Aromatic neomenthylamides as flavouring agents
A plant and insect technology, applied in the fields of chemicals for biological control, botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of instability of antisense sequences, difficulties in instability of antisense sequences, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0219] This example describes the identification of nucleotide sequences useful in the control of corn rootworm when provided as a double-stranded RNA molecule in the corn rootworm diet.
[0220] Maize rootworm cDNA libraries (LIB 149, LIB 150, LD33027, LIB3373) were constructed from whole larvae as well as from excised midgut segments, and nucleotide sequence information was obtained (see, Andersen et al., submitted July 2002). US Patent Application Serial No. 10 / 205,189, dated 24 March, the entirety of which is expressly incorporated herein by reference). In addition, cDNA libraries were constructed from whole larvae at different developmental stages and at different times in each developmental stage to maximize the number of different EST sequences from Diabrotica species. Libraries LIB5444 and LIB5462 were constructed from mRNA pools obtained from first instar (1 g) and third instar (2.9 g) Western corn rootworm larvae, respectively. The resulting insects were snap-frozen...
Embodiment 2
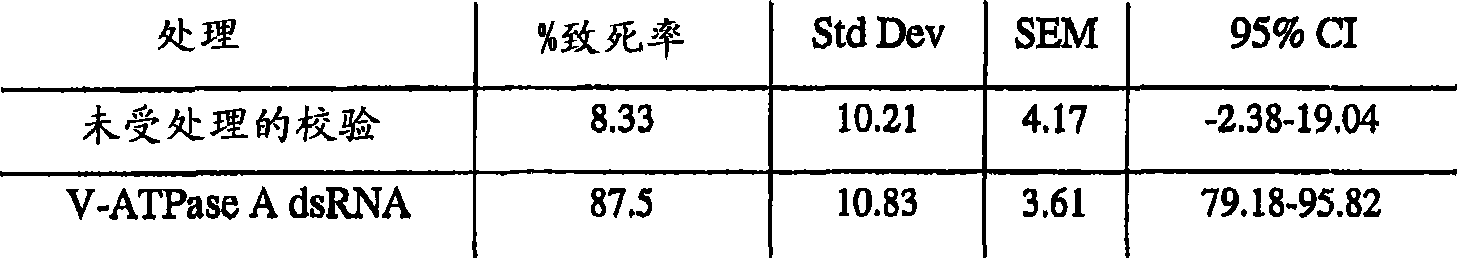
[0323] This example describes significant pest suppression achieved by feeding an invertebrate pest a diet containing double-stranded RNA sequences obtained from the pest.
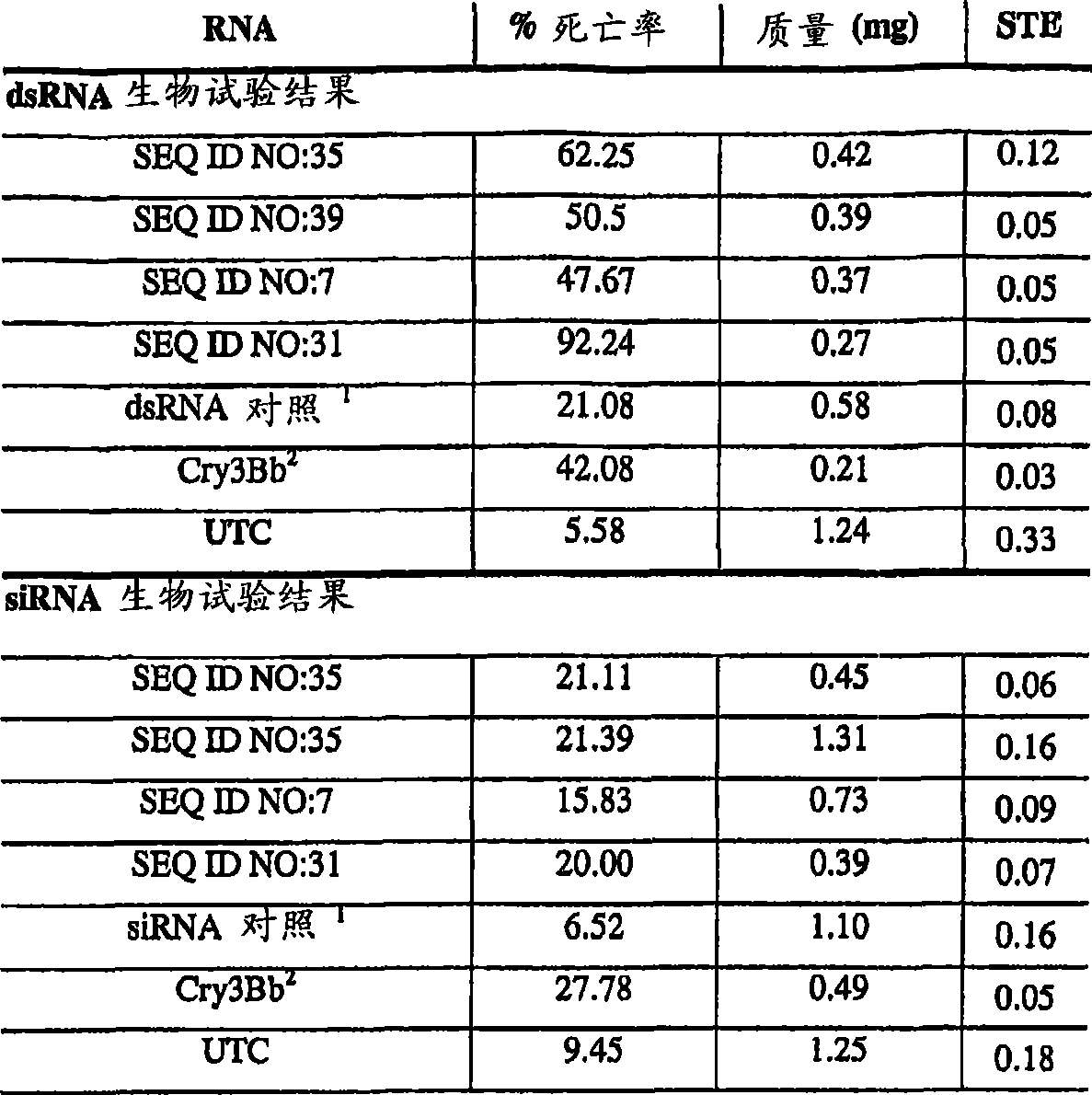
