Method for judging decode halt of LDPC code based on checksum error mode
A technology of LDPC code and error mode, which is applied in the field of decoding control of low density parity check codes, and can solve the problems of low decoding performance in high signal-to-noise ratio regions, high selection difficulty, and increased average iteration amount.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
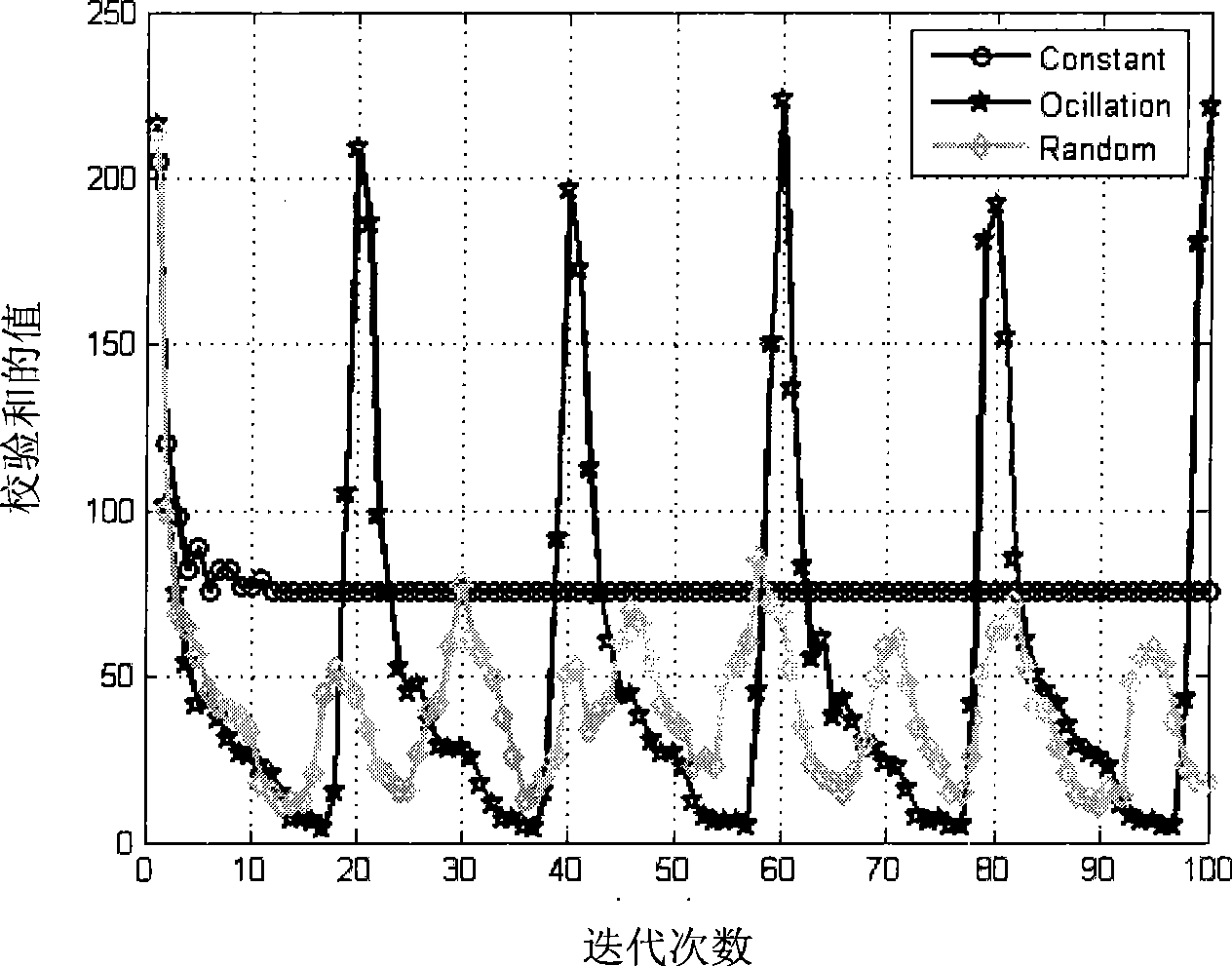
[0032] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
