Method of improving fermentability of early flocculating malt
An early-setting malt technology, applied in the field of tannic acid to improve the fermentability of early-setting malt, to achieve the effect of improving poor fermentation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] (fermentability improvement effect of gallic tannin)
[0053] The fermentability-improving effect of the gallic tannin in the low beer wort using early-setting malt was tested.
[0054] (method)
[0055] In a 500ml fermentation test tube, gallic tannins (0g-2g / Kg malt = 0g-20g / 2000 G·10min Kg centrifuged yeast), and then fermented at 12°C.
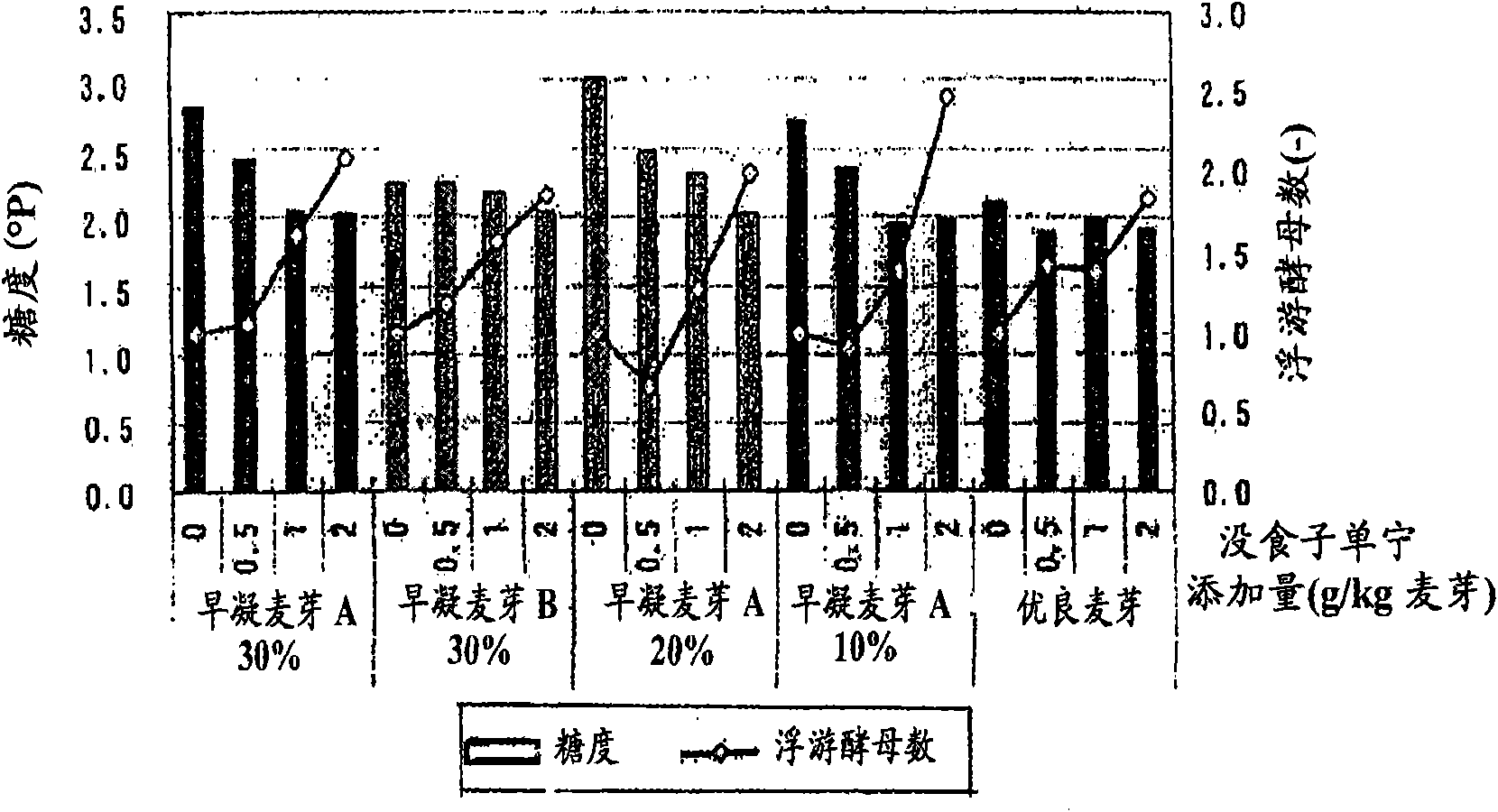
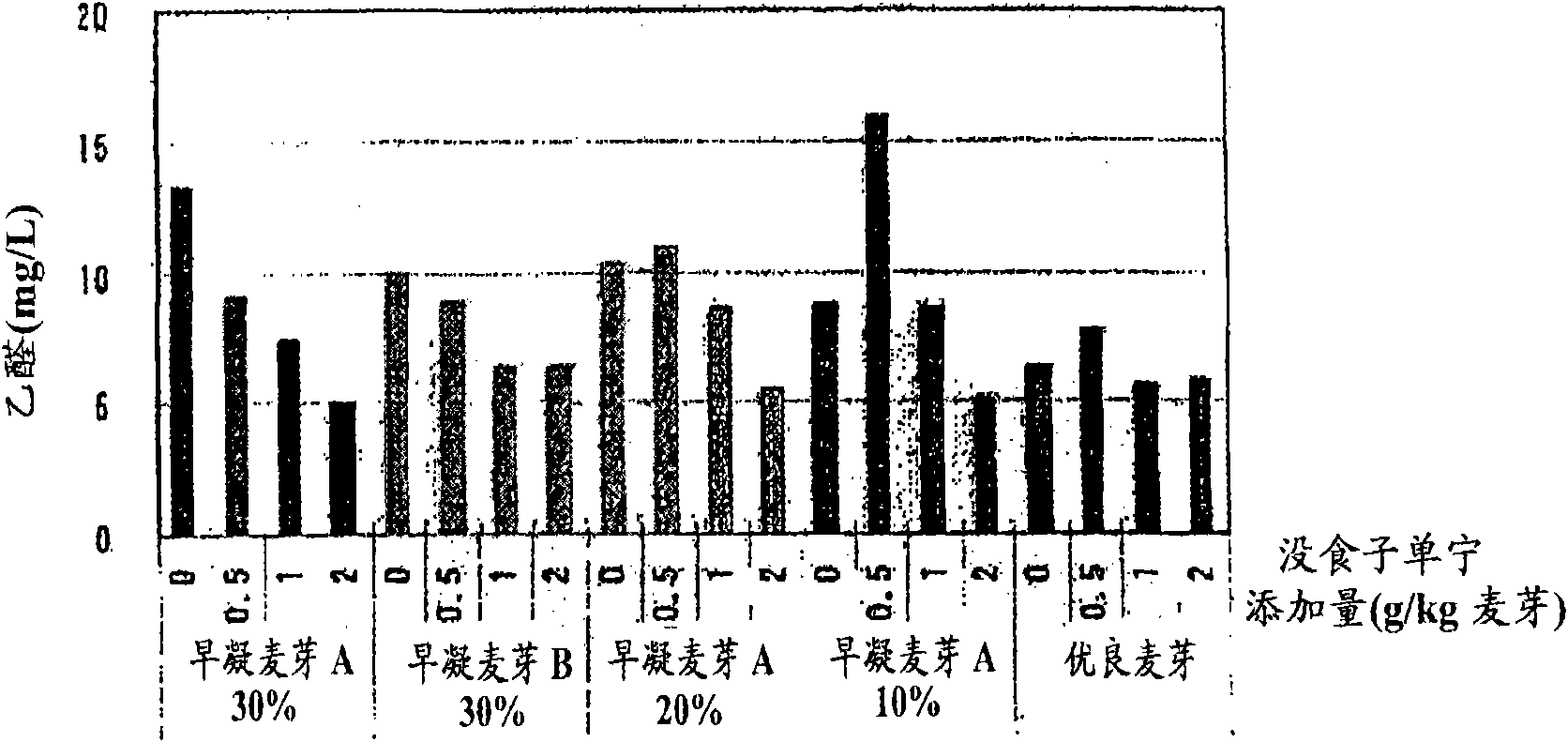
[0056] (result)
[0057] The results of chemical analyzes during and at the end of the fermentation are shown in Figure 1-2 . figure 1 The relationship between the ratio of pale early-setting malt and the concentration of gallic tannins (the number of planktonic cells on the 7th day of main fermentation · sugar content) is shown in . figure 1 In the figure, the number of floating yeasts (-) represents the ratio of floating yeasts when the added yeast was regarded as 1. figure 2 The relationship between the proportion of pale early setting malt and the concentration of gallic tannins is shown in (Acetaldehyde analysis value...
Embodiment 2
[0060] (addition time of gallo tannins)
[0061] The fermentability improvement effect by adding time of different gallic tannins was tested.
[0062] (method)
[0063] In a 500-ml fermentation test tube, using the low-color early-setting malt (20%) using the low-colored early-setting malt (20%), different expressions were confirmed under the following conditions.
[0064] (a) Add gallotannin (2g / Kg malt=20g / 2000G·10minKg centrifugal yeast) to cold wort.
[0065] (b) Add gallotannin (0.1 g / 2000 G·10 min Kg centrifuged yeast) to the yeast.
[0066] (c) Gallotannin (2g / Kg malt) was added to cold wort, and centrifugation was then performed to completely remove the protein fraction.
