Low swelling biocompatibility hydrogel
A hydrogel and swelling technology, applied in tissue regeneration, prosthetics, surgery, etc., can solve problems such as inapplicability around the spine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Example 1: Low swelling hydrogel formulation
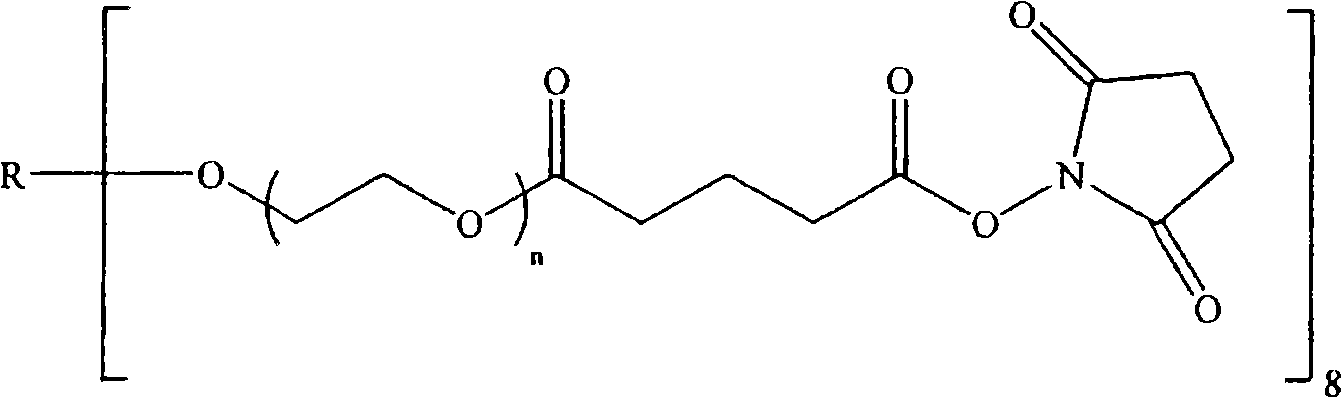
[0078] To prepare the hydrogel, trilysine containing primary amine functional groups and electrophilic functional groups containing succinimidyl esters (specifically, succinimide Imidoglutarate, SG) was reacted with a multi-armed polyethylene glycol (PEG) electrophilic precursor, polyethylene glycol with a total MW of approximately 20,000 MW at each end of the four arms (4a) ( Sometimes this article is also referred to as 4a20k SG).
[0079] Then, in addition to using a 6-arm (6a) or 8-arm (8a) precursor (with a functional group at the end of each arm) containing PEG arms with a total MW of about 10,000 (10k) or 20,000 (20k) instead of the four-arm precursor, the Still with a 1:1 electrophile-nucleophile functional group ratio, essentially the same hydrogels were produced.
[0080] Taking 4a20k SG as an example, the detailed steps for preparing the hydrogel are as follows. Mix trilysine into 0.075 M borate buffer at a co...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: The role of the osmotic environment in swelling
[0090] Hydrogels were prepared by using 4a20k SG as described in Example 1, and exposed to physiologically buffered saline with a pH value of 7.0-7.4 and an osmotic pressure of approximately 300 mOs or to a high-strength solution of the same saline (double -strength solution) to test the role of osmotic environment in swelling. When n = 3 (hydrogel plug per molar concentration of PBS), the degree of swelling from gelation to equilibrium swelling (recorded at 24 hours) averaged 68% for normal saline and 57% for high strength saline. These results suggest that differences in osmotic pressure inherent in the swelling environment do not account for the reduced swelling of hydrogels prepared with precursors with different arm lengths, since the change in swelling as arm length increases is too small to cause the typically observed to a larger change.
