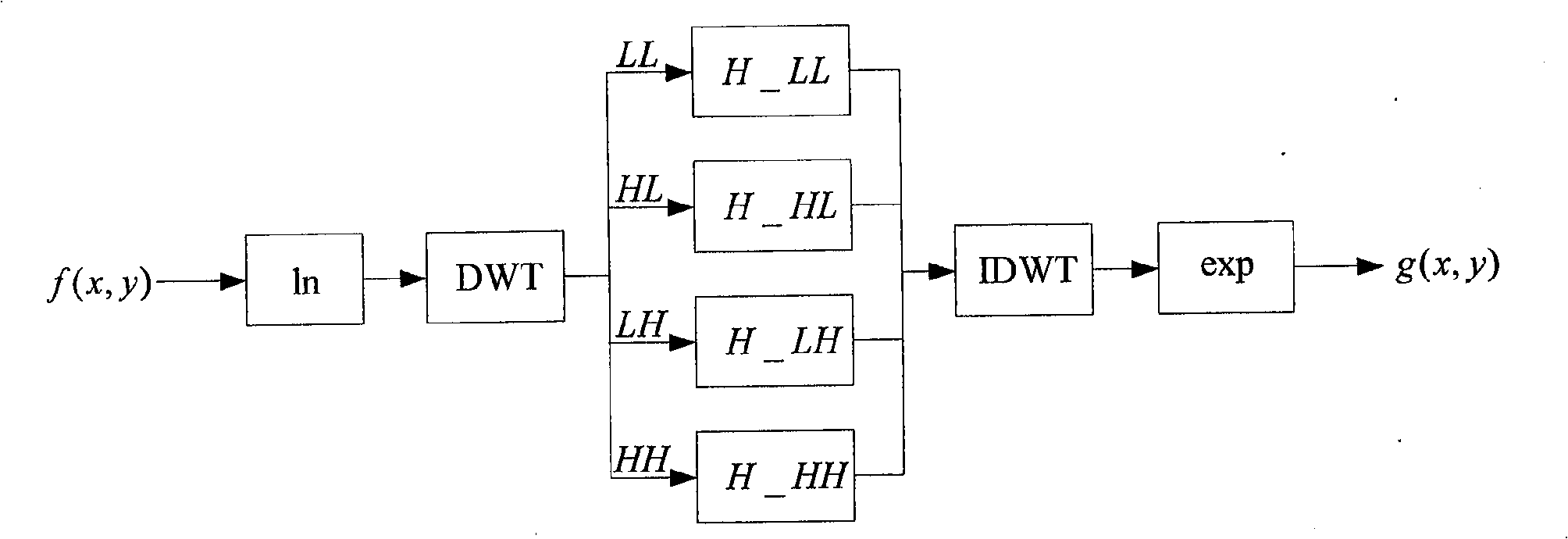
Method for detecting cooked image based on small wave domain homomorphic filtering
A homomorphic filtering and wavelet domain technology, applied in the field of blind detection of image content authenticity, can solve the problem of ineffective detection of image authenticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
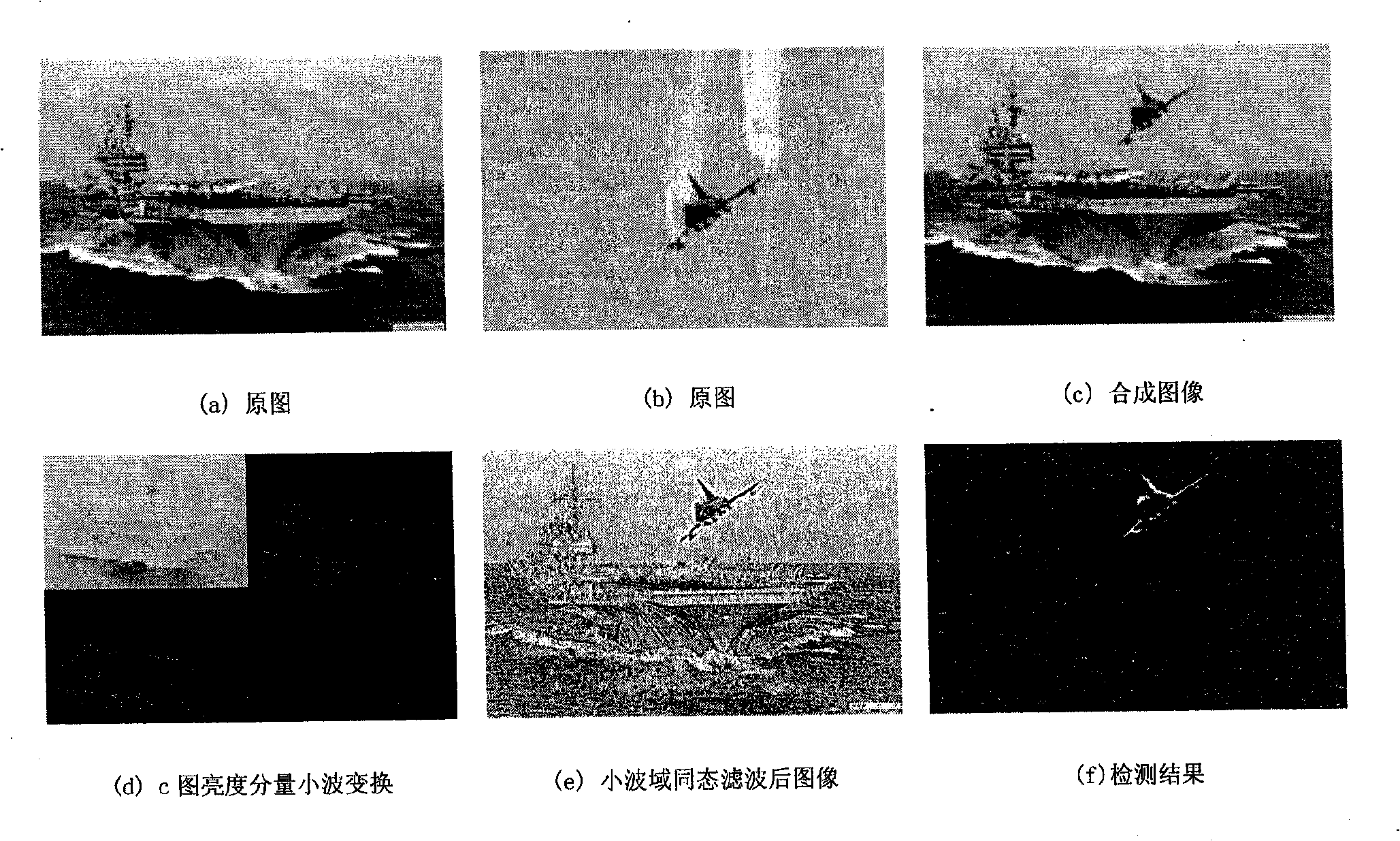
[0037] figure 2 (a) and (b) are the original images, and (c) is a forged image, which is obtained by copying the aircraft in the original image (b) to (a), and using post-processing operations such as edge blurring. The forged image (c) is detected by wavelet domain homomorphic filtering. (d) shows the wavelet transform of the brightness component of the forged image, (e) is the image after homomorphic filtering in the wavelet domain, and (f) is the detection result.
