Data deletion method, system and graph database server based on oltp
A data and data recording technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve problems such as data rewriting and out-of-sync
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
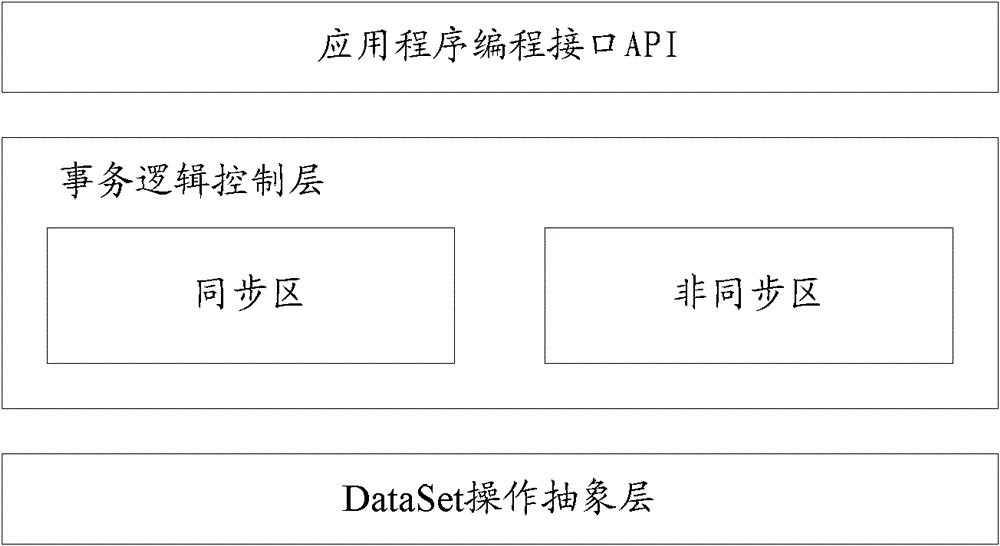
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0254] see Figure 9 , is the block diagram of the first embodiment of the graph database server of the present application:
[0255] The graph database server includes: a receiving unit 910 , a searching unit 920 , an obtaining unit 930 and a deleting unit 940 .
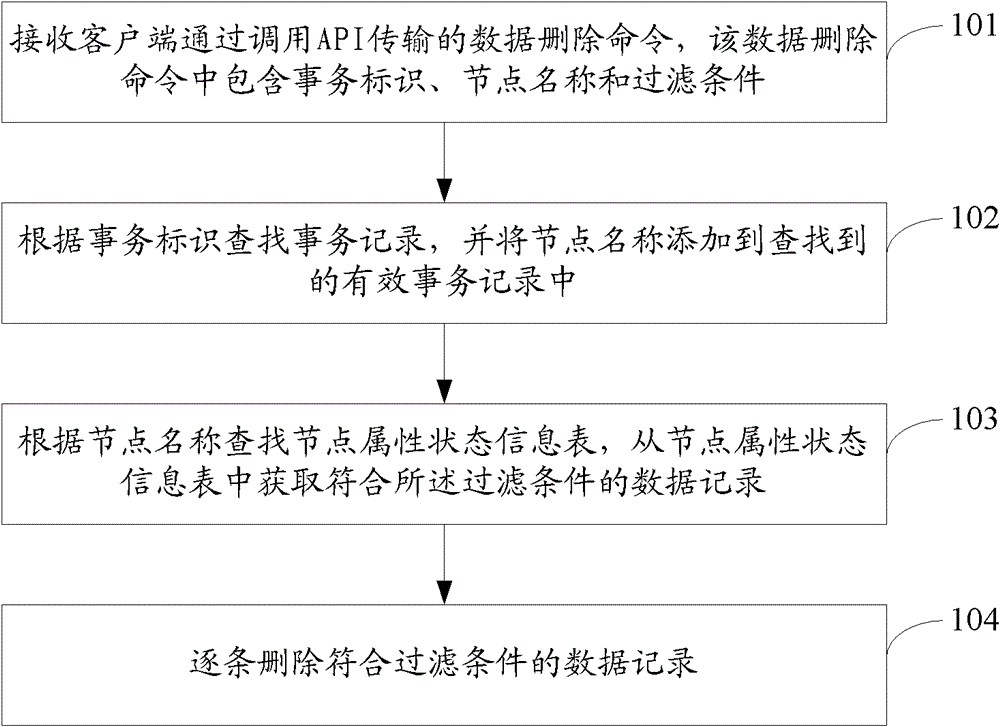
[0256] Wherein, the receiving unit 910 is configured to receive a data deletion command transmitted by the client by calling an application programming interface API, and the data deletion command includes a transaction identifier, a node name and a filter condition;
[0257] A search unit 920, configured to search for a transaction record according to the transaction identifier, and add the node name to the found valid transaction record;
[0258] An acquisition unit 930, configured to search a node attribute state information table according to the node name, and obtain data records meeting the filter condition from the node attribute state information table;
[0259] A deleting unit 940, configured to delete th...
