Electronic shelf label system and display method
A technology of electronic shelf labels and display methods, which is applied in display shelves, display hangers, applications, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to deal with, delay in commodity display operations, and updates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
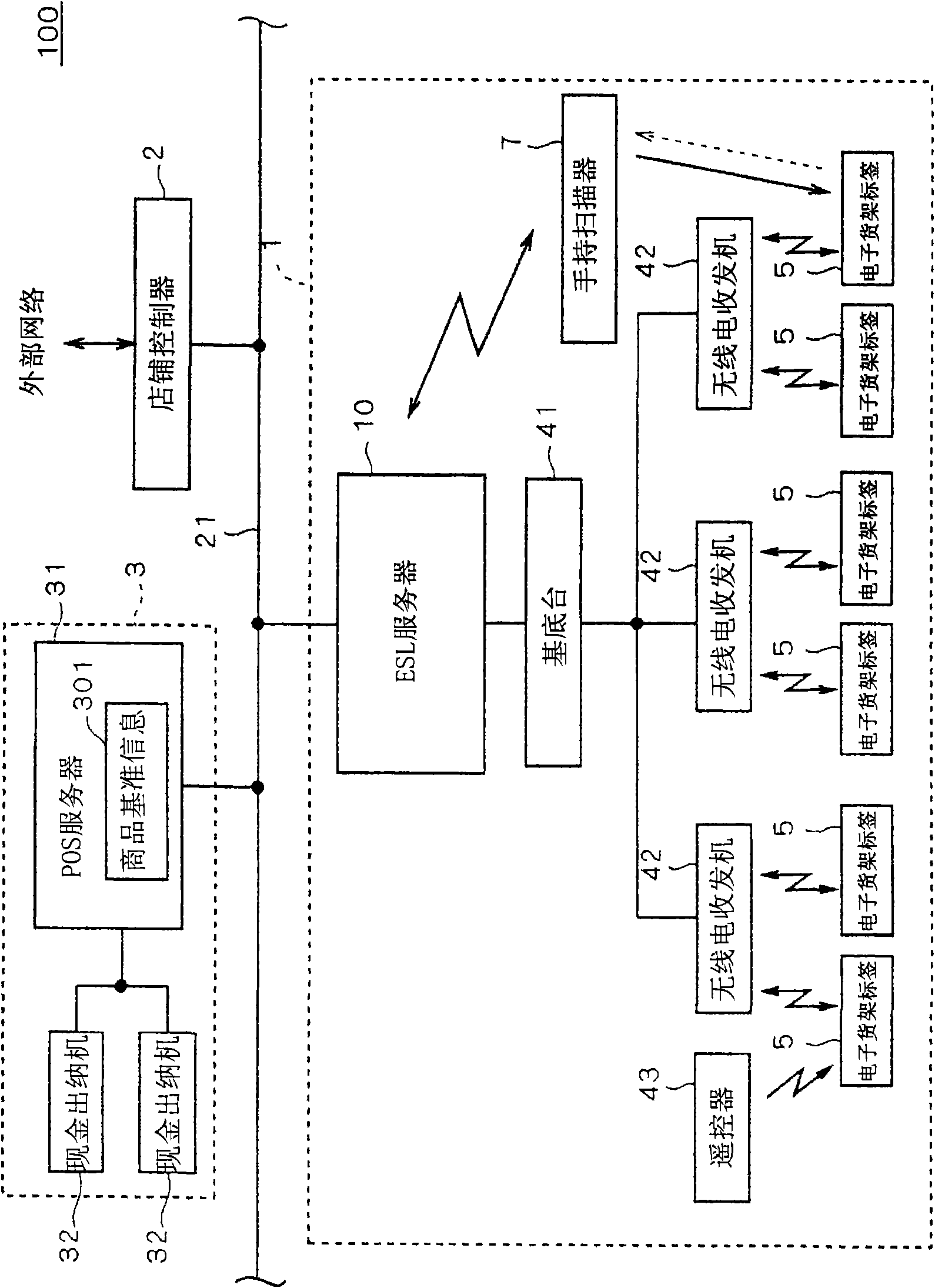
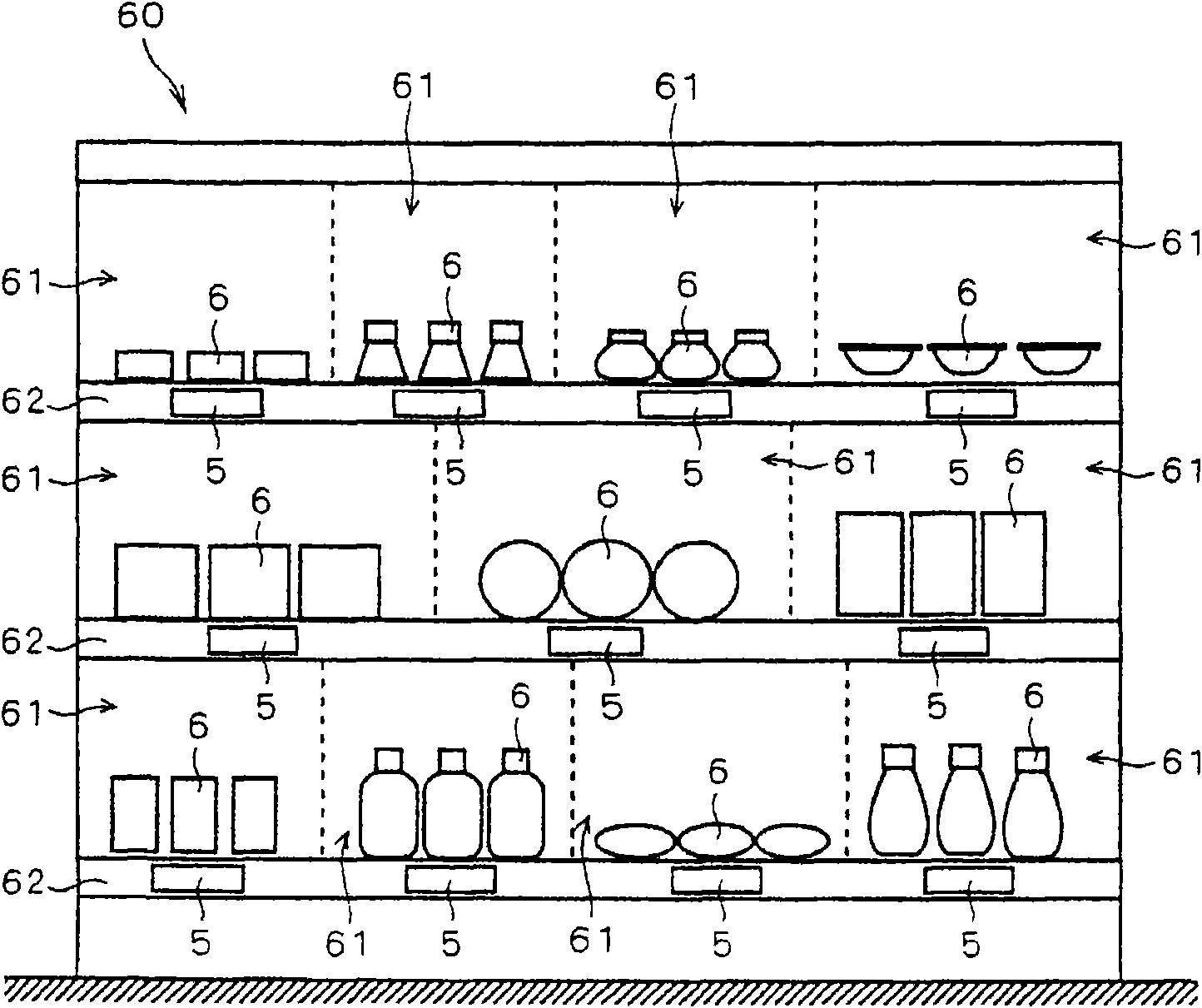
[0046] figure 1 It is a diagram showing a configuration example of a store information system 100 including the electronic shelf label system 1 of the present invention. also, figure 2 It is a diagram showing how the electronic shelf labels 5 included in the electronic shelf label system 1 are arranged on the commodity shelves 60 .
[0047] Such as figure 2 As shown, the commodity shelf 60 is divided into a plurality of spaces called compartments 61 , and commodities 6 of the same type are collectively placed in each compartment 61 . That is, one shelf 61 physically corresponds to one kind of commodity 6 placed on the shelf 61 in a one-to-one manner. In addition, a barcode indicating a product code (product identification information) for identifying the type of product is attached to each product 6 by labeling or printing. Furthermore, the product code is not limited to a barcode, and may be represented by, for example, a QR code or the like.