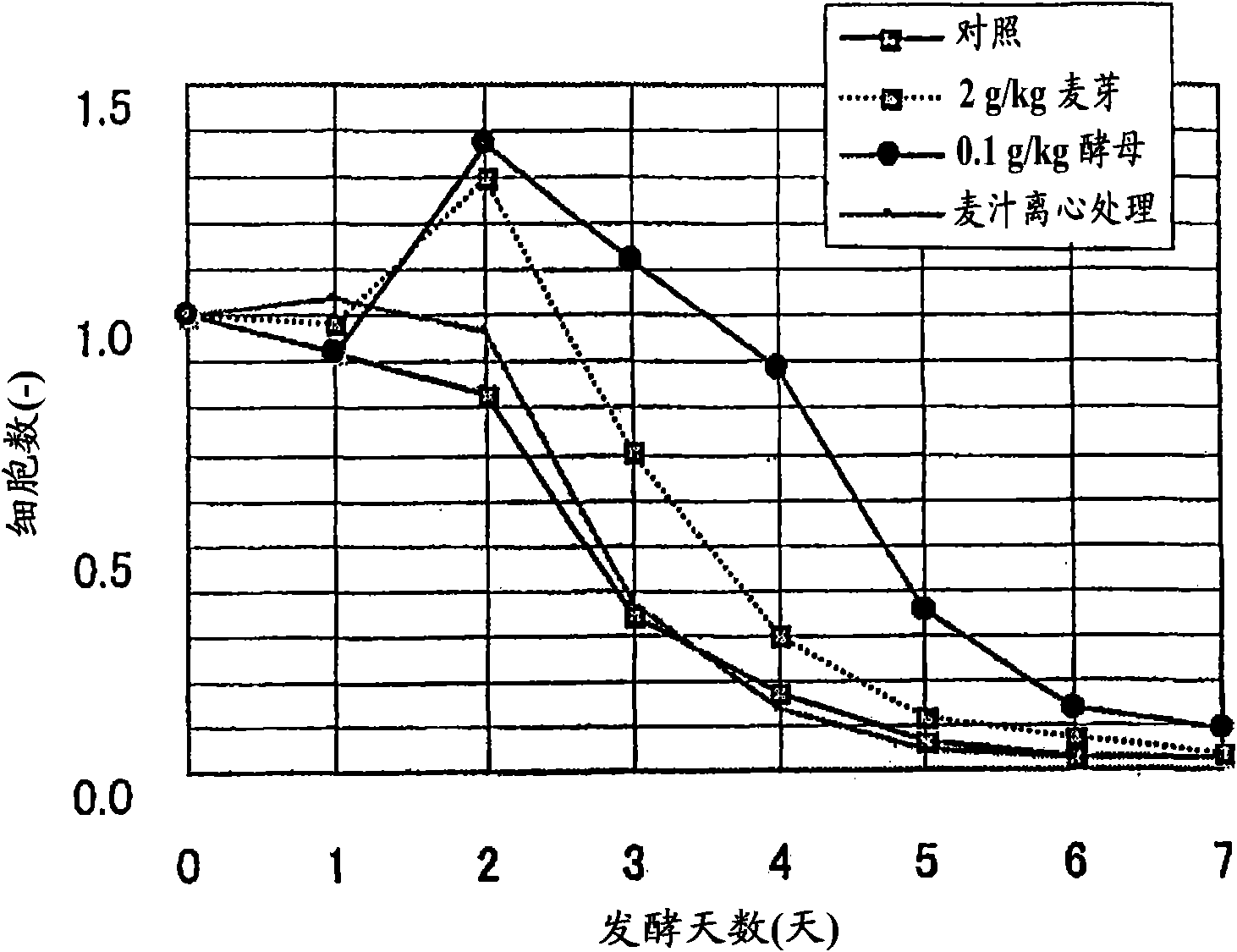
[0067] (result)
[0068] The results are shown in image 3 and Figure 4 . image 3 The improvement effect of the fermentability of gallic tannin (the change in the number of planktonic cells in the main fermentation) was shown in Figure 4 The fermentability-improving effect of gallic tannins ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] (The upper limit of the added amount of gallotannin)
[0076] Test on the influence of excessive addition of gallic tannins.
[0077] (method)
[0078] In a 500ml fermentation test tube, 0g, 2g, 4g / Kg malt = 0g, 20g, 40g / 2000G·10minKg gallotannins of centrifuged yeast were added to the cold wort of the low-colored early-setting malt. Fermentation was then carried out at 12°C.
[0079] (result)
[0080] The results of chemical analyzes during and at the end of the fermentation are shown in Figure 11 , 12 . Figure 11 Shows the result of confirming the optimum addition amount of gallotannin (change in the number of planktonic cells in the main fermentation), Figure 12 The result of confirming the optimal addition amount of gallotannin (extract consumption change in main fermentation) is shown. As shown in the figure, the effect of gallic tannins depends on the added concentration, but in the case of 4g / Kg malt = 40g / Kg yeast, it was observed that the yeast extrac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com