Spent fuel reprocessing method
A spent fuel and fuel technology, applied in nuclear power generation, climate sustainability, greenhouse gas reduction, etc., can solve the problems of high nuclear non-proliferation, difficult nuclear non-proliferation, and inability to reprocess processes, etc., to achieve nuclear non-proliferation High diffusivity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
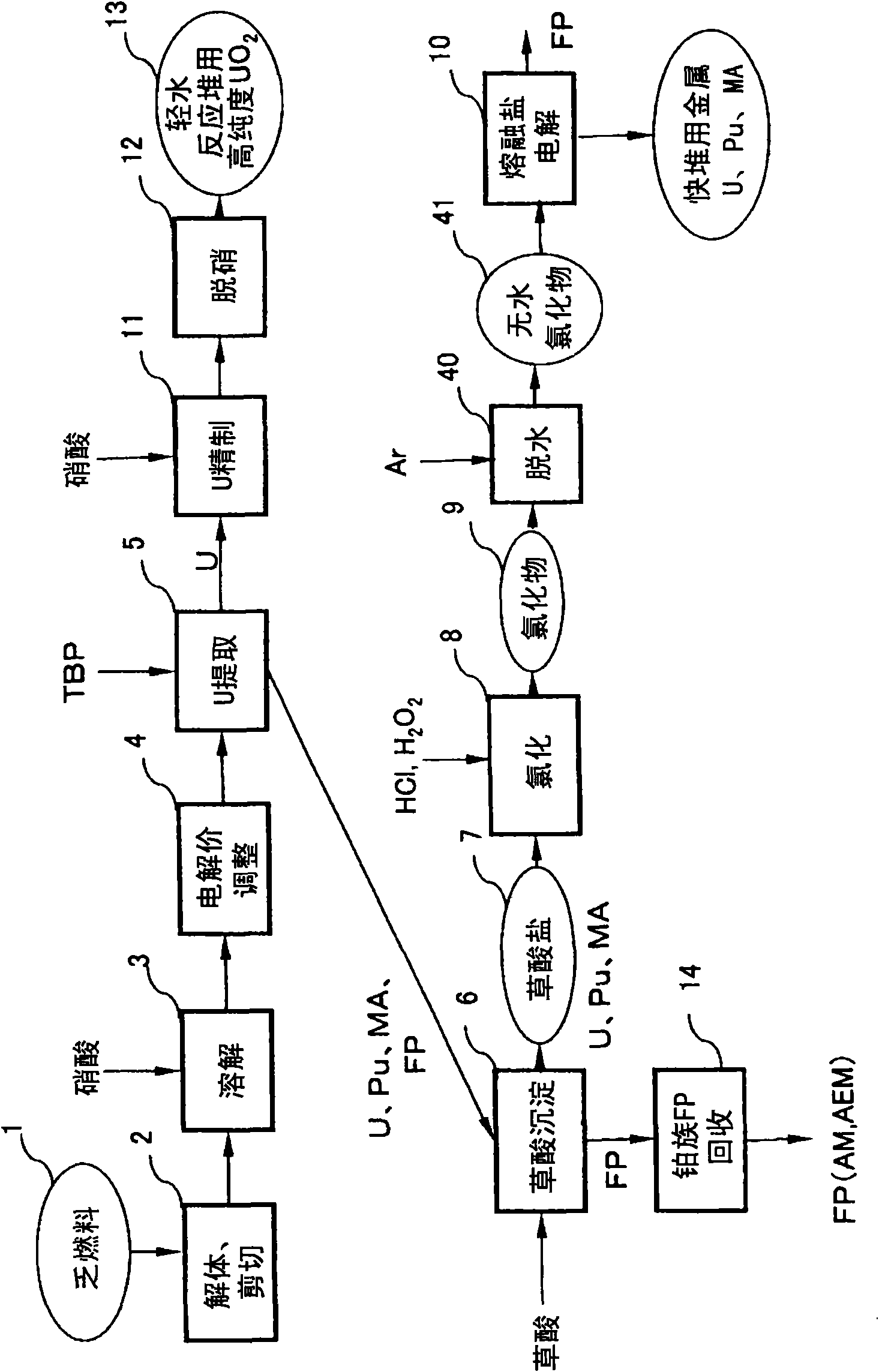
[0054] First, refer to figure 1 and figure 2 A first embodiment of the spent fuel reprocessing method of the present invention will be described.
[0055] figure 1 It is a flowchart showing the first embodiment of the spent fuel reprocessing method of the present invention. figure 1 In the dismantling and shearing step 2, the spent oxide fuel 1 is first dismantled and sheared. Then, in the dissolving step 3, the whole amount is dissolved with nitric acid. At this time, U exists in a hexavalent state and Pu exists in a tetravalent state.
