Radio communication device and radio communication method
A wireless communication device and signal transmission technology, applied in multiplex communication, modulated carrier system, transmission system, etc., can solve the problem of low correlation of antenna received signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
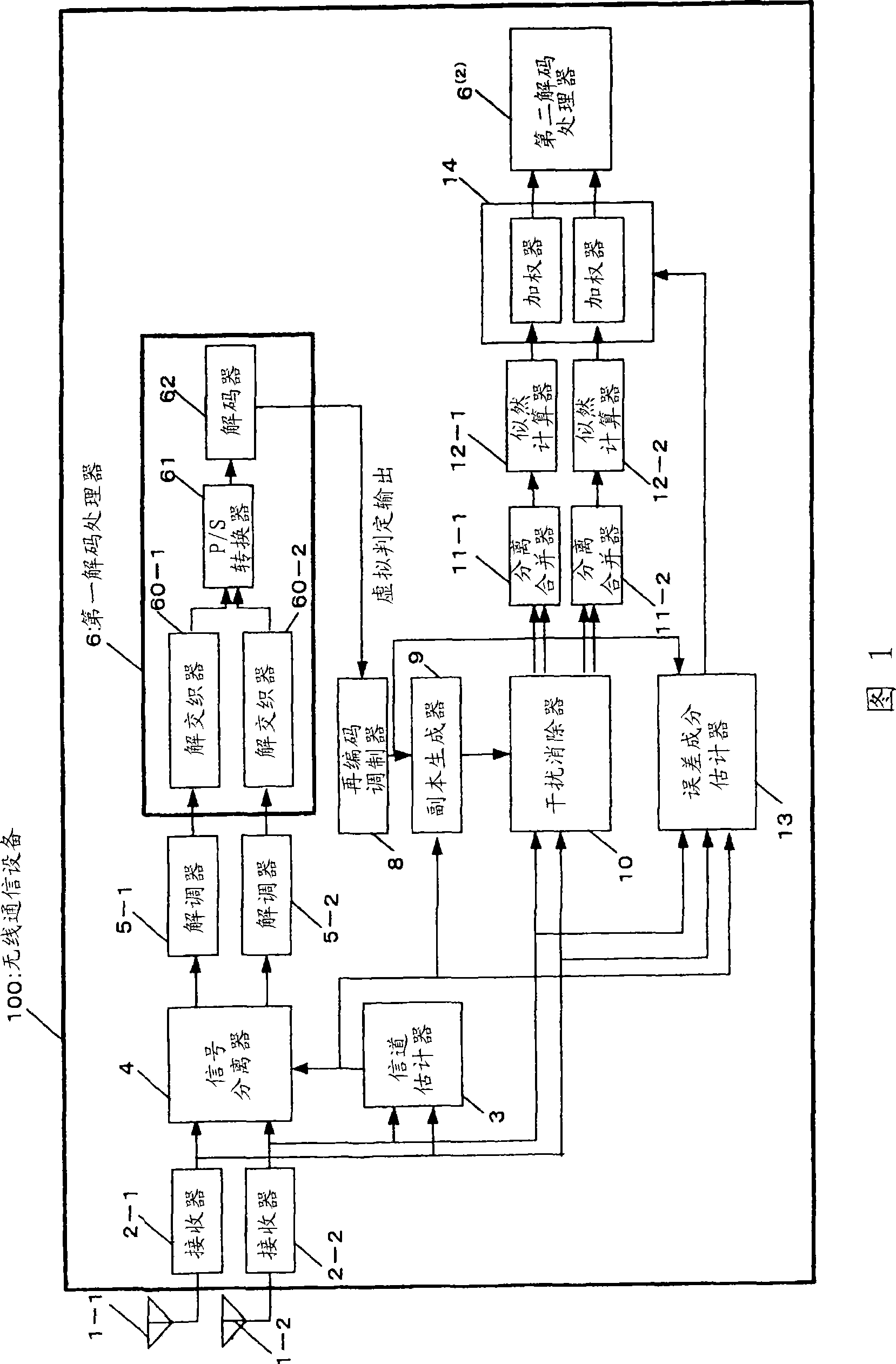
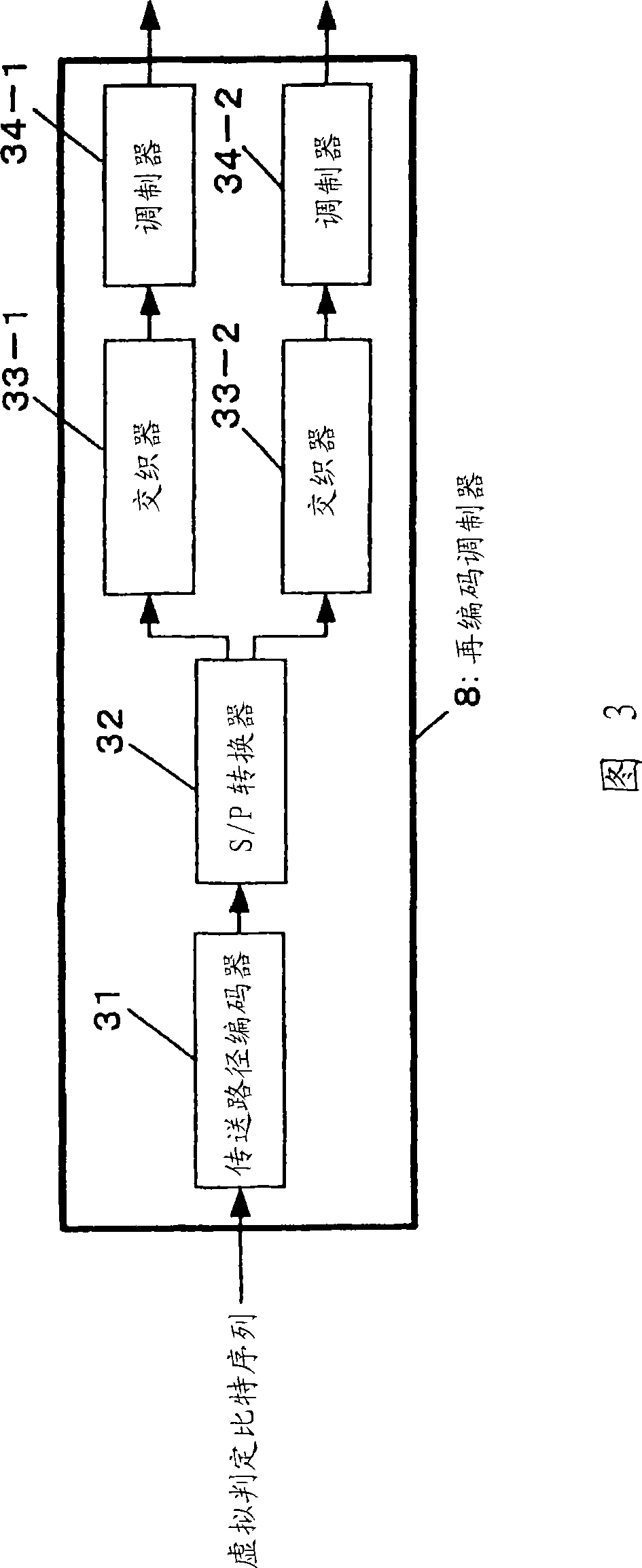
[0116] FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the configuration of a wireless communication device 100 in the first embodiment of the present invention. Only the reception configuration is shown in the wireless communication device 100 of FIG. 1 , whereas the transmission configuration is shown in the wireless communication device 100 a of FIG. 2 . The reception configuration in the embodiment is a configuration in which iterative decoding is performed using a Parallel Interference Canceller (PIC). The operation will be discussed below in the order of Figures 1 and 2:
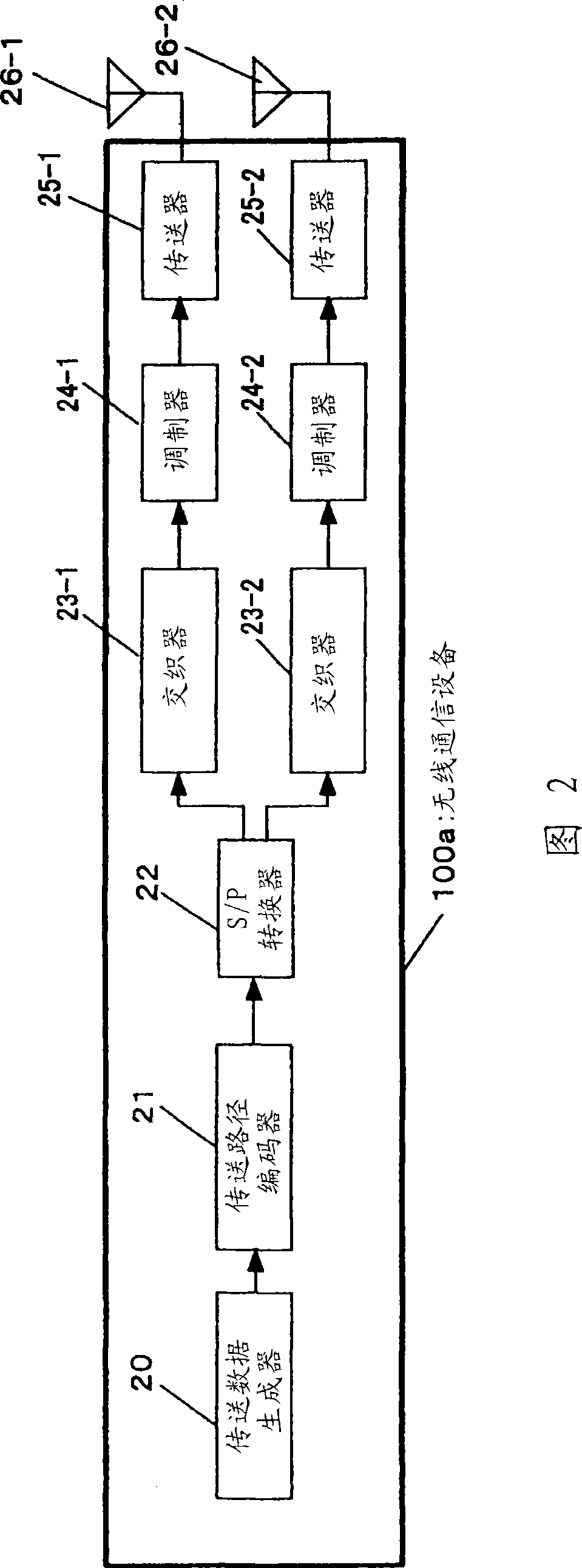
