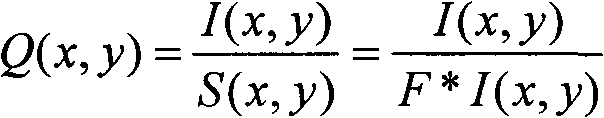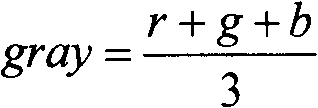Method for illuminating/normalizing image and method for identifying image by using same
A normalization and image technology, applied in the field of pattern recognition, to achieve the effect of enhancing effectiveness and overcoming the influence of lighting factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
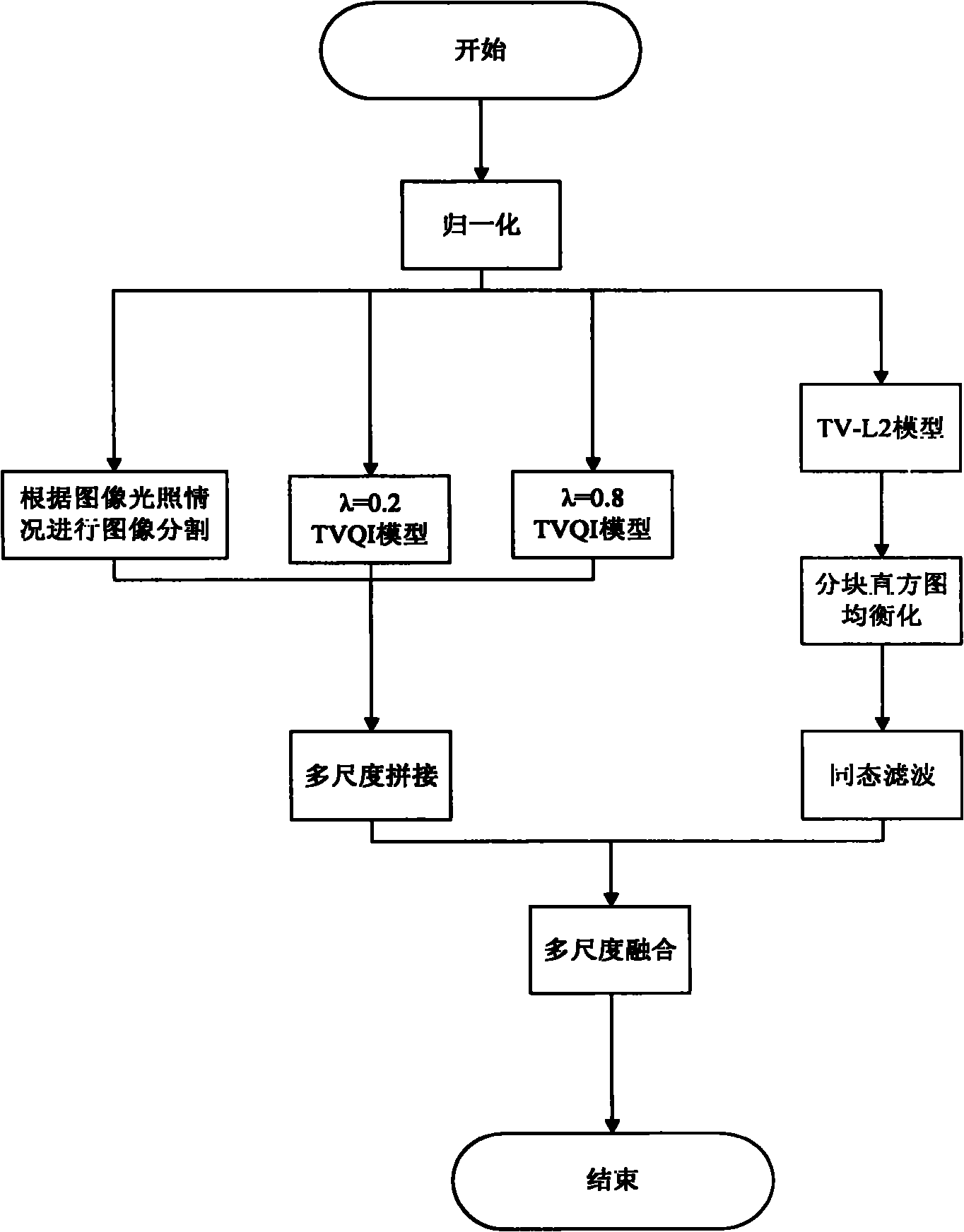
[0046] The illumination normalization in this embodiment is improved on the basis of the TVQI model.
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for performing illumination normalization processing on an image includes the following steps:
[0048] (1) Normalize the input image to a 100×100 grayscale image I
[0049] If the input image is a grayscale image, modify the image pixels to 100×100;
[0050] If the input image is a color image, the color image is converted into a grayscale image by the following formula:
[0051] gray = r + g + b 3
[0052] In the formula, r, g, and b represent the values of the red, green, and blue components in the color image, respectively, and gray represents the gray value of the grayscale image.
[0053] (2) Segment the input image into shadow areas and normal light areas
[0054] The method of dividing the inp...
Embodiment 2
[0139] The illumination normalization in this embodiment is improved on the basis of the LTV model.
[0140] LTV model comes from: "Total variation models for variable lighting face recognition" Chen, Terrence; Yin, Wotao; Zhou, Xiang Sean; Comaniciu, Dorin; Huang, Thomas S. Source: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, v 28, n 9 , p 1519-1524, September 2006.
[0141] The LTV model and the TVQI model come from the same article. The difference between the two is that TVQI uses a quotient operation, and LTV uses a logarithmic operation. Using the LTV model differs from using the TVQI model only in steps (3) and (4).
[0142] Only the differences from Embodiment 1 will be described below.
[0143] Step 3: Use the LTV model to process the normalized input image obtained in step 1 to obtain λ L1 = 0.2, the small-scale part v of the face image λ=0.2 . The specific steps are:
[0144] A. Perform logarithmic operations on the input image
[0145] f(x,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com