no. 2 example
[0260] see Figure 10 , which is a block diagram of the second embodiment of the graph database server of the present application:
[0261] The graph database server includes: a receiving unit 1001, a generating unit 1002, a setting unit 1003, a searching unit 1004, a first judging unit 1005, a first executing unit 1006, an acquiring unit 1007, a second judging unit 1008, a second executing unit 1009 and Delete cell 1010 .
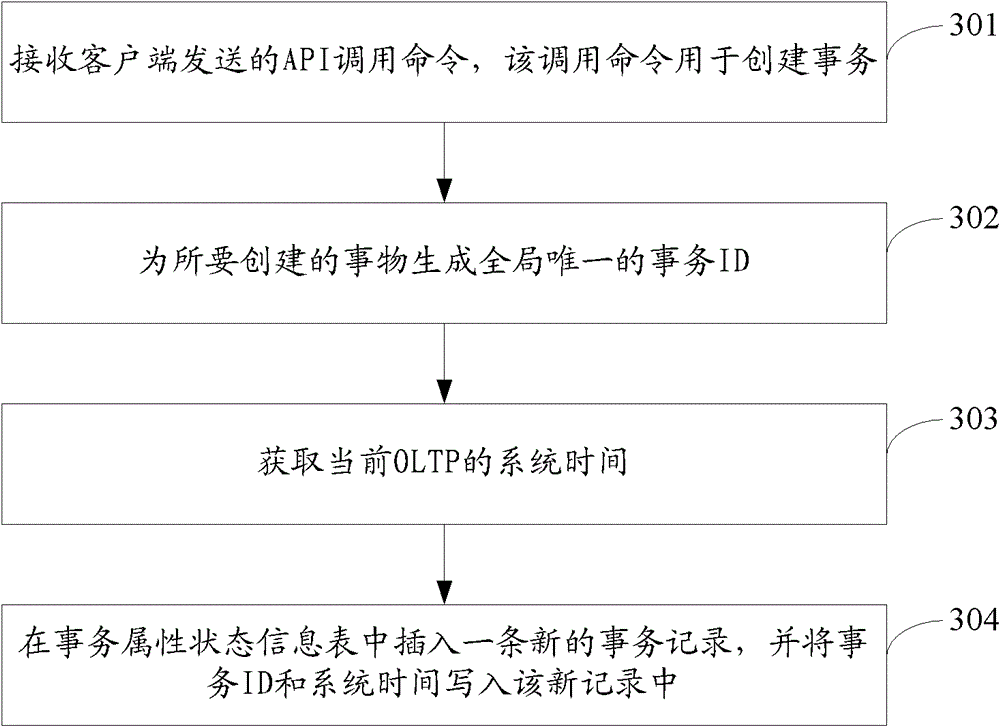
[0262] The receiving unit 1001 is configured to receive the transaction creation command transmitted by the client by calling the API;
[0263] A generating unit 1002, configured to generate a new transaction record in the transaction attribute status information table according to the transaction creation command, and assign a unique transaction identifier to the new transaction record;
[0264] A setting unit 1003, configured to set the commit attribute and the rollback attribute of the transaction record as non-executed;
[0265] The receiving unit 1...
no. 3 example
[0276] see Figure 11 , which is a block diagram of the third embodiment of the graph database server of the present application:
[0277] The graph database server includes: a receiving unit 1110 , a searching unit 1120 , an obtaining unit 1130 , a deleting unit 1140 , a submitting unit 1150 and a rollback unit 1160 .
[0278] The receiving unit 1110 is configured to receive a data deletion command transmitted by the client by calling an application programming interface API, and the data deletion command includes a transaction identifier, a node name and a filter condition;
[0279] A search unit 1120, configured to search for a transaction record according to the transaction identifier, and add the node name to the found valid transaction record;
[0280] The obtaining unit 1130 is configured to search a node attribute state information table according to the node name, and obtain data records meeting the filter condition from the node attribute state information table;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com