Polypropylene resin foamed beads and foam moldings
A foam molding, polypropylene-based technology, applied in the field of foam molding, can solve the problems of aging time increase, foam molding shrinkage, surface deterioration, etc., to achieve excellent dimensional stability and good melt adhesion , excellent surface effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
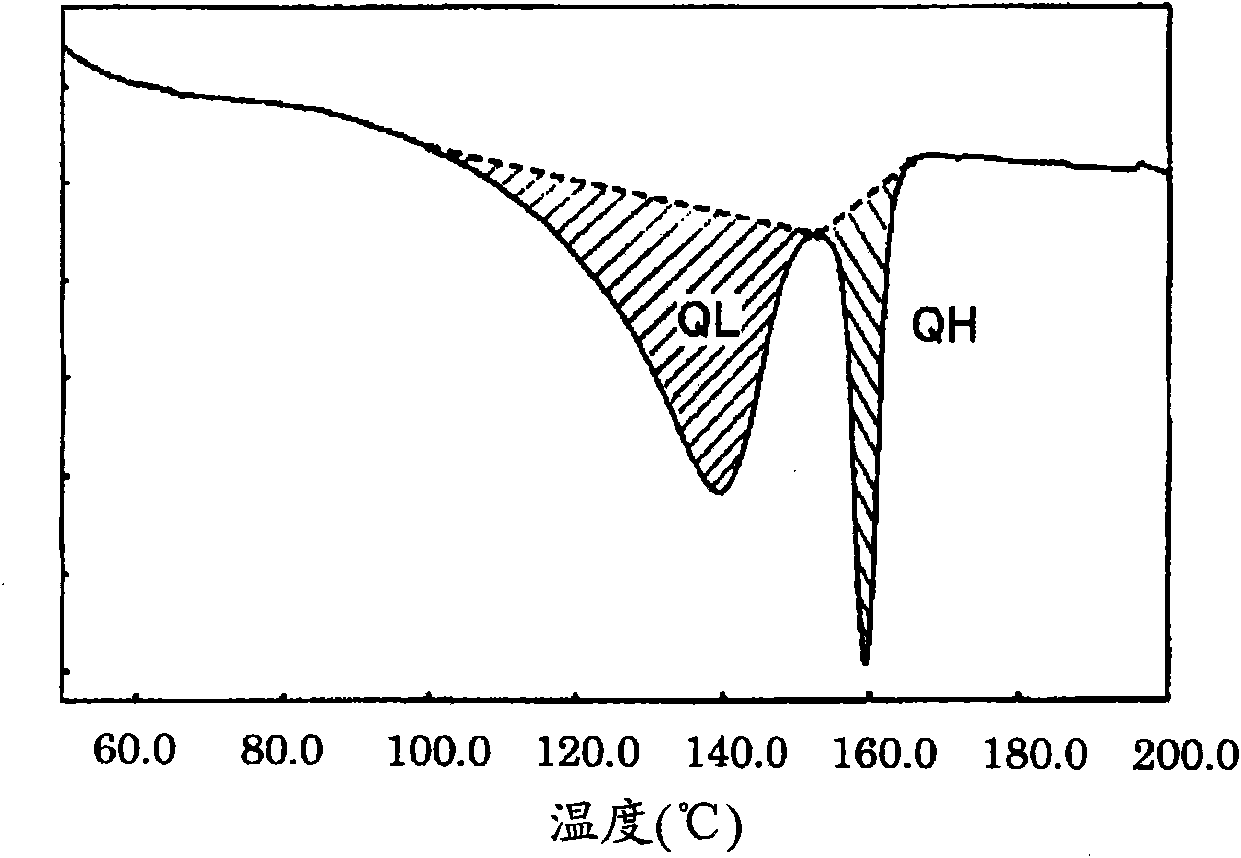
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
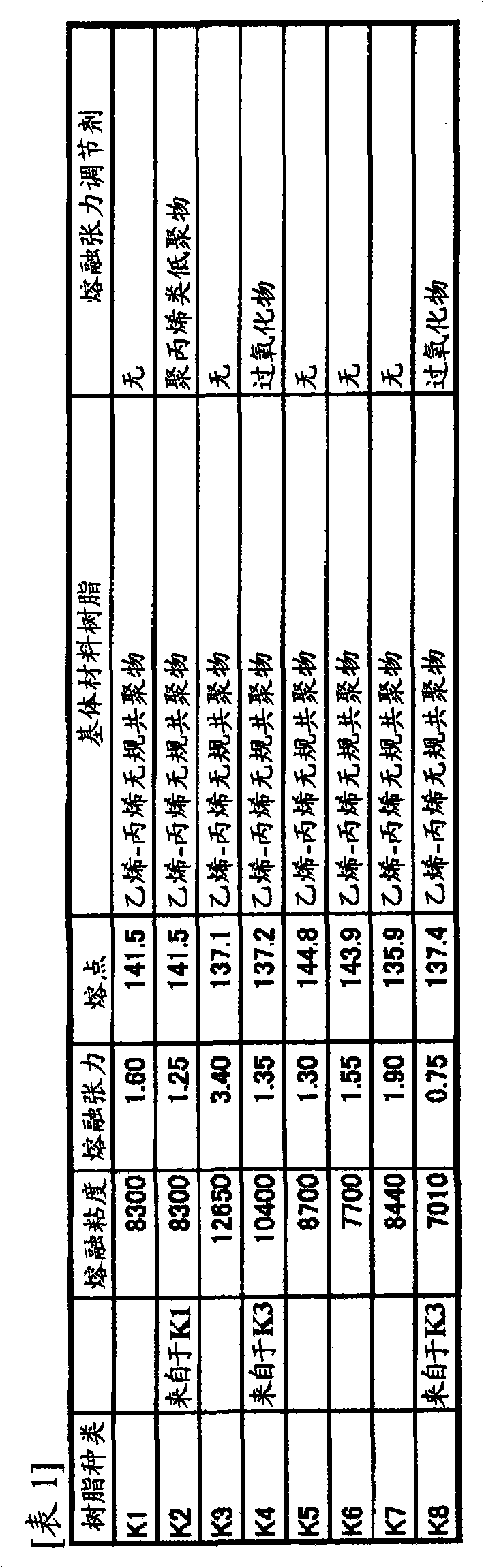
[0098] As the polypropylene resin, an ethylene-propylene random copolymer (K1) having a melting point of 141.5° C. described in Table 1 was used. After dry blending the resin with 0.1 parts by weight of talc as a bubble nucleating agent, Melt-kneading was performed in an extruder (manufactured by Osaka Seiki Works Co., Ltd., model 20VSE-50-28). The melted and kneaded resin was extruded into strips from a circular die with a diameter of 2 mm, then water-cooled, and then cut with a pelletizer to obtain a polypropylene-based resin with a weight of 1.2 mg per pellet. particle.
[0099] 100 parts by weight of the obtained polypropylene-based resin particles, 300 parts by weight of water, 2 parts by weight of calcium phosphate (manufactured by Taiping Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) as a dispersant, and 0.04 parts by weight of sodium alkylsulfonate as a dispersing aid were charged to capacity. Into a 4.5 L pressure-resistant autoclave, 28 parts by weight of isobutane was added as a bl...
