Matching a watermark to a host sampling rate
A sampling rate, matching technology, applied in speech analysis, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of wasting watermarking channels, expensive computing overhead, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding the accumulation of errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
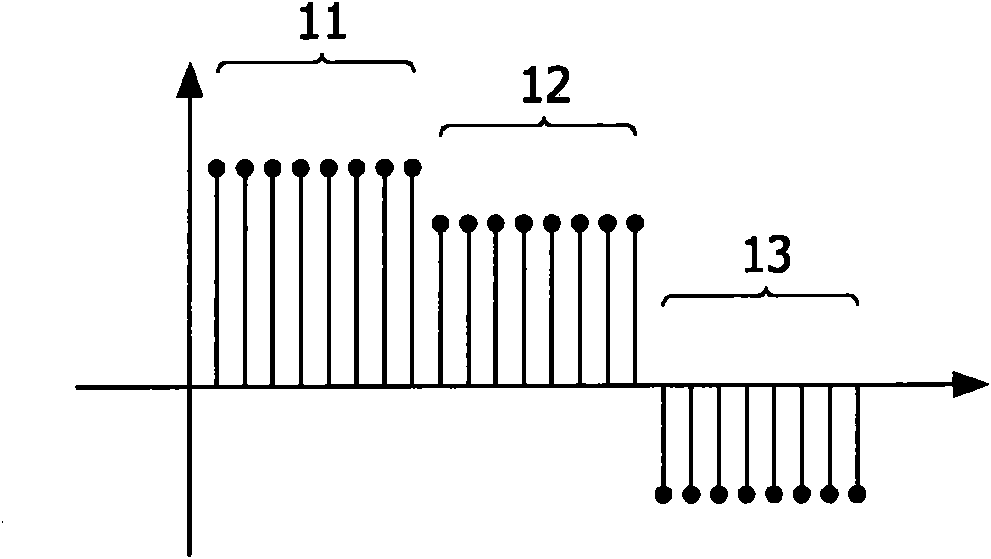
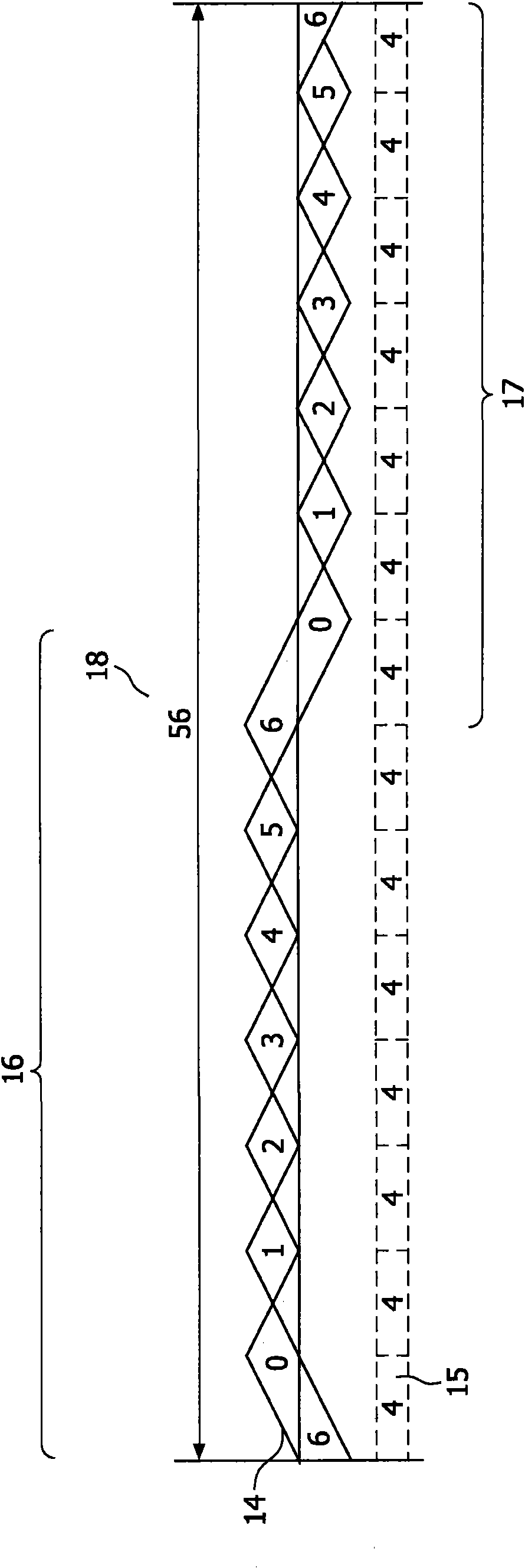
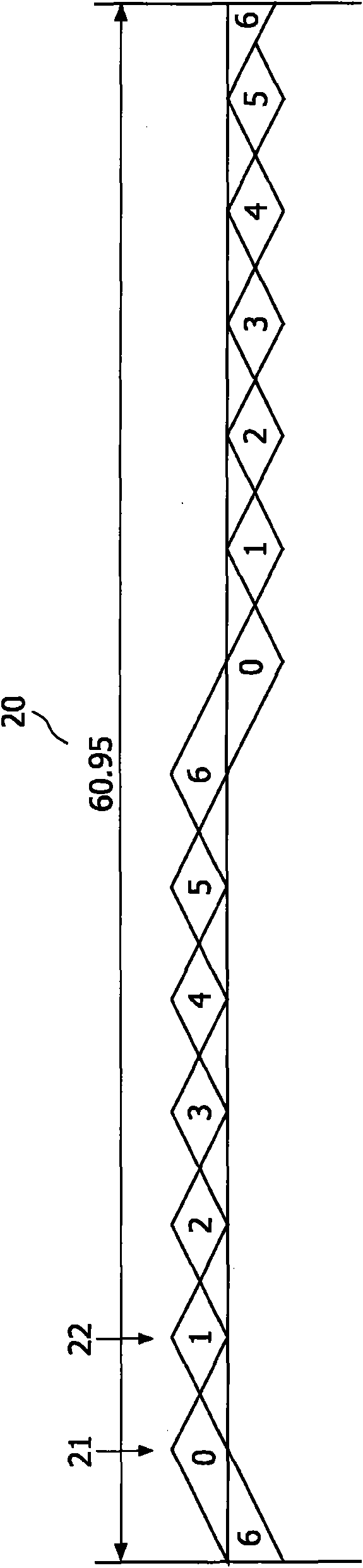
[0033] Generating, embedding and detecting watermarks in multimedia signals can be done in many ways. Published patent applications WO 03 / 083858, WO 03 / 083860 and WO 05 / 029466 disclose such methods and are hereby incorporated by reference. In the present invention, a watermark sampled at a first sampling rate is matched with a main multimedia signal sampled at a second sampling rate. After the watermark has been matched to the sampling rate of the multimedia signal, the matched watermark can be embedded into the multimedia signal by known embedding techniques, eg as disclosed by the above three published patent applications. The watermark may be embedded at the same location continuously after the matching process and possibly by the same device, however the matched watermark may also be transmitted via a communication line (such as the Internet or other computer network) or via a record carrier for use in another A later implementation at an address.
[0034] Figure 1A Sch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com