[0324] An artificial diet sufficient to feed corn rootworm larvae was prepared by applying samples of double-stranded RNA sequences obtained from six different corn rootworm cDNA library sequences. Corn rootworm larvae were allowed to eat the diet for several days and were monitored for mortality, morbidity and stunting compared to corn rootworms that were only allowed to eat a control diet. Nucleotide sequences for use in meals were obtained from the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:35, SEQ ID NO:29, SEQ ID NO:47, SEQ ID NO:52, SEQ ID NO:7 and SEQ ID NO:31 Each of them corresponds to a nucleotide sequence obtained from a maize rootworm cDNA library, and their deduced amino acid sequence translations correspond to annotated 40kDa V-ATPase homolog, EF1α homolog, 26S proteosome subunit, respectively Homologs, j...
Embodiment 3
[0338] This example describes nucleotide sequences for expression in plant cells, and the effect of providing such nucleotide sequences in the corn rootworm diet.
[0339] The CHD3 coding sequence obtained from the corn rootworm cDNA library was used to construct the nucleotide sequence encoding the stabilized double-stranded RNA. The cDNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 171 encoding a CHD3 amino acid sequence orthologue or a portion of a homologue was used to construct primer pairs for thermal amplification reactions using the corn rootworm genome template DNA. The primer pair set forth in SEQ ID NO:5 and SEQ ID NO:6 was able to amplify double-stranded genomic amplicons, one of which displayed the sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:7. Three nucleotide sequence fragments were generated from the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:7. Using the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 7 as a template, in a thermal amplification reaction, with a pair of thermal amplification primer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com