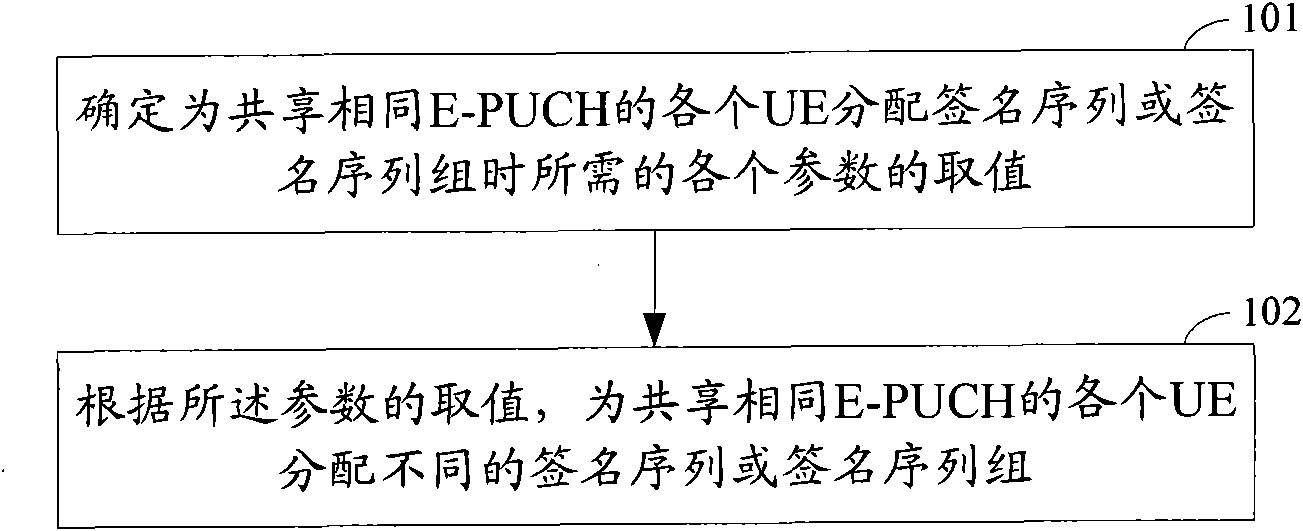
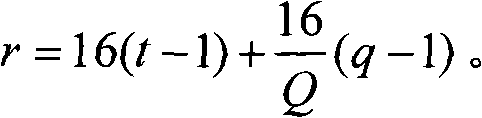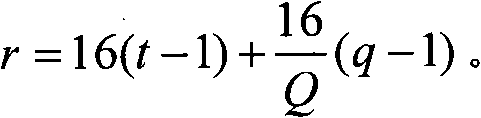Distribution method of signature sequence or signature sequence group on E-HICH
A signature sequence and distribution method technology, applied to electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to determine control information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0259] The E-PUCH in the first embodiment is a method for assigning a signature sequence when scheduling the E-PUCH.
[0260] In the embodiment of the present invention, when the E-PUCH is a scheduling E-PUCH, the control information is ACK / NACK information. Therefore, different signature sequences can be allocated to each UE with the same scheduled E-PUCH, so that when NODEB needs to return ACK information (or NACK information) to each UE with the same scheduled E-PUCH, NODEB can share the same sequence with the UE The reverse sequence (or original sequence) of the signature sequence corresponding to the ACK / NACK information is sent to each UE through the E-HICH.
[0261] We may set the spreading factor of the scheduled E-PUCH allocated to the UE as Q, where Q=1, 2, 4, 8. Therefore, the number of signature sequences on each E-HICH corresponding to each time slot occupied by the scheduled E-PUCH is: The number of signature sequences on the E-HICH pair corresponding to each ...
Embodiment 2
[0323] The method for allocating signature sequence groups when the E-PUCH described in the second embodiment is a semi-static E-PUCH.
[0324] In an embodiment of the present invention, when the E-PUCH is a semi-static E-PUCH, the control information is ACK / NACK information and TPC&SS instruction information. Therefore, different signature sequence groups can be allocated to each UE with the same semi-static E-PUCH, so that when the NODEB needs to send the UE's ACK information (or NACK information) to the UE, the NODEB will assign the above signature sequence to the UE The inverse sequence (or original sequence) of the first signature sequence in the group is sent to the UE through E-HICH; and when NODEB needs to send a certain TPC&SS instruction information of UE to UE, NODEB will communicate with the TPC&SS instruction information The corresponding original sequence or reverse sequence of the signature sequence in the above signature sequence group is sent to the UE through...
Embodiment 3
[0471] Embodiment 3: a method of sending the logic ID of the signature sequence assigned to the UE to the UE through the information bits selected on the E-AGCH.
[0472] Specifically, according to the space division multiplexing factor K, the K MID The Midamble Shifts are divided into K subgroups, and the mapping relationship between channel codes and Midamble Shifts in each of the K subgroups is preset. When multiple UEs share the same scheduled E-PUCH, the mapping relationship between the channel code of the scheduled E-PUCH allocated to any UE and the Midamble Shift allocated to the UE follows the k-th subgroup of the K subgroups When the mapping relationship between the channel code and Midamble Shift specified in , the group number k of the k-th subgroup is sent to the UE through the information bits selected on the E-AGCH. For each UE sharing the same scheduled E-PUCH, the group number of each UE is different.
[0473] When K=8, use the N=3 bits selected on the E-AGCH...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com