Semiconductor memory device and method for fabricating the same
A technology for storage devices and manufacturing methods, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, information storage, etc., can solve problems such as data disappearance and chip ID can no longer be read
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
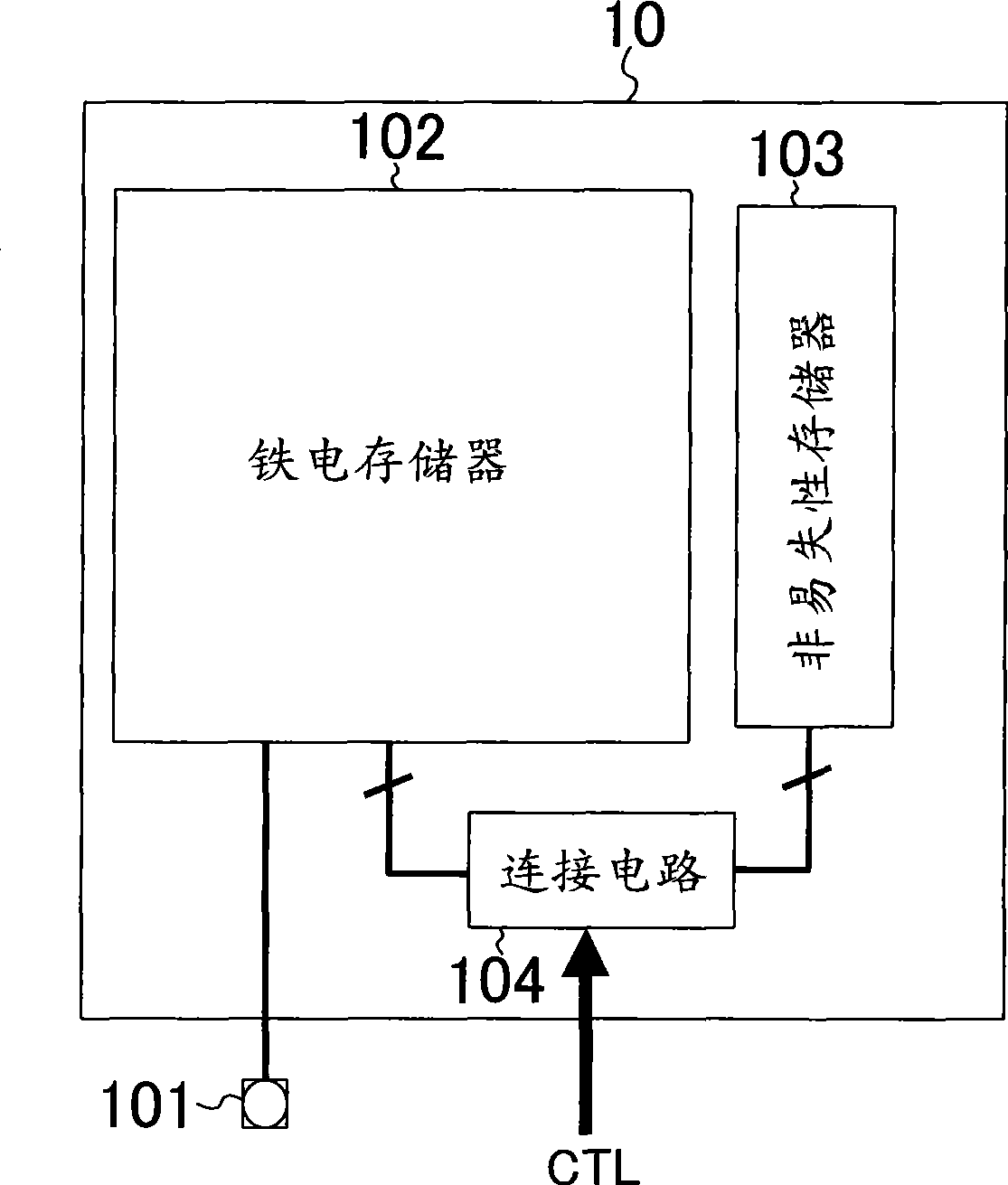
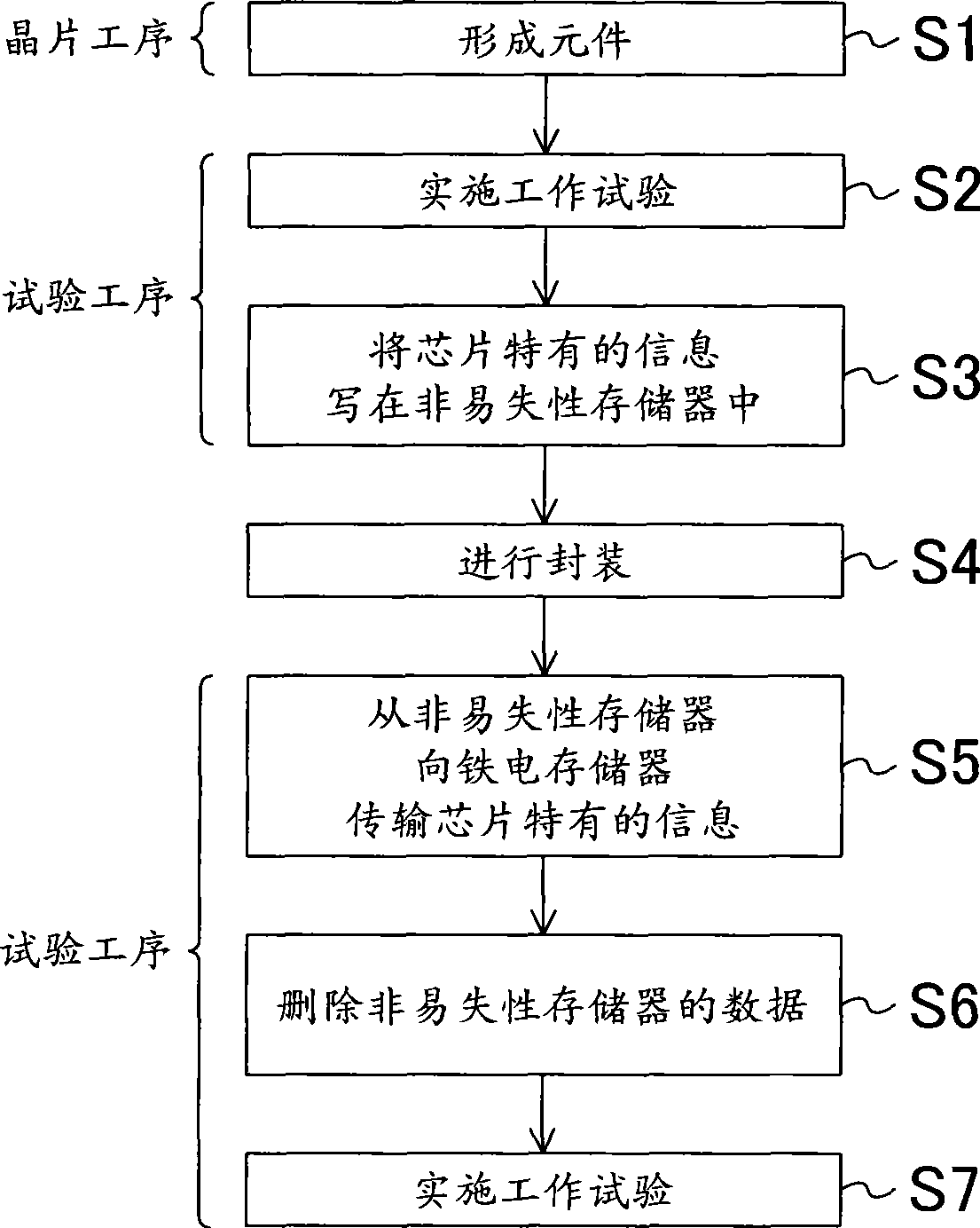
[0020] figure 1 The structure of the semiconductor storage device (hereinafter, this semiconductor storage device will also be simply referred to as a "chip") according to the first embodiment is shown. In the chip 10 according to the present embodiment, the terminal 101 is a terminal for reading or writing data to the ferroelectric memory 102 . The nonvolatile memory 103 is a memory whose ability to hold data at high temperatures is higher than that of the ferroelectric memory 102 . Specifically, a fuse that can be physically cut (physical fuse), a fuse that can be cut electrically (eFUSE: Electronic Fuse), or a nonvolatile memory composed of CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistors (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) can be used. Semiconductor nonvolatile memory) and the like constitute the nonvolatile memory 103, and the nonvolatile memory 103 can also be constituted by combining the above-mentioned components according to circumstances. The connec...
