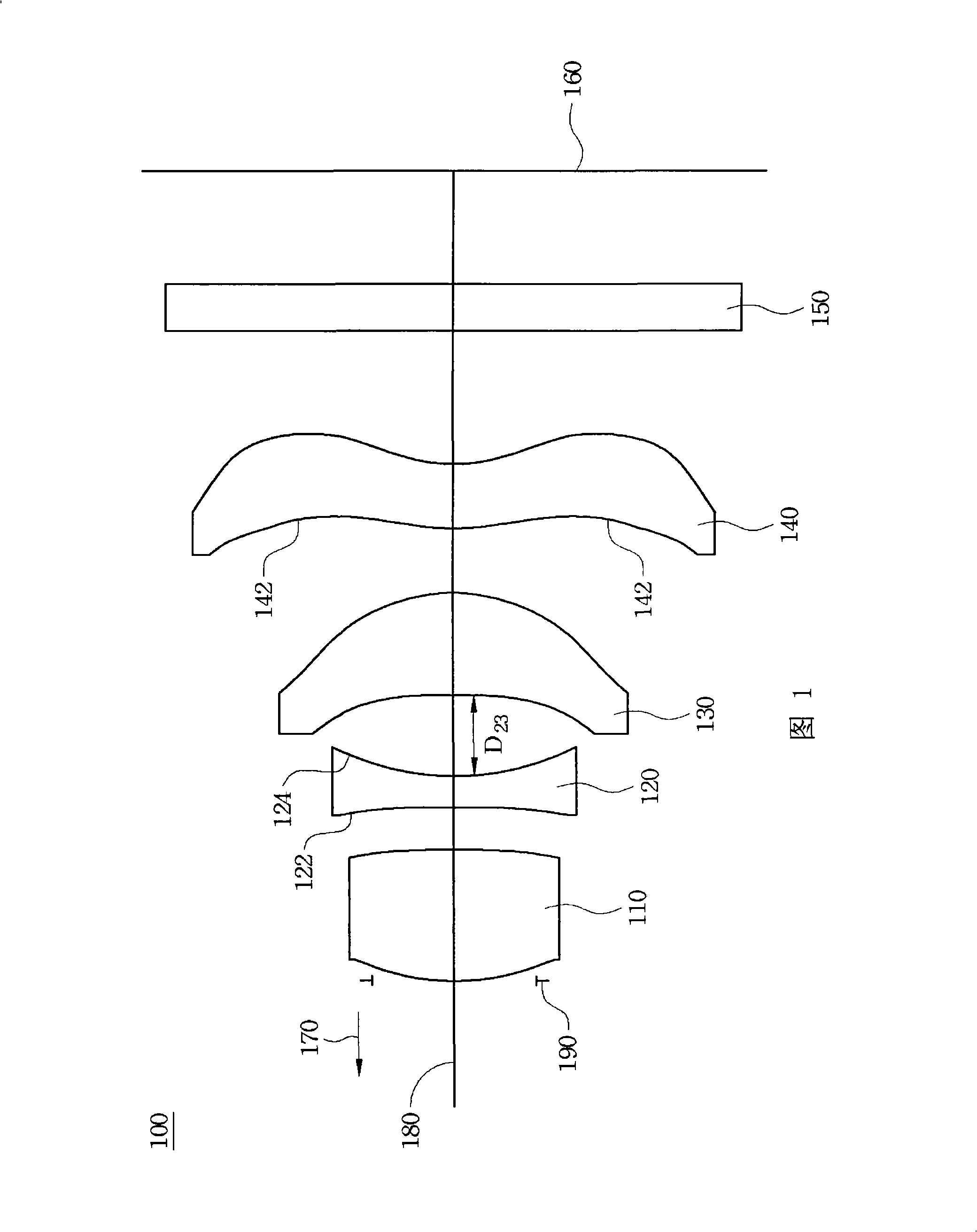
[0057] Table 1 lists the parameters of each surface of the optical system of the fixed-focus lens in turn, wherein STO. is the aperture stop, and FS is the filter. S11 and S12 denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the first positive lens, S21 and S22 respectively denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the second negative lens, S31 and S32 respectively denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the third crescent positive lens , S41 and S42 represent the object end surface and the imaging end surface of the fourth negative lens, respectively.