Embodiment 3
[0091] Example 3: Low-swelling hydrogels tested in vivo
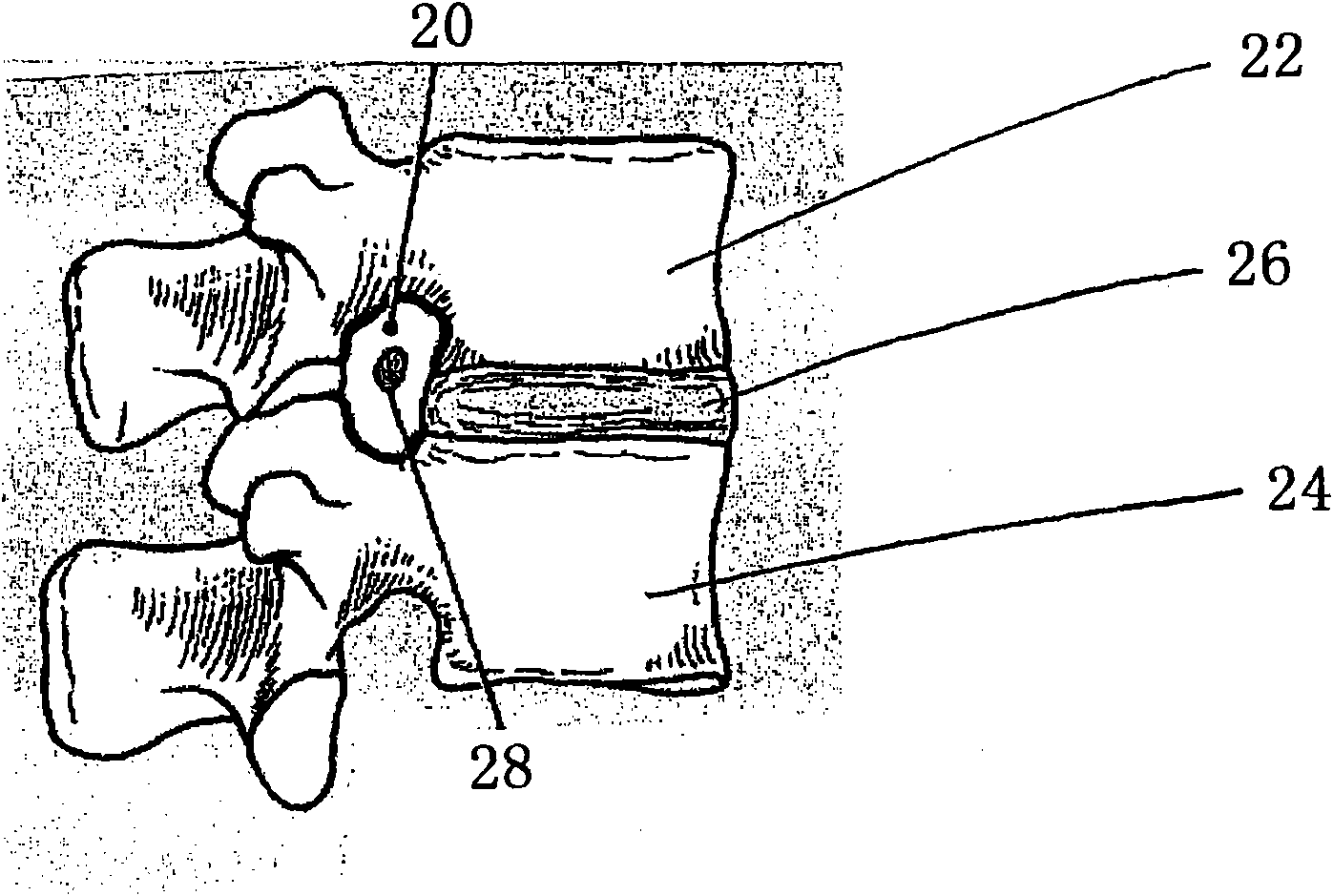
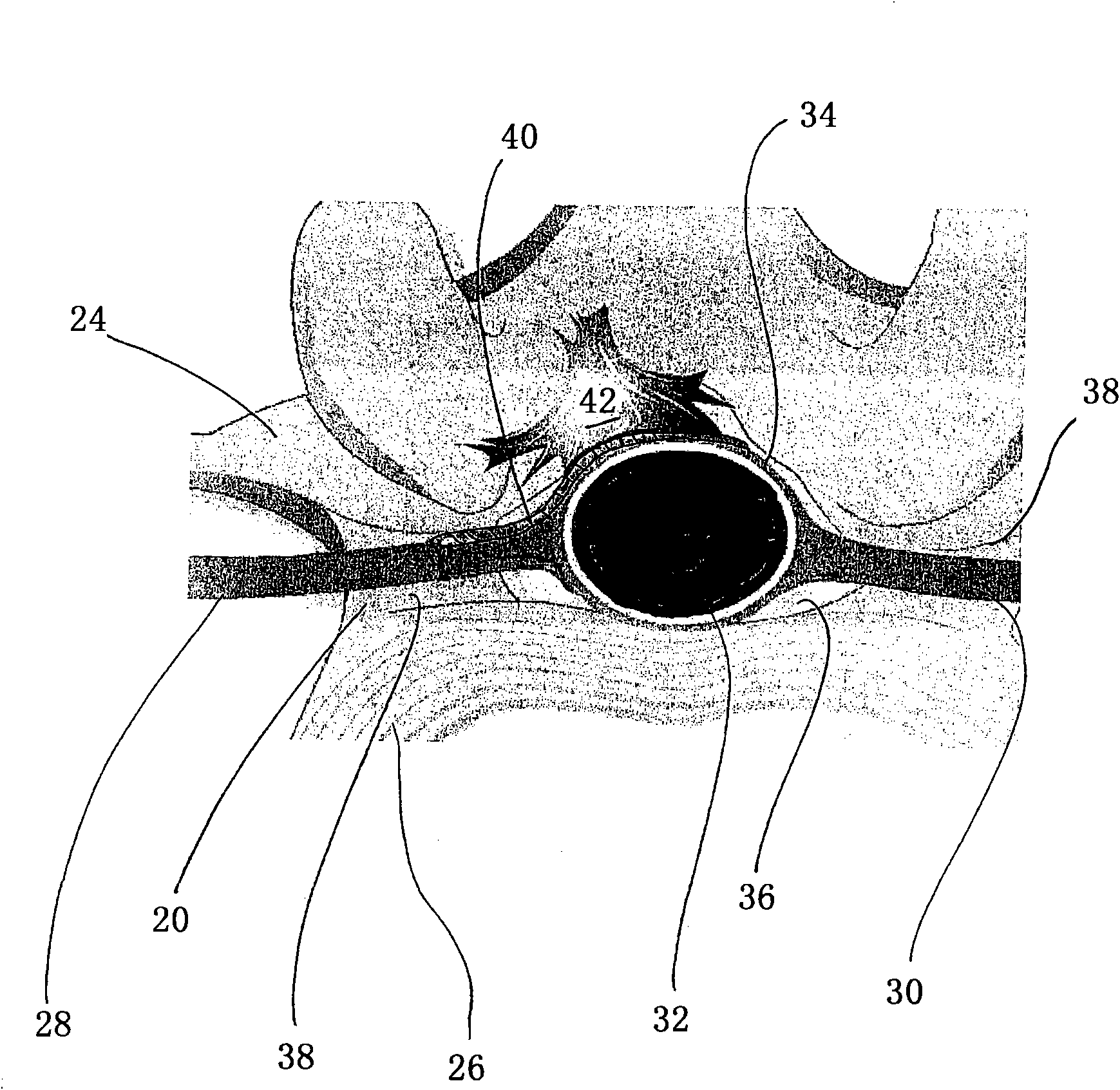
[0092] Implantation of low-swelling hydrogels in living spines. Formulation 1 is a hydrogel prepared by reacting a trilysine precursor reactive with 8a15k SG under conditions as described in Example 1 and Table 1. The precursor is administered using a dual chamber applicator that mixes the solution and places it at the site of application.
[0093] All 15 dogs underwent full width laminectomies at L2 and L5, after which a midline 1 cm dural incision was made and then sutured. Animals were randomly selected as control groups (n = 5 animals; no additional treatment before suturing), or used Dual-chamber pipette (Hemaedics, Malibu, CA) (n = 5 animals) or MICROMYST TM A dual chamber dispenser (Confluent Surgical Instruments, Waltham, MA) (n = 5 animals) used Formulation 1 at both sites of the laminectomy. Formulation 1 was observed to adhere to the tissue within seconds of its application.
[0094] All animals were op...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| gel time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com