Method and apparatus for sending digital image
A technology of digital images and sending methods, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as affecting user experience and not being able to see immediately, and achieve the effect of improving experience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
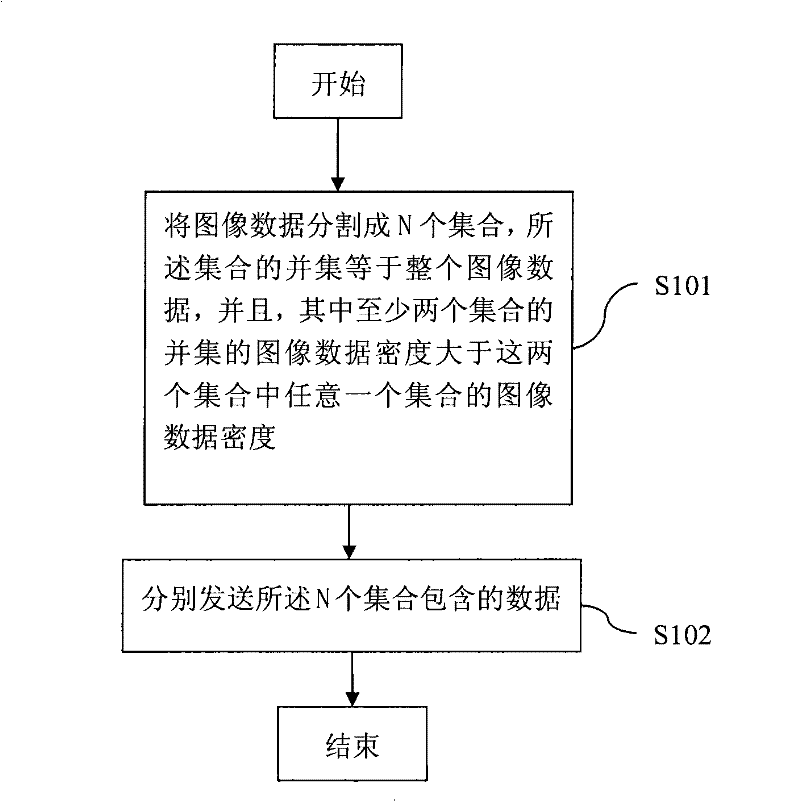
[0037] figure 1 It is the flowchart of this embodiment. It includes the following steps:
[0038] S101. Divide the image data into N sets, the union of the sets is equal to the entire image data, and the image data density of the union of at least two sets is greater than the image data density of any one of the two sets;
[0039] The image data density here is defined as follows: if the pixels corresponding to this set form a single connected domain, the data density is equal to the amount of data contained in the set divided by the number of pixels, if it is a complex connected domain or not, then Data density can be defined as the amount of data contained in the collection divided by the number of pixels in the entire image. The so-called connected domain means that any two points in the area can be connected by a curve in the area. If any closed curve in the connected domain can be continuously shrunk to a point in the area without crossing the boundary of the area, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] In this embodiment, P Mod Q represents an operation of dividing an integer P by an integer Q to obtain a remainder.