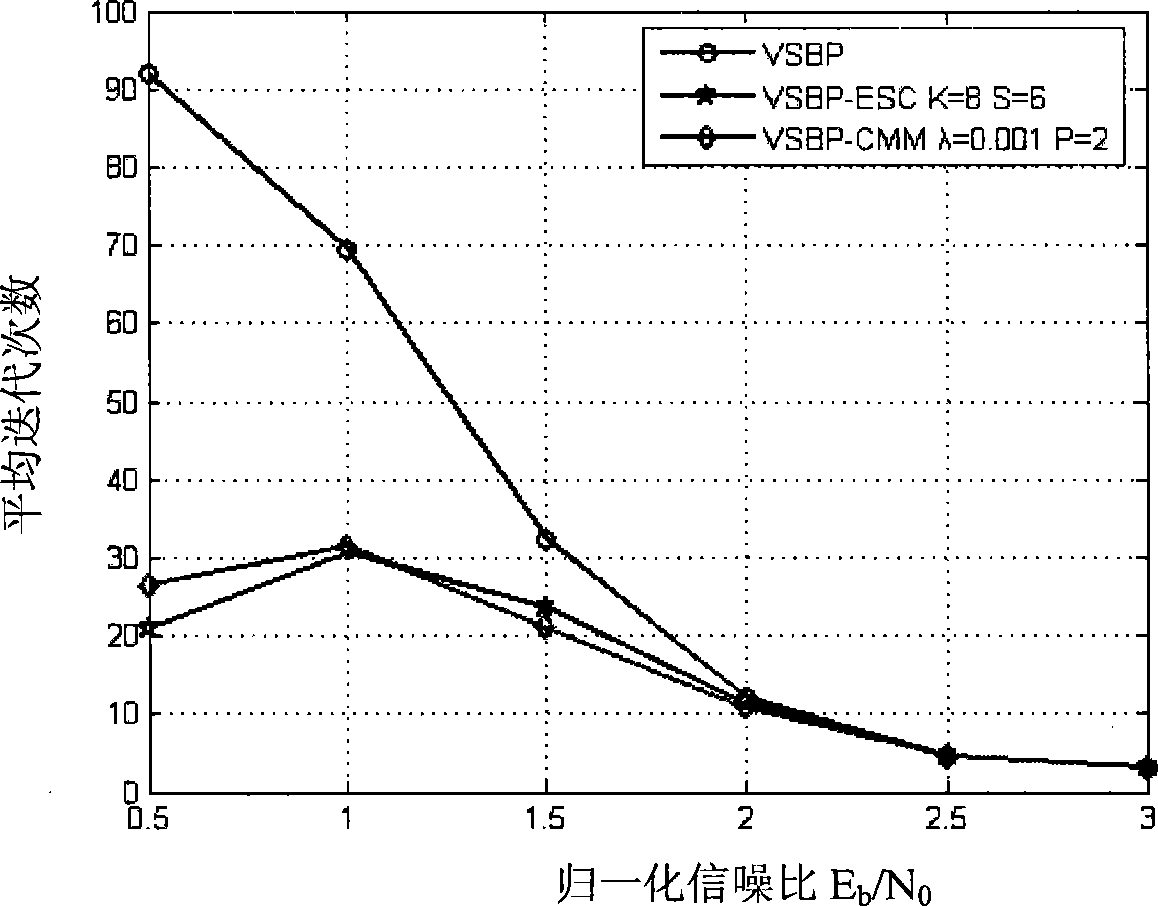
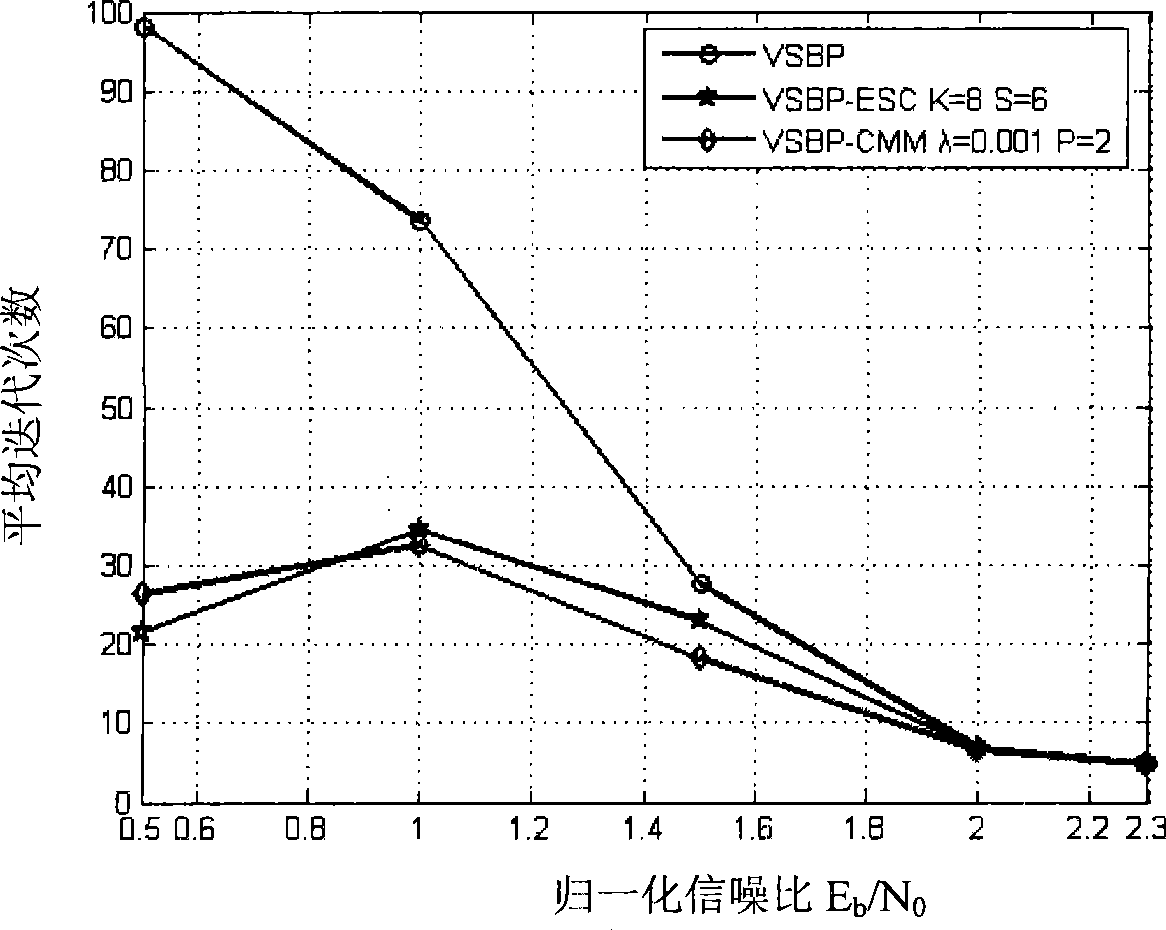
[0033] In order to verify the performance of the decoding stop decision criterion, the present invention adopts the belief propagation method to perform iterative decoding, respectively constructing the 1 / 2 code rate (1008,504) regular LDPC code constructed by the Gallager method and the 1 / 2 code constructed by the PEG method The (504, 252) quasi-cyclic LDPC code with high rate is simulated by computer in AWGN channel. Attached Figure 2-3The quasi-cyclic LDPC (504, 252) codes and Gallager (1008, 504) rule LDPC codes based on the PEG algorithm are the curves of the average number of iterations with the signal-to-noise ratio under different decoding stop criteria, where VSBP is the standard decoding The serial iterative decoding algorithm with stop decision criterion, VSBP-CMM is a serial iterative decoding algorithm with CMM decoding stop decision criterion, and VSBP-ESC (E...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com