FLP-containing pBBR1MCS-2 recombinant plasmid and method for modifying zymomonas mobilis genome DNA
A technology of Zymomonas mobilis and recombinant plasmids, which is applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering, can solve the problems of inefficiency, difficulty in satisfying the application research of Zymomonas mobilis molecular biology transformation, singleness, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
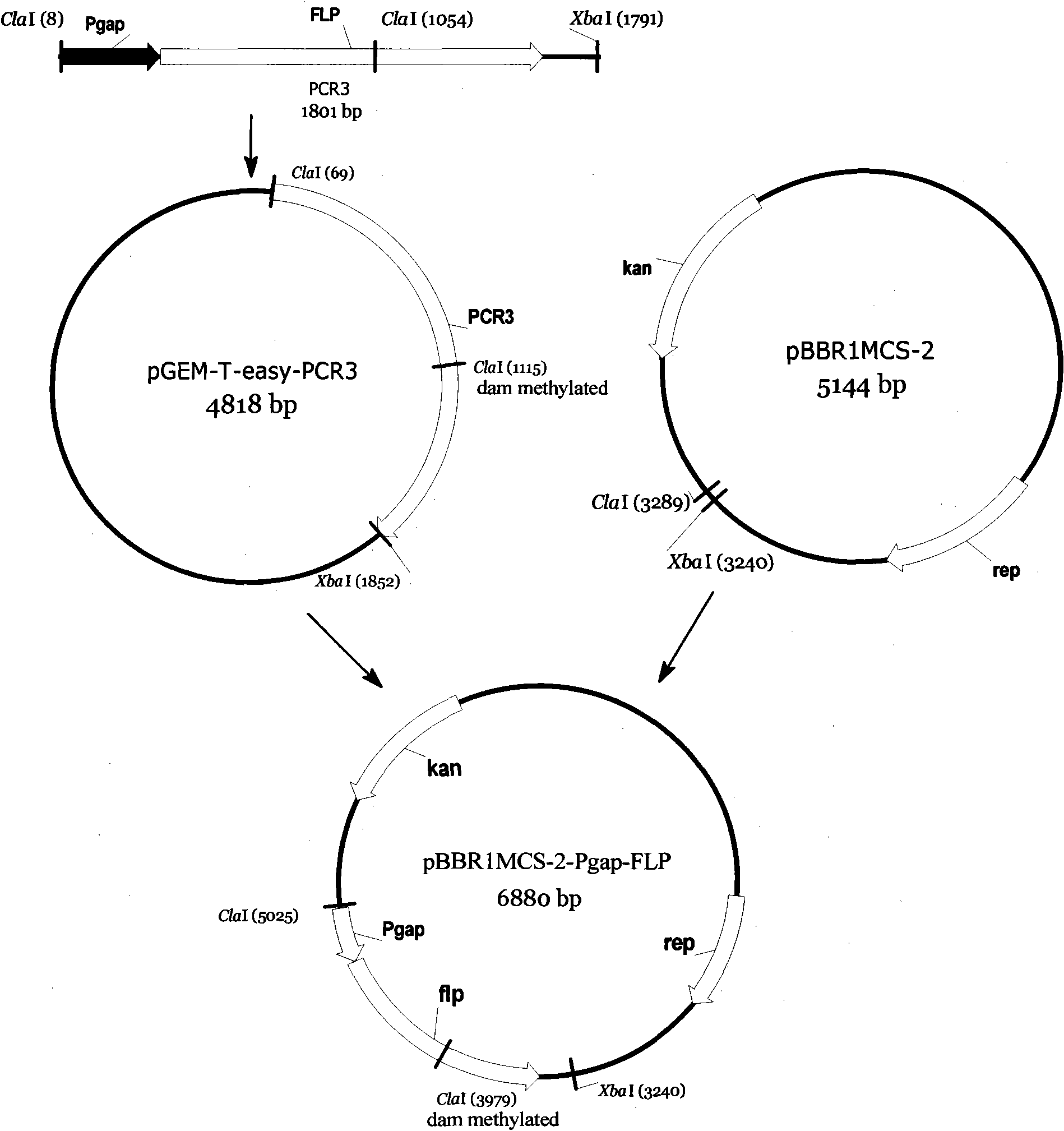
[0033] Construction of embodiment 1pBBR1MCS-2-Pgap-FLP
[0034] For a schematic diagram of this build see figure 1 , see Table 1 for the primers P1 to P4 involved.