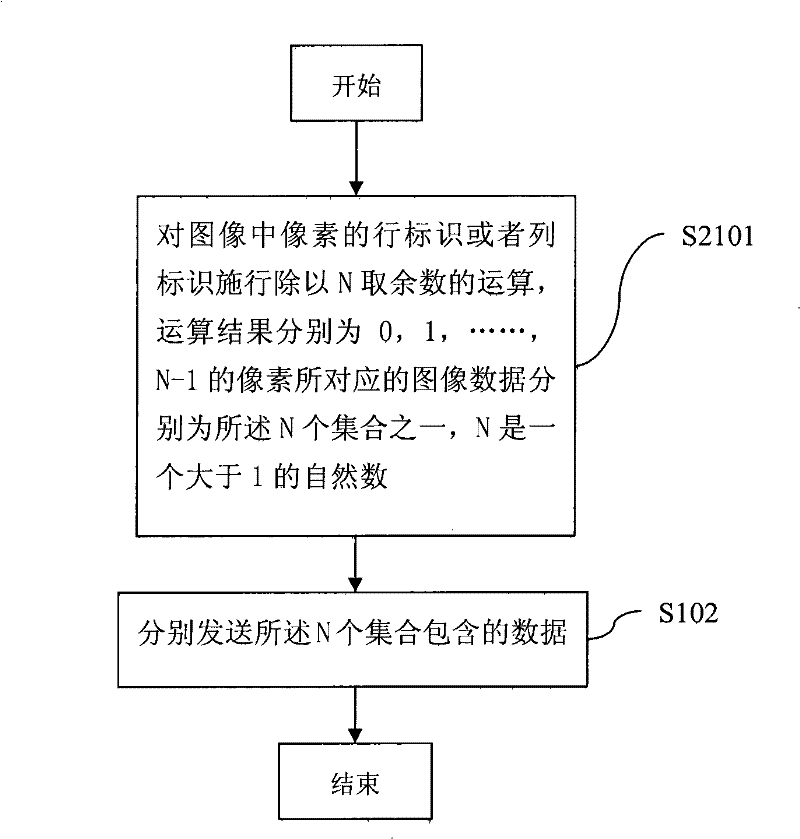
[0045] Such as figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, S101 in Embodiment 1 specifically includes:
[0046] S2101, performing an operation of dividing the row identifier or column identifier of the pixel in the image by N to obtain a remainder, and the image data corresponding to the pixels whose operation results are 0, 1, ..., N-1 are respectively the described One of N sets.
[0047] Here, the row ID and the column ID refer to the sequence numbers of the row and column respectively. The display effect of this embodiment at the receiving end is that rows or columns at a certain distance are displayed sequentially, like the effect of closing a shutter.
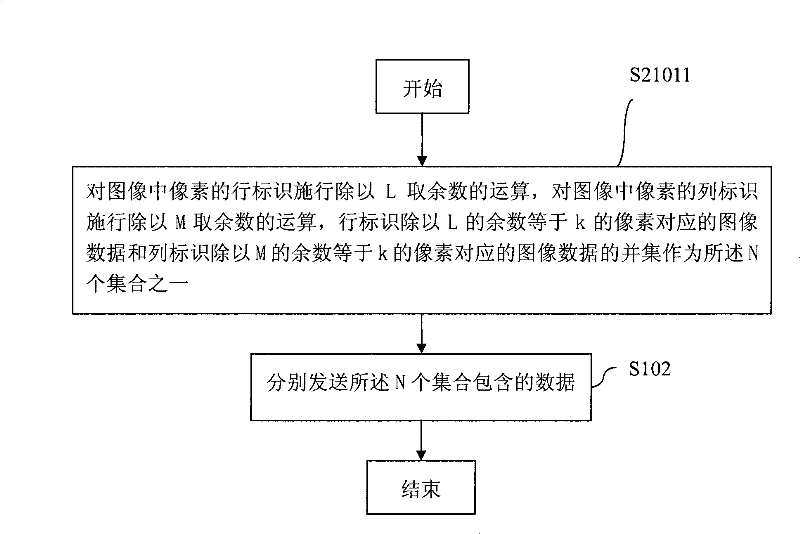
[0048] This embodiment can also be modified as follows, such as Figure 2a As shown, the aforementioned S2101 is specifically:
[0049] S21011, performing an operation of dividing the row identifie...
Embodiment 3
[0053] In this embodiment, image data is divided into sets according to color channels. Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, S101 in Embodiment 1 is specifically:
[0054] S3101. Get the data of each color channel in the image into N sets respectively, where N is equal to the number of color channels.
[0055] Here, the color channels store the values of each color component in the image respectively. Taking the common RGB image as an example, the image includes three color channels of red (R), green (G), and blue (B), which respectively store the red color of each pixel. , green and blue values. Classify the data of each color channel into N sets (N is equal to the number of color channels), and then send the image data included in the N sets respectively. The display effect at the receiving end is to gradually display an image from phantom color to true color. For example, when transmitting an RGB image, the data of the red, green, and blue channels are transm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com