[0048] On the frame 62 o...
Embodiment approach 2
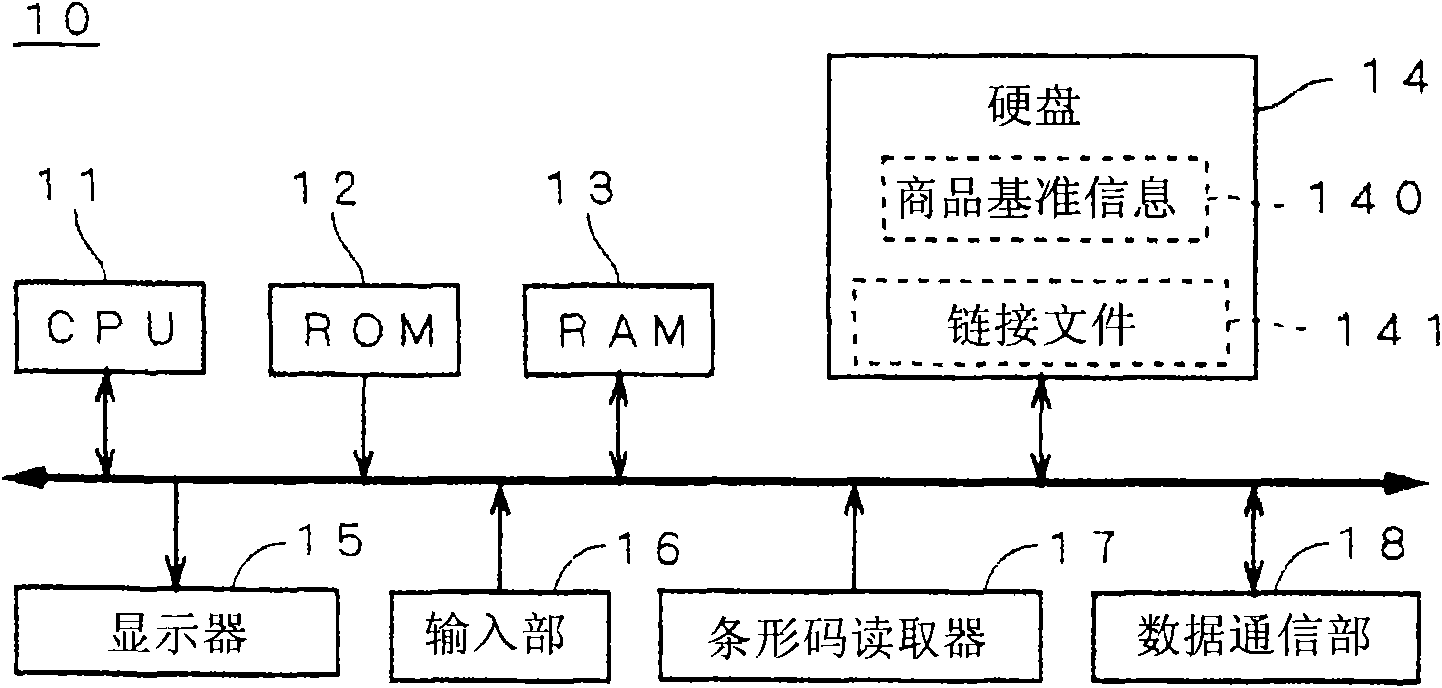
[0181] In the first embodiment described above, when the product 6 is associated with the electronic shelf label 5 using the handheld scanner 7, when the CPU 11 of the ESL server 10 determines that the product 6 has not been registered in the product reference information 140 ( Step S32), the handheld scanner 7 displays the screen 151 that urges the input of the temporary information 132 (steps S34 and Figure 11 ). This is based on the premise that the data communication unit 78 of the handheld scanner 7 can communicate with the ESL server 10 bidirectionally.
[0182] However, the data communication unit 78 of the handheld scanner 7 may be configured to only transmit data to and from the ESL server 10 , and may not be able to receive data from the ESL server 10 . In this case, the hand-held scanner 7 cannot know whether the product 6 to be processed is registered in the product reference information 140 in the ELS server 10, and the hand-held scanner 7 cannot display only th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com