[0035] Table 1. Primers used for construction and identification of Zymomonas mobilis engineering strains in the present invention
[0036]
[0037] Using the genomic DNA of Zymomonas mobilis sequencing strain ZM4 as a template, primers P1 and P2 were designed according to the published ZM4 genome sequence AE008692, and a 347bp ZM4-containing glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene gap promoter was amplified The product of the region is named PCR1;
[0038] Using the pCP20 plasmid as a template, a 1474bp product containing the Saccharomyces cerevisiae site-specific recombinase gene FLP was amplified with P3 and P4, which was named PCR2;
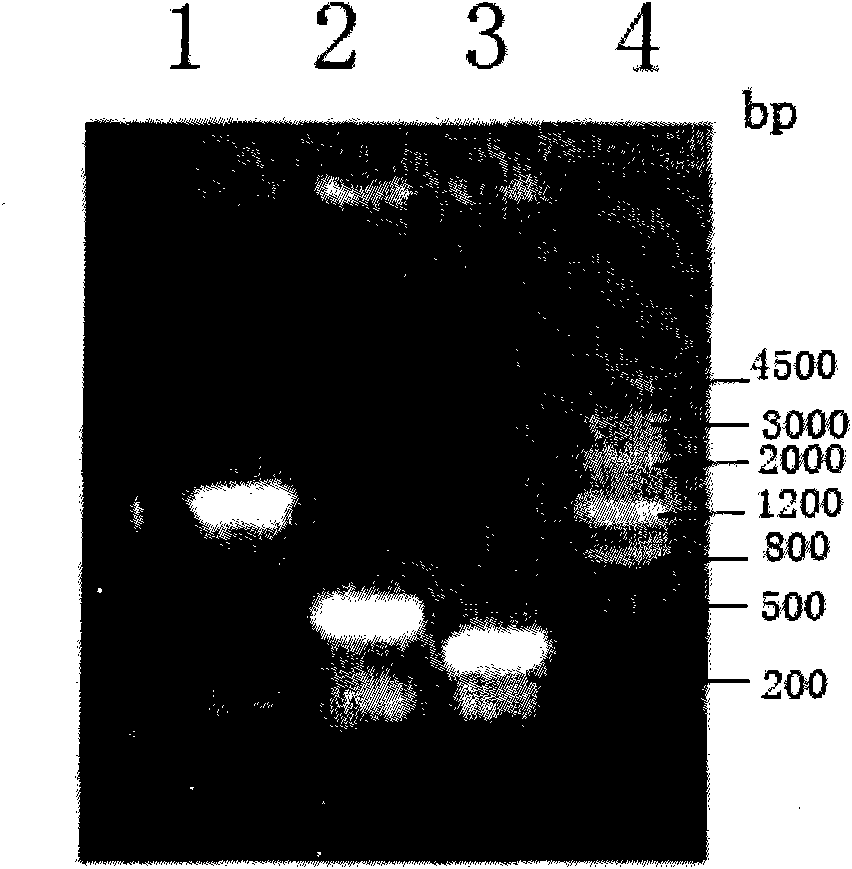
[0039] Then PCR1 and PCR2 were used as templates, and P1 and P4 were used as primers to amplify to obtain a 1801bp product, which was named PCR3. PCR3 contained ClaI ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: Construction of ZM4 (ldh::FRT) strain ZM4 (ldh::FRT) modified by inactivation of the lactate dehydrogenase gene ldh of Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 genome
[0043] 1. At site 1 (lactate dehydrogenase gene ldh) of Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 genomic DNA, integrate a DNA fragment (ie FRT-cml-FRT) containing two FRT sites in the same direction, said DNA fragment The selection marker gene chloramphenicol gene cml is contained between the two FRT sites of , and the strain ZM4 (ldh::FRT-cml-FRT) modified at site 1 is obtained. For the construction of this bacterial strain, see the literature (Zou Shaolan, Hong Jiefang , Ma Yuanyuan et al. Construction of targeted integration plasmids for Zymomonas mobilis, Journal of Nankai University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 42(6): 42-47);
