Method and apparatus for dynamically regulating visual angle of screen
A technology of dynamic adjustment and screen viewing angle, which is applied to static indicators, instrument parts, program control in sequence/logic controllers, etc., can solve problems such as inconvenient, prevent data leakage and increase convenience Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
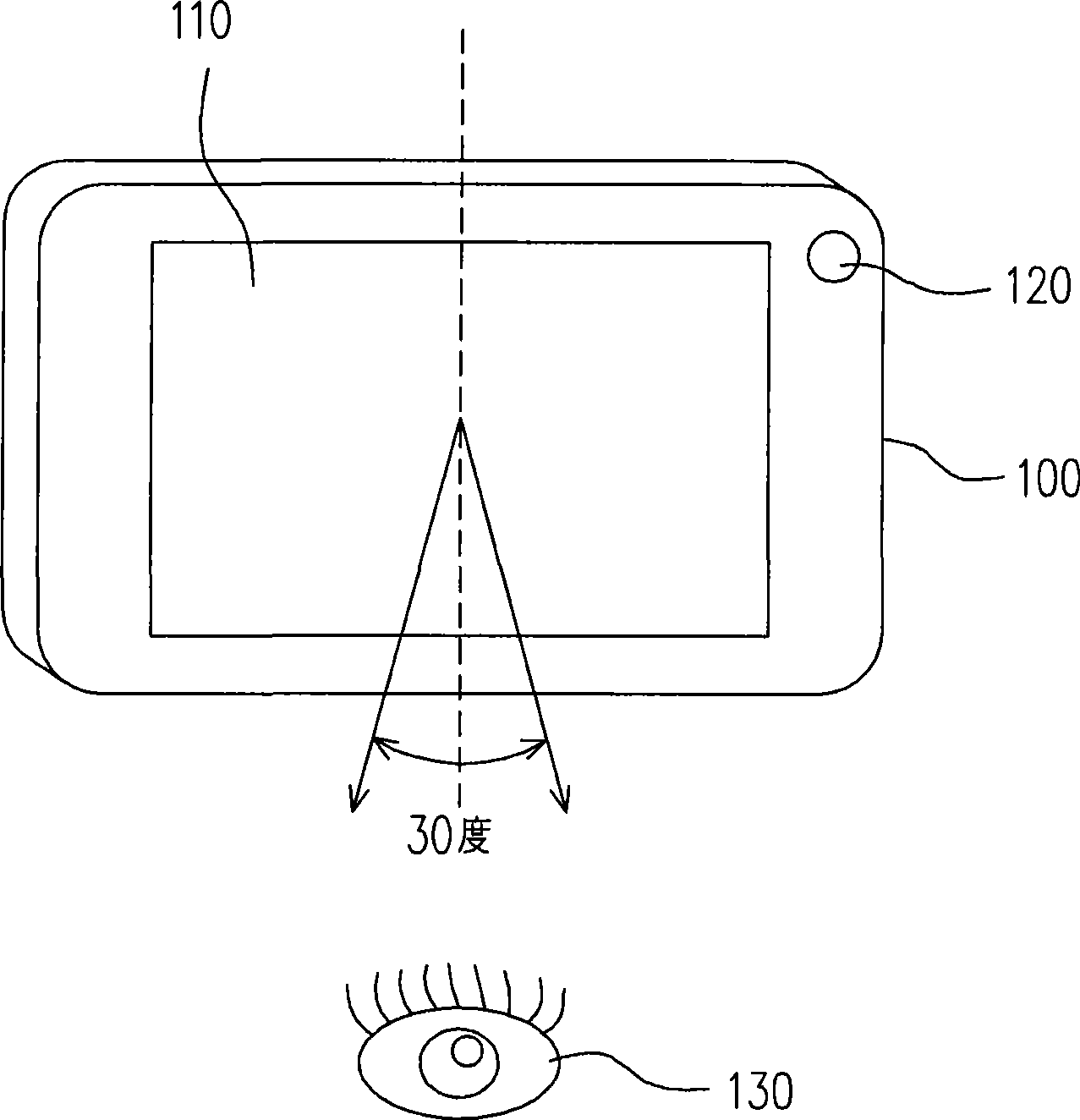
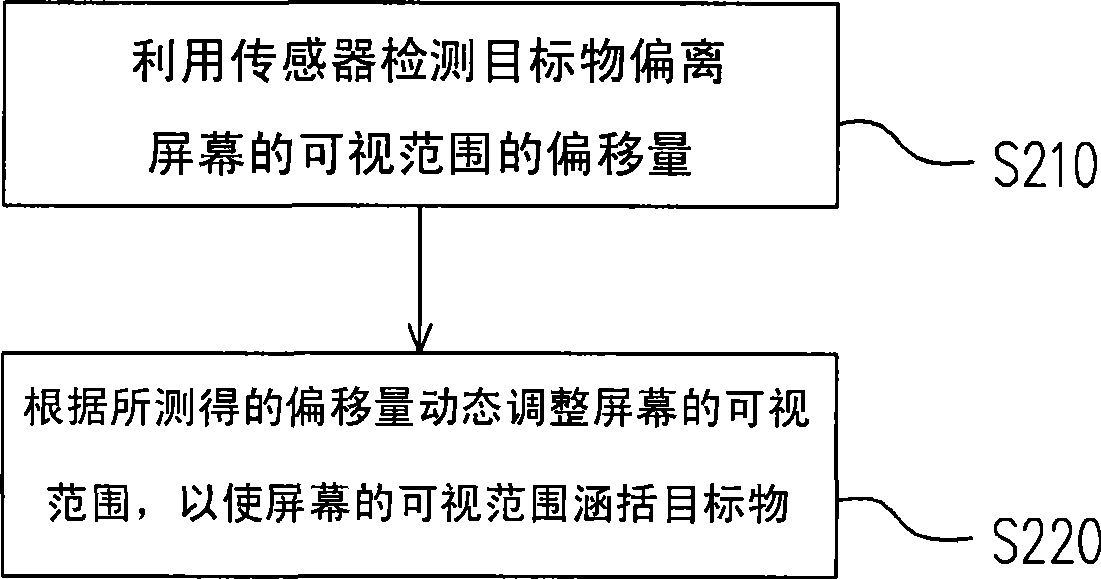
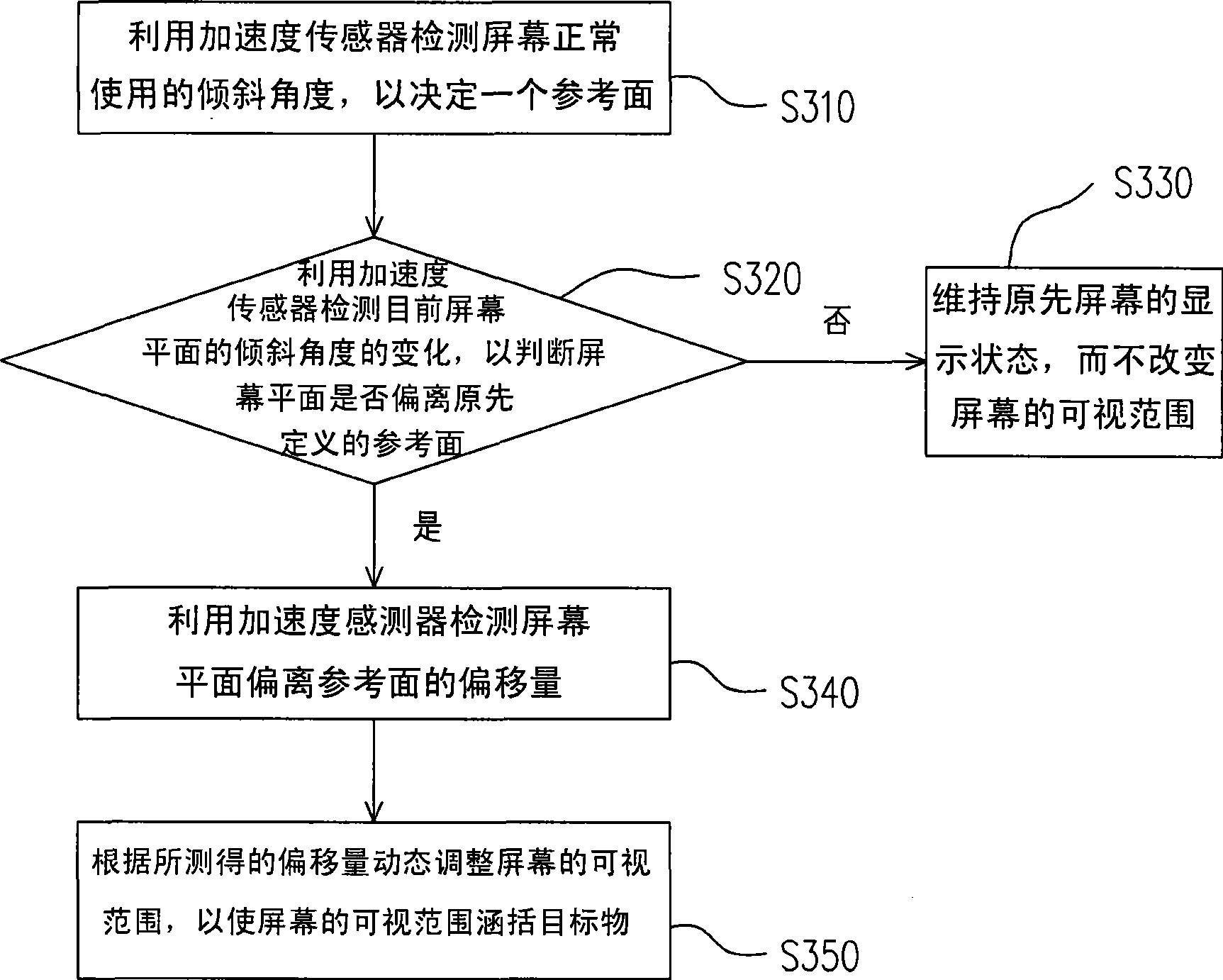
[0043]Generally speaking, the best viewing angle for the user is to align the head with the center of the screen. Therefore, the current method of limiting the viewing angle of the screen is to limit the viewing range of the screen to a certain angle on the front of the screen. However, the viewing angle of the handheld electronic device may change at any time due to factors such as the user's holding method, viewing posture, or external light. At this time, it is necessary to find out the inclination of the handheld electronic device Angle or displacement of the user, and timely and appropriate correction of the viewing angle of the screen, so that the user can still see the screen image under various circumstances. The present invention is a set of method and device for dynamically adjusting the viewing angle of a screen developed based on the above concepts. In order to make the content of the present invention clearer, the following specific examples are given as examples ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com