Ultraviolet disinfection auxiliary device for water dispenser
A technology of ultraviolet disinfection and auxiliary devices, applied in beverage preparation devices, light water/sewage treatment, household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of water quality bacteriological indicators exceeding the standard, microorganisms have no resistance, no bactericidal effect, etc., and achieve fast sterilization speed , Increased added value, high sterilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
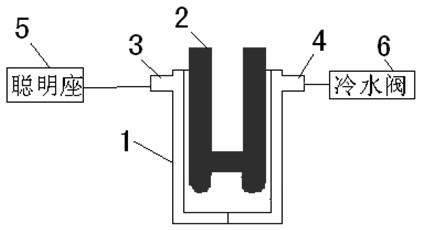
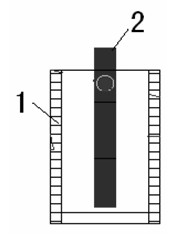
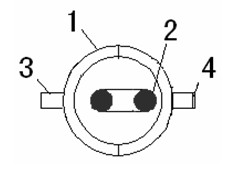
[0014] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 As shown, the present invention is achieved in this way, the center of the water filter 1 is equipped with an ultraviolet lamp 2, the water filter 1 is made of ordinary glass with a ring column, and the outer wall of the water filter 1 is pasted with a layer of black Shading paper or coated with a layer of opaque material, both sides of the upper end of the water filter 1 are respectively connected with a water inlet 3 and an outlet pipe 4, the inlet pipe 3 is connected to the smart seat 5 of the water dispenser, and the outlet pipe 4 is connected to the cold water valve 6 of the water dispenser , the ultraviolet lamp 2 is H type, the lamp tube length of the ultraviolet lamp is equivalent to the height of the water filter, and the ultraviolet wavelength of the ultraviolet lamp 2 is mainly between 200-300nm. Since the design of the UV disinfection auxiliary device of the water dispenser is generally larger than that of the heatin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com