Starch emulsion defoaming pump
A starch emulsion and defoaming technology, which is applied in the direction of pumps, pump components, non-variable pumps, etc., can solve the problems of low production efficiency of potato starch emulsion defoaming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
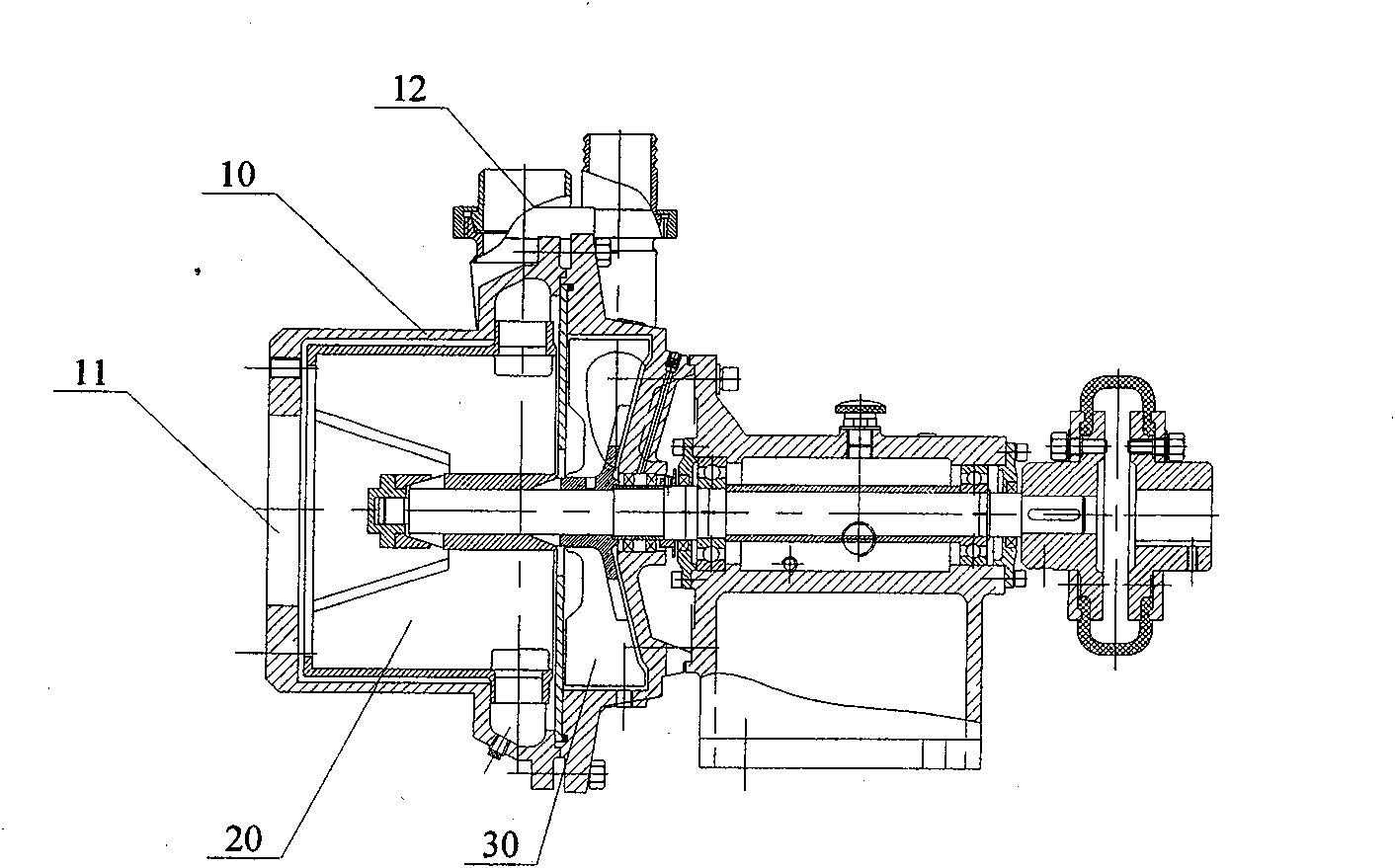
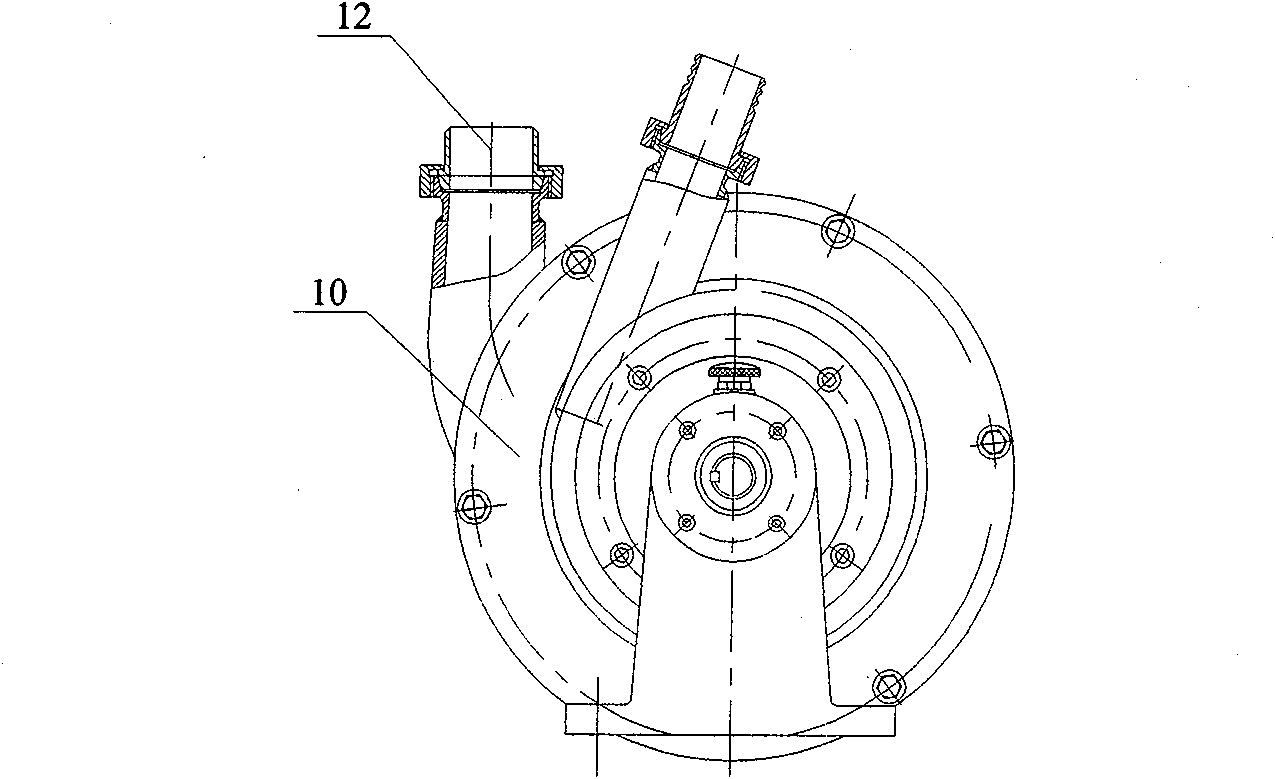
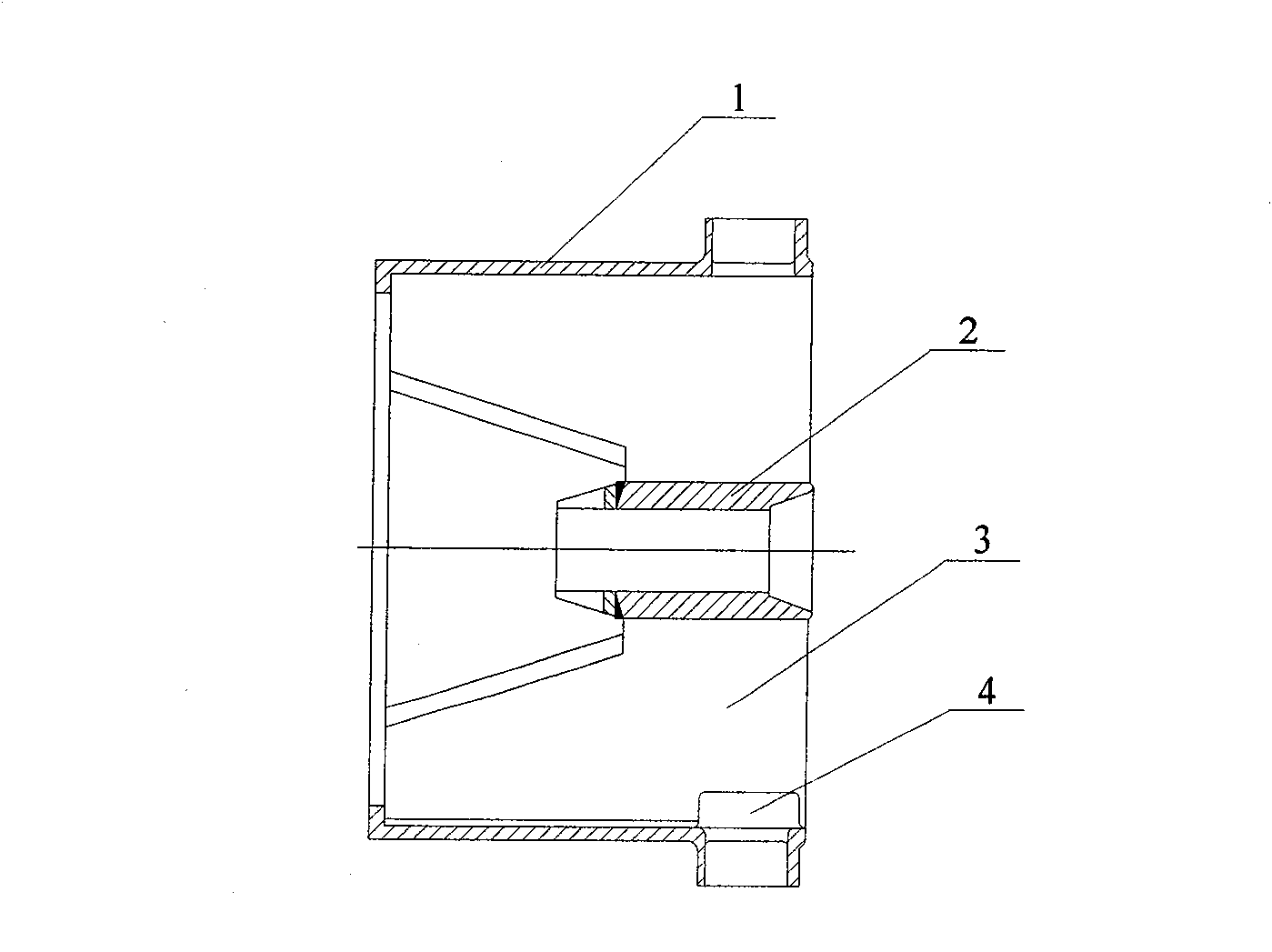
[0014] The invention provides a starch emulsion defoaming pump, which is used for defoaming potato starch emulsion. Its structure is as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, including the pump body 10, the primary impeller 20 and the secondary impeller 30, the inside of the pump body 10 is provided with first and second chambers in turn from left to right, and the primary impeller 20 and the secondary impeller 30 are respectively Set in the first and second chambers, the front end of the pump body 10 is provided with a potato starch emulsion inlet 11 communicating with the first chamber, and the outer wall of the pump body 10 is provided with a potato starch emulsion leading to the first chamber. Discharge port 12; the primary impeller 20 and the secondary impeller 30 are coaxially arranged on a pump shaft, and with the rotation of the pump shaft, the primary impeller 20 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com