[0044] 2. Introduce pBBR1MCS-2-Pgap-FLP into the strain ZM4(ldh::FRT-cml-FRT) constructed in step 1. by electroporation, and screen out the deletion of the two FRT sites due to FLP expression. ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: Construction of ZM4 (ldh::FRT) (gfo::FRT-tktA talB) modified by inactivation of the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene gfo in Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 (ldh::FRT) genome
[0056]1. At site 2 (glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene gfo) of Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 (ldh::FRT) genomic DNA, a DNA fragment (ie FRT-cml- FRT-tktAtalB), the DNA fragment contains the selectable marker gene cml between the two FRT sites, resulting in modified ZM4 at site 2 (ldh::FRT) (gfo::FRT-cml-FRT-tktA- talB) strain
[0057] (1) Construction of integrated plasmid pUC19-gfoR-FRT-cml-FRT-tktA-talB-gfoL
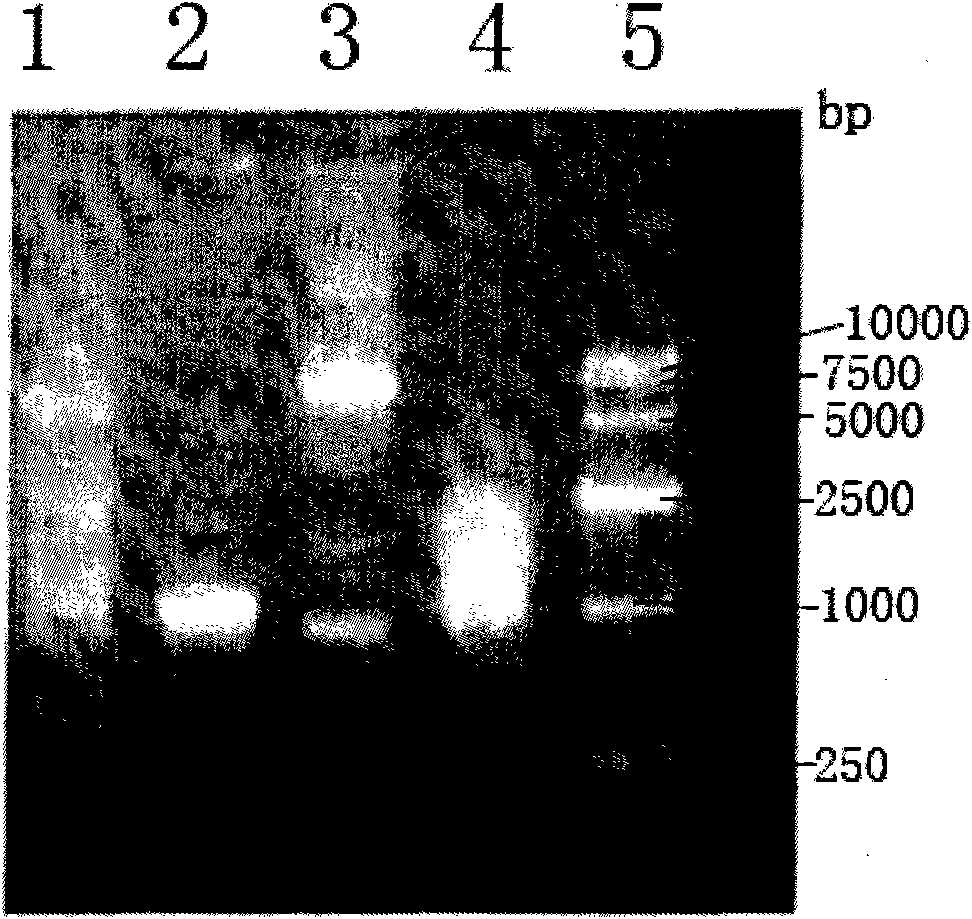
[0058] See the whole construction process image 3 . The cloning primers P7 to P10 and identification primers P11 to P12 used are shown in Table 1.
[0059] Primers P7 to P10 were designed according to the published ZM4 whole genome sequence AE008692. Using the genomic DNA of the Zymomonas mobilis sequencing strain ZM4 as a template, PCR was amplified with P7 and P8 to obtain PCR1, whi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com