[0117] First, the transmission operation of the wireless communication device 100a will be discussed with reference to FIG. 2 . The wireless communication device 100a performs spatial multiplexing transmission of M transmission sequences from a plurality (M, M>1) of antennas 26-1 to 26-M (hereinafter will be referred to as spatial multiplexing streams) . FIG. 2 shows the configuration of the wireless communication devi...
no. 2 example 1
[0203]FIG. 9 is a diagram showing the configuration of a wireless communication device 200 in the second embodiment of the present invention. Only the reception configuration is shown in the wireless communication device 200 of FIG. 9 , whereas the transmission configuration is shown in the wireless communication device 201 of FIG. 10 . In the first embodiment, a transmission and reception configuration for performing space multiplexing transmission is shown, and a second embodiment shows a case where M=1 in the first embodiment, no space is performed Transmit and receive configurations for multiplexed transports. This operation will be discussed in order using FIGS. 9 and 10 below.
[0204] First, the transmission operation of the wireless communication device 201 will be discussed with reference to FIG. 10 . The wireless communication device 201 transmits a transmission sequence (hereinafter will be referred to as a transmission stream) from an antenna 26 . In FIG. 10, th...
no. 3 example
[0257] FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the configuration of a wireless communication device 100b in the third embodiment of the present invention. In the wireless communication device 100b of FIG. 4, only the reception configuration is shown, and the transmission configuration is the same as that of the wireless communication device 100a shown in FIG. 2, and thus the transmission operation will not be discussed again.
[0258] As a reception configuration in this embodiment, it shows a configuration in which iterative decoding is performed using a parallel interference canceller (PIC). The third embodiment differs from the first embodiment in that a wireless communication device has an error component estimator 15 for estimating an error component based on an input signal, which is different from the error component estimator 13 in the first embodiment. That is, error component estimator 15 estimates error components based on the outputs of stream reception quality estimator 7 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com