Run-flat tire
A run-flat tire and tread technology, which is applied to the reinforcement layer of pneumatic tires, special tires, tire parts, etc., can solve the problems of non-driving performance research, high-speed straight running stability and low fuel consumption research, and achieve Excellent run-flat performance, excellent high-speed straight running stability, low dry performance and low wet performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~5 and comparative example 1~4
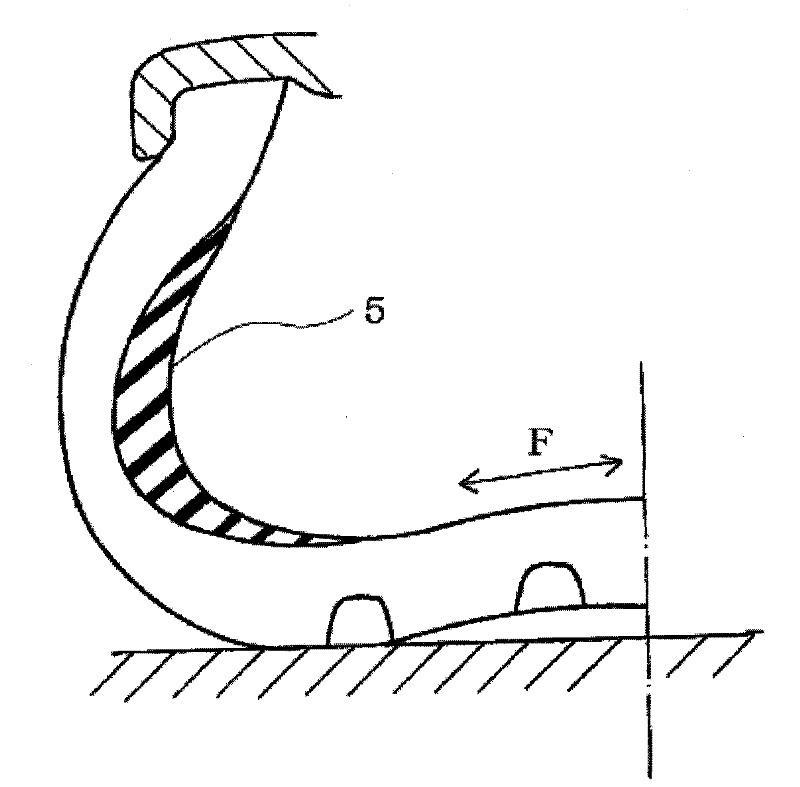
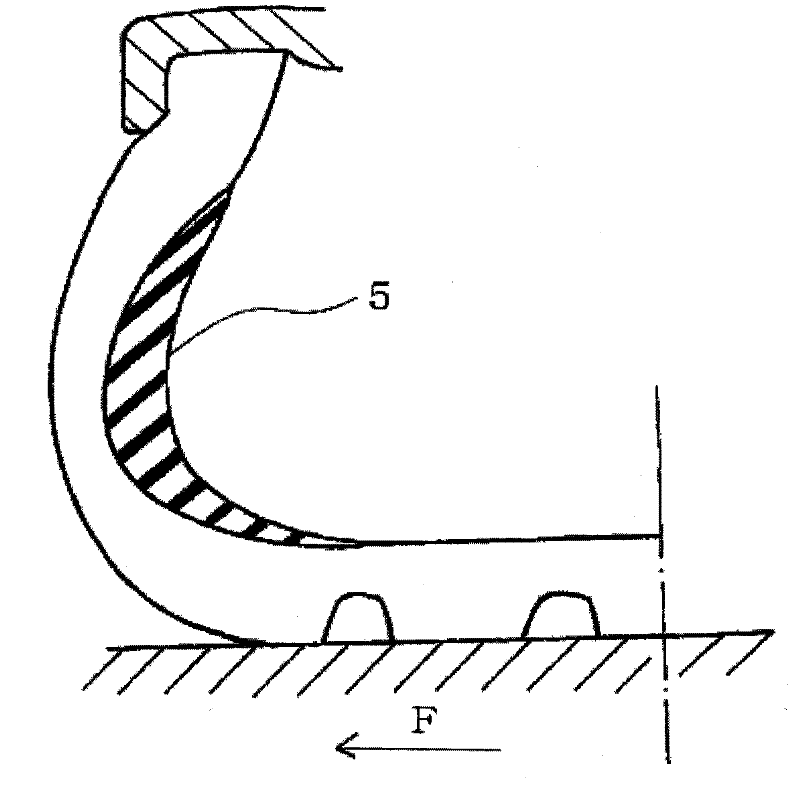
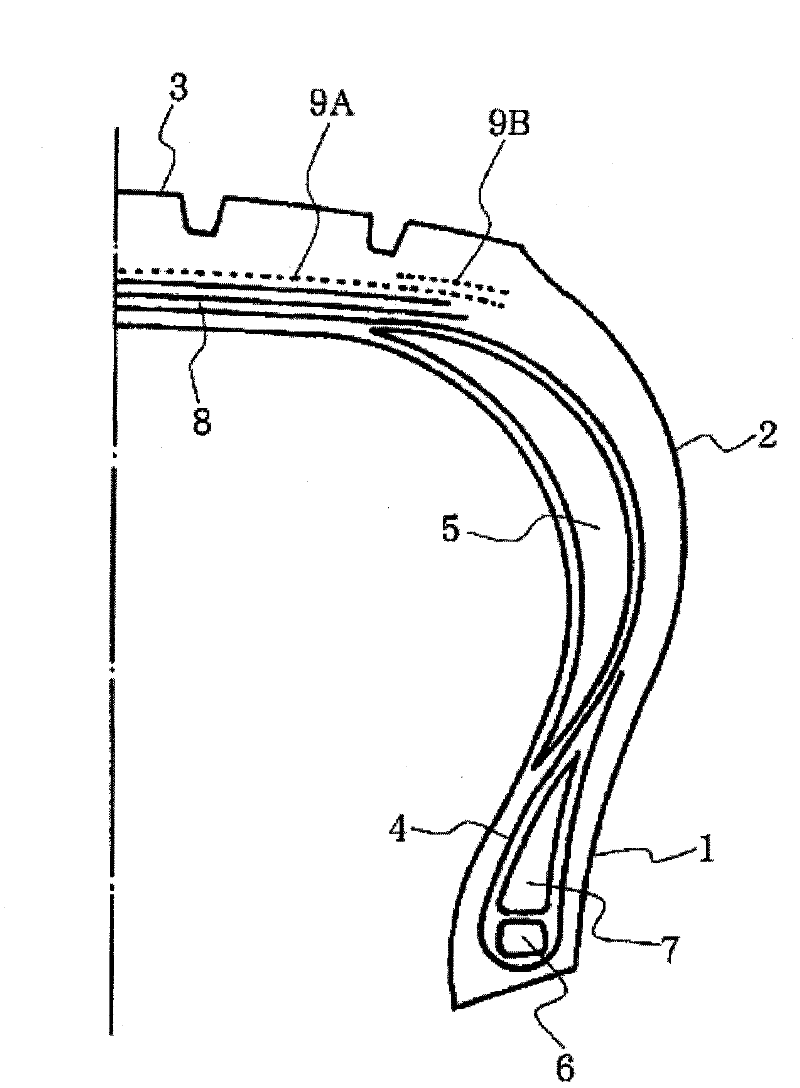
[0060] made as image 3 The sidewall-reinforced run-flat tire shown includes two layers of intersecting belt layers and tread rubber in order in the radial direction of the crown portion of the carcass layer. . Materials satisfying the conditions shown in Tables 2 and 3 below were used as the belt layers of the respective Examples and Comparative Examples. The tire size is 225 / 45R17, and the angle of the cross belt layer is ±62° with respect to the tire width direction. The compounding of the tread rubber used is shown in Table 1 below.
[0061] Table 1
[0062]
[0063] Table 2
[0064]
[0065] Each of the obtained test tires was evaluated as described below. The results are shown in Table 3 below together with the measured values of the dynamic storage elastic modulus E' at 30°C and the loss tangent tanδ at 60°C of the tread rubber.
[0066] Determination of E' and tanδ
[0067] The dynamic storage elastic modulus (E') at 30°C and the loss tangent (tanδ...
Embodiment 6
[0085] The conditions related to the tread rubber and the intersecting belt layers were the same as in Reference Example 2, and a sidewall-reinforced run-flat tire having sidewall reinforcing rubber was produced.
[0086] Total strain energy loss evaluation
[0087] For each of the obtained test tires, the strain energy loss in the tread portion was analytically calculated, and the sum thereof was obtained. In addition, the differences between the test tires having the same structure except for the belt structure (between Reference Example 1 and Reference Example 2 and between Comparative Example 5 and Example 6) were obtained, respectively. The resulting rate of change of the total strain energy loss.
[0088] The results are collectively shown in Table 4 below.
[0089] Table 4
[0090]
[0091] As shown in Table 4 above, when comparing the normal tire of Reference Example 1 and the run-flat tire of Comparative Example 5 to which the same belt structure (1) was app...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| iodine adsorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| oil absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com