[0058]
[0059] Other optical properties of the fixed-focus lens of the first embodiment are listed in Table 2:
[0060]
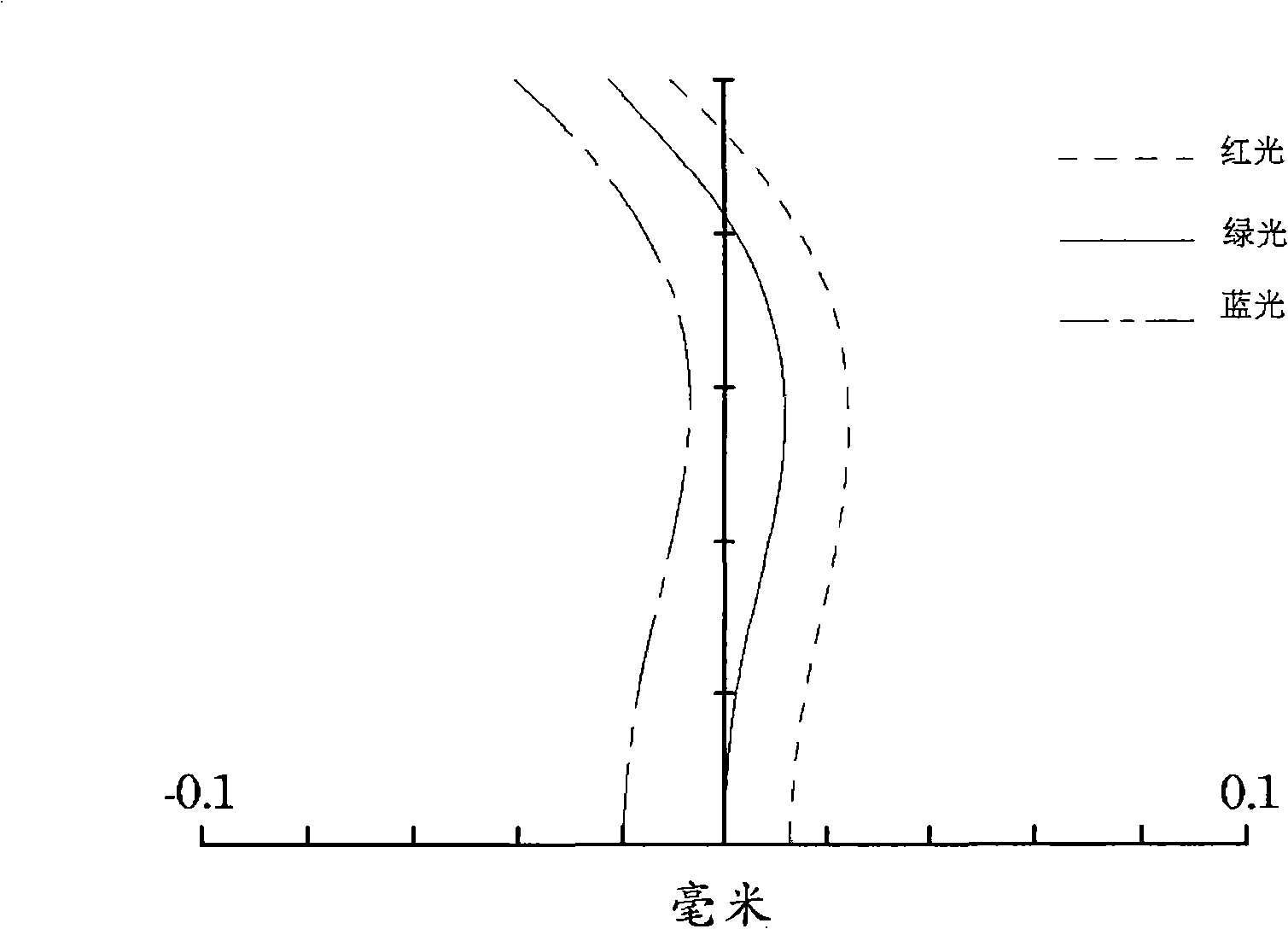
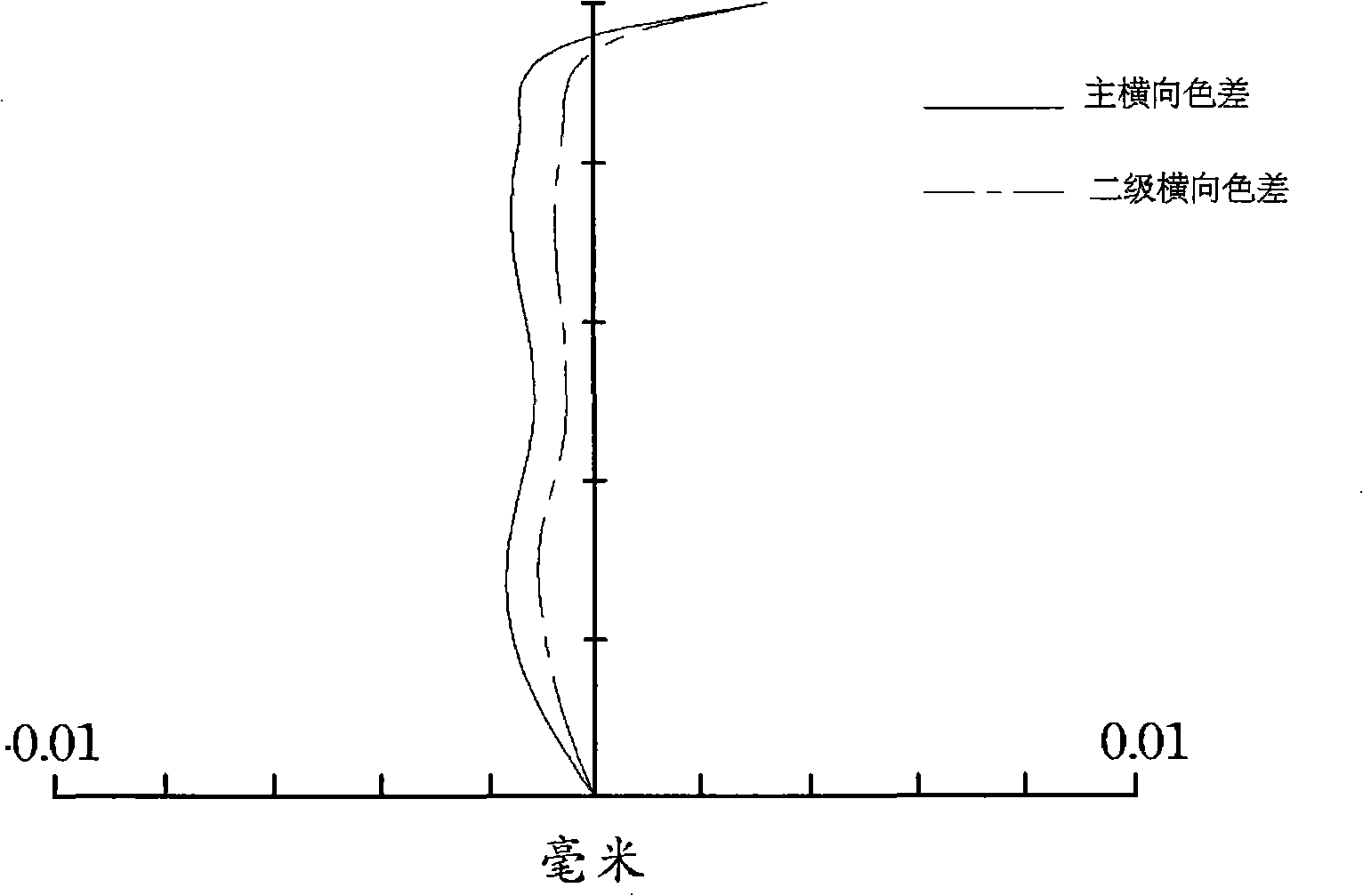
[0061] It can be seen from Table 2 that the f12 / f parameter value of the fixed-focus lens is 1.608, which meets the condition (1). R S32 The / f parameter value is 0.17, which meets the condition (2). The parameter value of D23 / L is 0.13, which meets the cond...
no. 2 example
[0070] The second embodiment discusses the case where the curvature of the object end surface of the second negative lens is designed to be a negative value. Table 5 sequentially lists the parameters of each surface of the optical system of the fixed-focus lens of the second embodiment, wherein STO. is the aperture stop, and FS is the filter. S11 and S12 denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the first positive lens, S21 and S22 respectively denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the second negative lens, S31 and S32 respectively denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the third crescent positive lens , S41 and S42 represent the object end surface and the imaging end surface of the fourth negative lens, respectively.
[0071]
[0072] Other optical characteristics of fixed focal length lenses are listed in Table 6:
[0073]
[0074] It can be seen from Table 6 that the f12 / f parameter value of the fixed-focus lens is ...
no. 3 example
[0081] The curvature of the object end surface of the second negative lens in this embodiment is not only negative, but also much smaller than that in the second embodiment. Table 9 sequentially lists the parameters of each surface of the optical system of the fixed-focus lens of the third embodiment, wherein STO. is the aperture stop, and FS is the filter. S11 and S12 denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the first positive lens, S21 and S22 respectively denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the second negative lens, S31 and S32 respectively denote the object end surface and imaging end surface of the third crescent positive lens , S41 and S42 represent the object end surface and the imaging end surface of the fourth negative lens, respectively.
[0082]
[0083] Other optical characteristics of the fixed focal length lens are listed in Table 10:
[0084]
[0085] It can be seen from Table 10 that the f12 / f parameter value of the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com