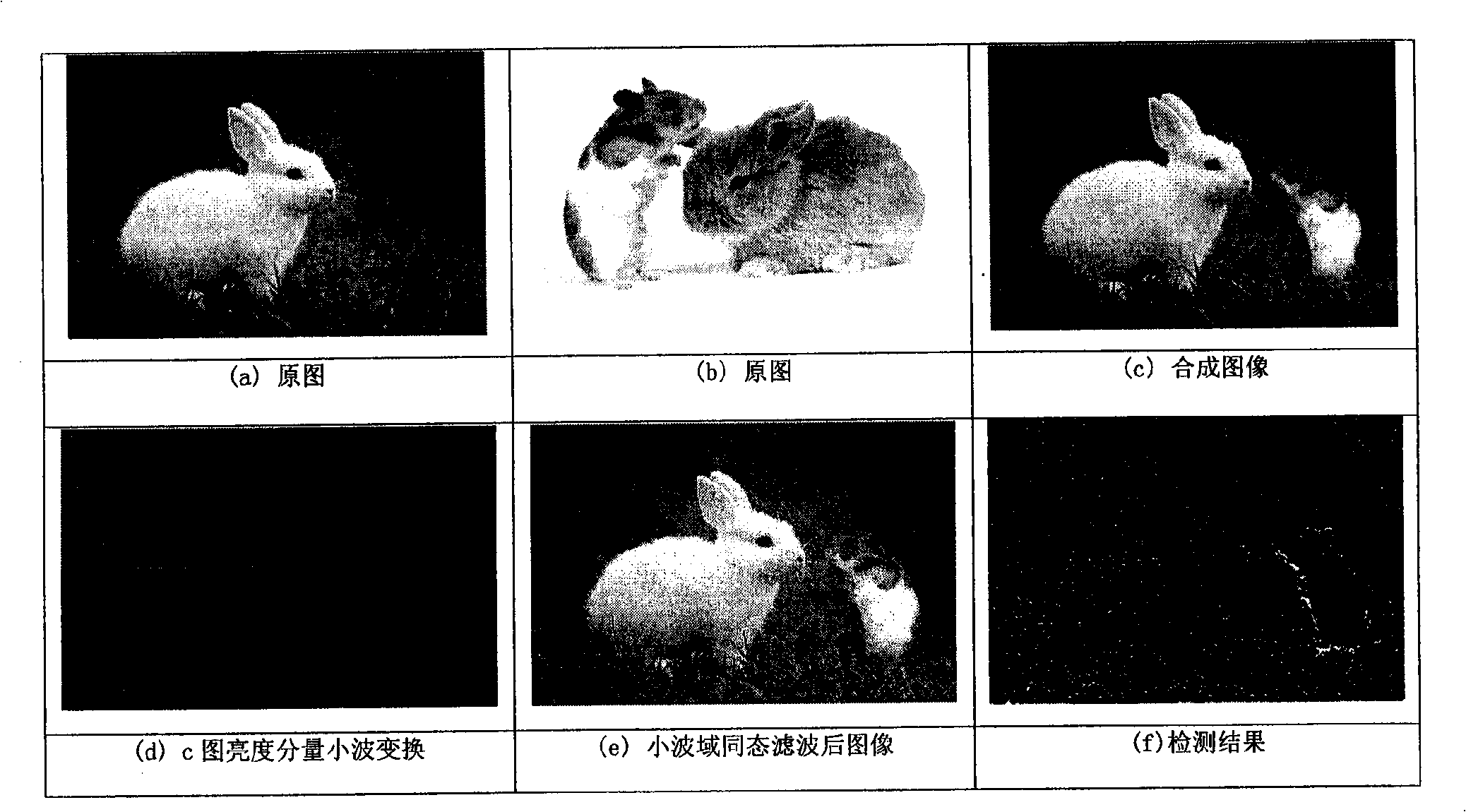
[0038] image 3 (a) and (b) are the original images, and (c) is a forged image, which is obtained by copying the mouse in the original image (b) to (a), and using post-processing operations such as edge blurring. We use wavelet domain homomorphic filtering to detect its fake image (c). (d) shows the wavelet transform of the brightness component of the forged image, (e) is the image after homomorphic filtering in the wavelet domain, and (f) is the detection result. The detection steps are as follows:
[003...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com