no. 2 approach
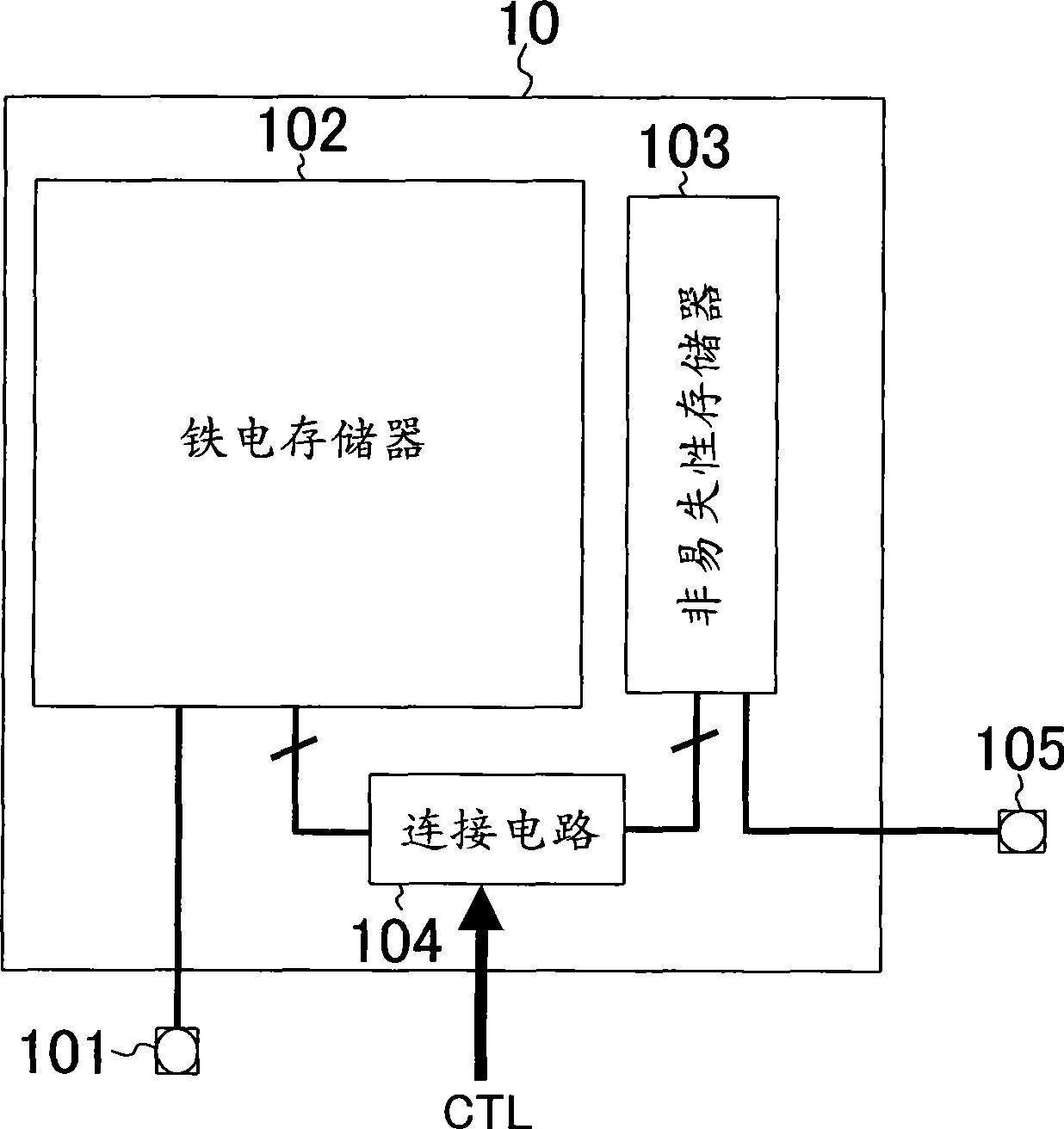
[0027] image 3 The structure of the semiconductor memory device according to the second embodiment is shown. The chip 10 according to this embodiment has a configuration in which a terminal 105 capable of accessing a nonvolatile memory 103 is added to the semiconductor memory device according to the first embodiment. According to this embodiment, the data written in the nonvolatile memory 103 can be directly read from the terminal 105 without going through the ferroelectric memory 102, and can be confirmed. In addition, when the nonvolatile memory 103 includes an electronic fuse or a complementary metal oxide semiconductor nonvolatile memory, it is possible to directly input the data to be written to the nonvolatile memory 103 from the terminal 105 without passing through the ferroelectric memory 102 . The data.
no. 3 approach
[0029] Figure 4The structure of the semiconductor memory device according to the third embodiment is shown. The chip 10 according to this embodiment has a structure in which the terminal 105 in the semiconductor memory device according to the second embodiment is not connected to the nonvolatile memory 103 but is connected to the connection circuit 104 . The connection circuit 104 switches the connection state between the ferroelectric memory 102 and the nonvolatile memory 103 and the connection state between the nonvolatile memory 103 and the terminal 106 . In the second embodiment, a data bus for interconnecting the nonvolatile memory 103 and the terminals 105 is required, but such a data bus is not required in the present embodiment. Therefore, according to the present embodiment, the chip area can be reduced to an area smaller than that of the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com