Embodiment 2
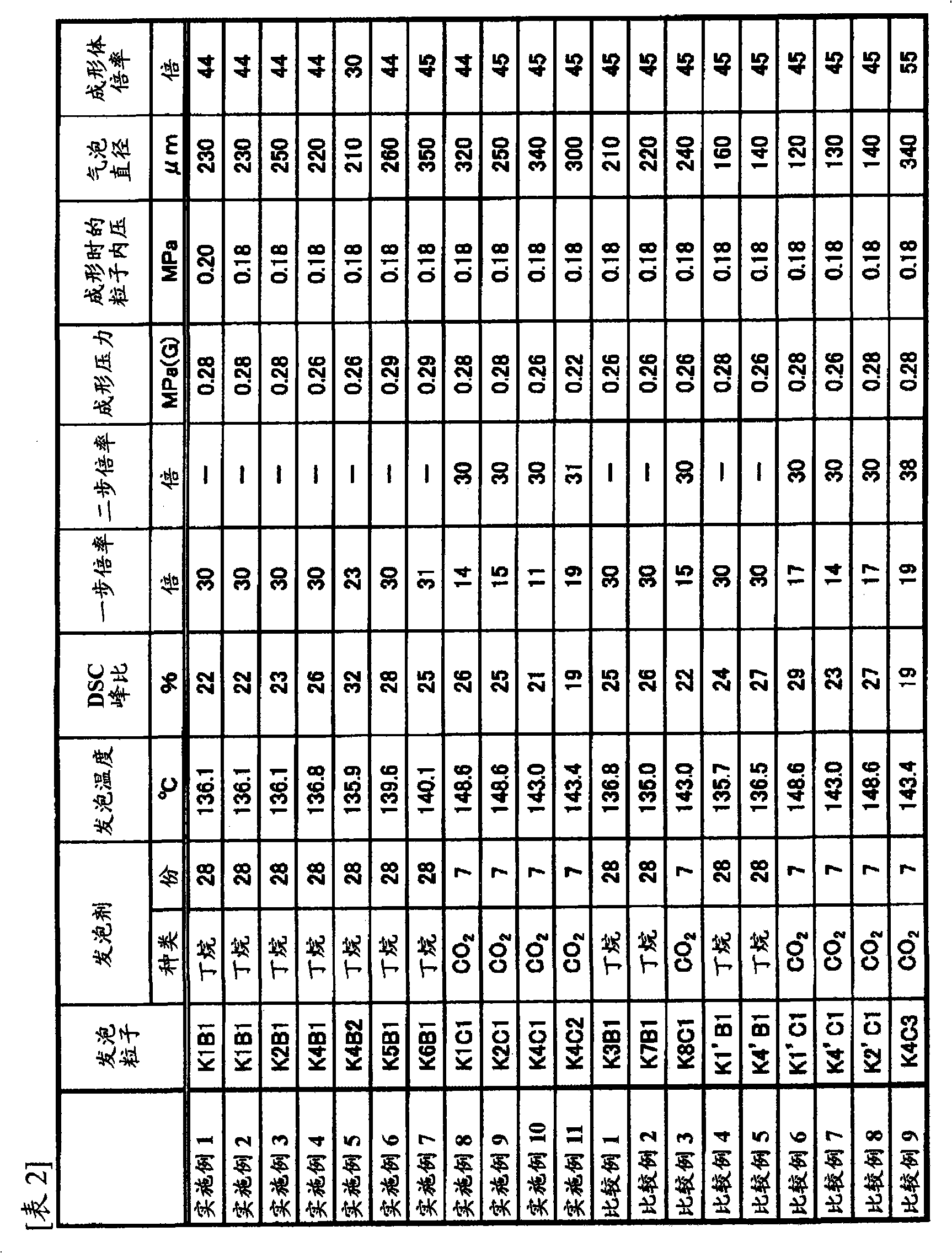
[0102] A foamed molded article was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the air pressure in the expanded polypropylene resin particles (K1B1) was set to 0.18 MPa when thermoforming the expanded polypropylene resin particles (K1B1). The evaluation results are shown in Table 3.
Embodiment 3
[0104] Except for using the following ethylene-propylene random copolymer (K2) as the polypropylene-based resin, polypropylene-based resin expanded particles (K2B1) and its expanded molded product were obtained in the same manner as in Example 2. The ethylene-propylene random copolymer (K2) used is obtained by using 5 parts by weight of an ethylene-propylene copolymer oligomer (Mv= 10000) and the obtained resin has a melting point of 141.5°C. The evaluation results are shown in Table 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com