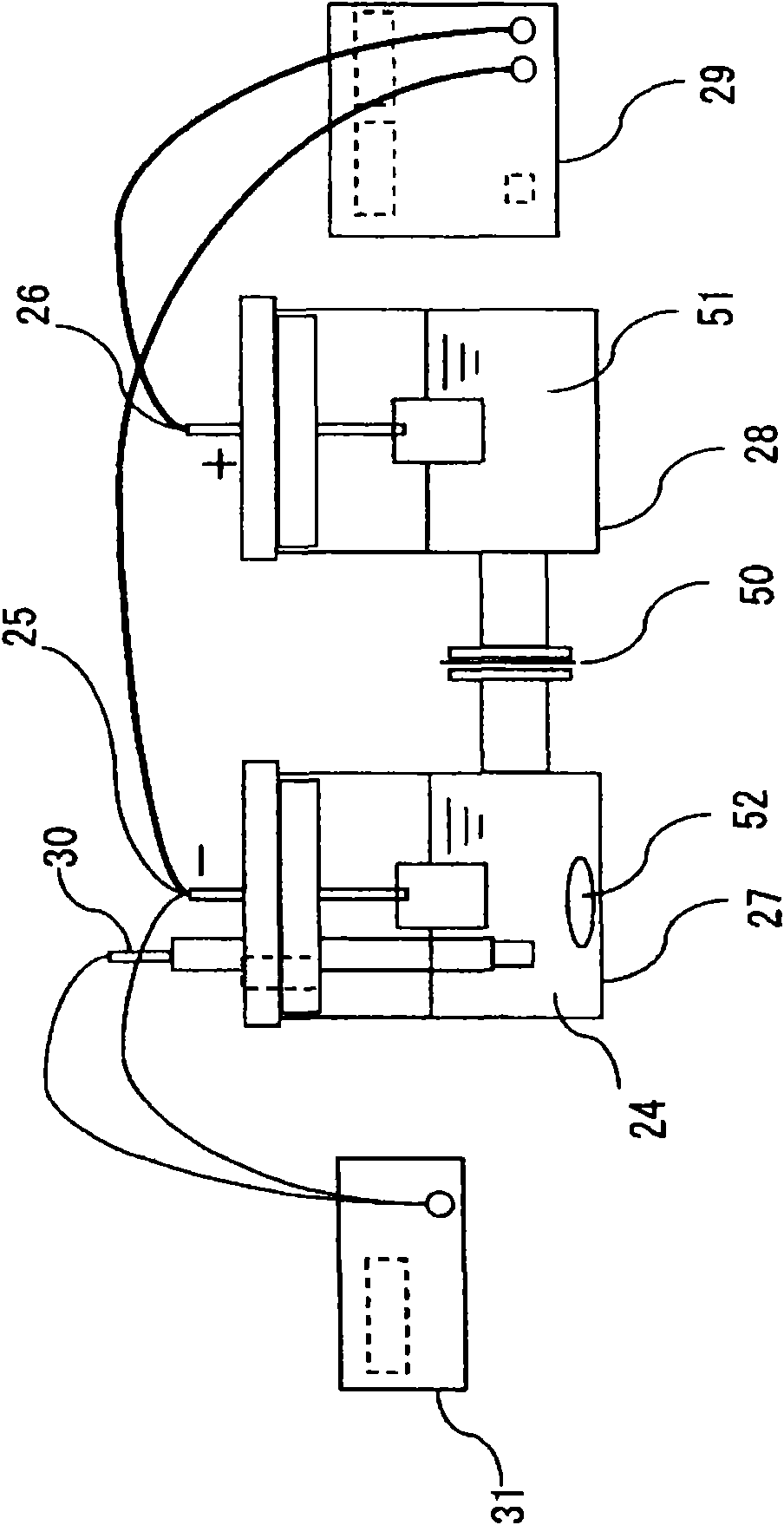
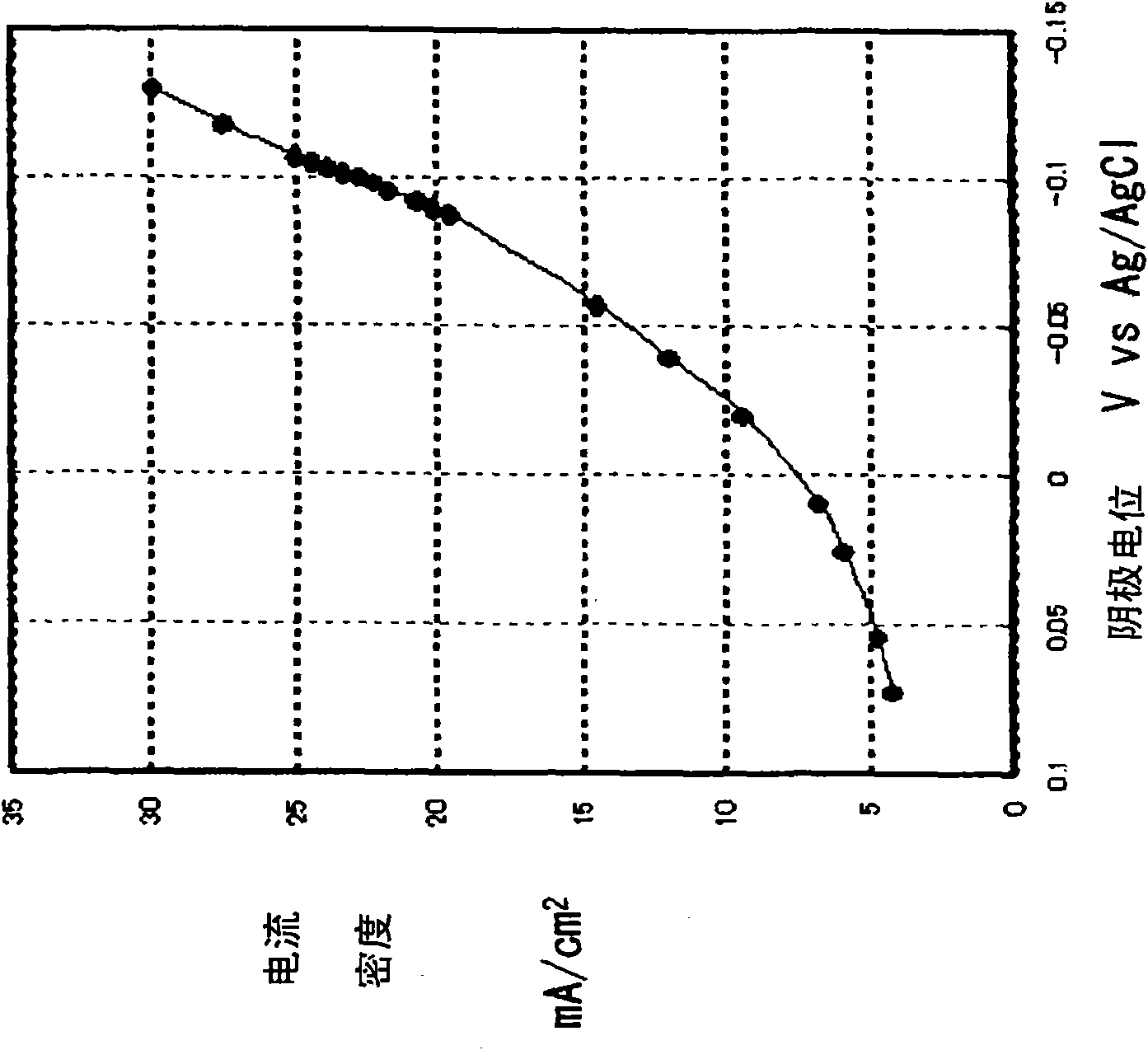
[0056] Then, in the electrolytic valence adjustment step 4, Pu is electrolytically reduced to trivalent. figure 2It is a schematic longitudinal sectional view showing an example of an apparatus used in the electrolytic value adjustment step 4 in the first embodiment. That is, in this device, the cathode chamber 27 is separated from the anode chamber 28 by the diaphragm 50 . Catholyte 24 is contained in cathodic chamber 27 , into whic...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0073] Below, refer to Figure 5 and Figure 6 A second embodiment of the spent fuel reprocessing method of the present invention will be described. Here, the same symbols are used for the same or similar parts as those of the first embodiment, and overlapping descriptions are omitted.
[0074] Figure 5 It is a flowchart showing the second embodiment of the spent fuel reprocessing method of the present invention. in addition, Figure 6 It is a schematic longitudinal sectional view showing an example of an apparatus used in the electrolytic reduction step in the second embodiment.
[0075] The steps up to the oxalic acid precipitation 7 for recovering U, Pu, minor actinides, rare earth elements, etc. in the oxalic acid precipitation step 6 are the same as those in the first embodiment.
[0076] In this second embodiment, in order to obtain metal U, Pu, and minor actinides, an oxidation dehydration step 15 and an electrolytic reduction step 17 are provided instead of the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com