Locking piece for connecting components
A technology for locking parts and components, applied in mechanical equipment, fixing devices, etc., can solve the problems of easy loosening of components and inability to adjust the size of the locking bayonet, so as to achieve the effect of firm connection and reduced use cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
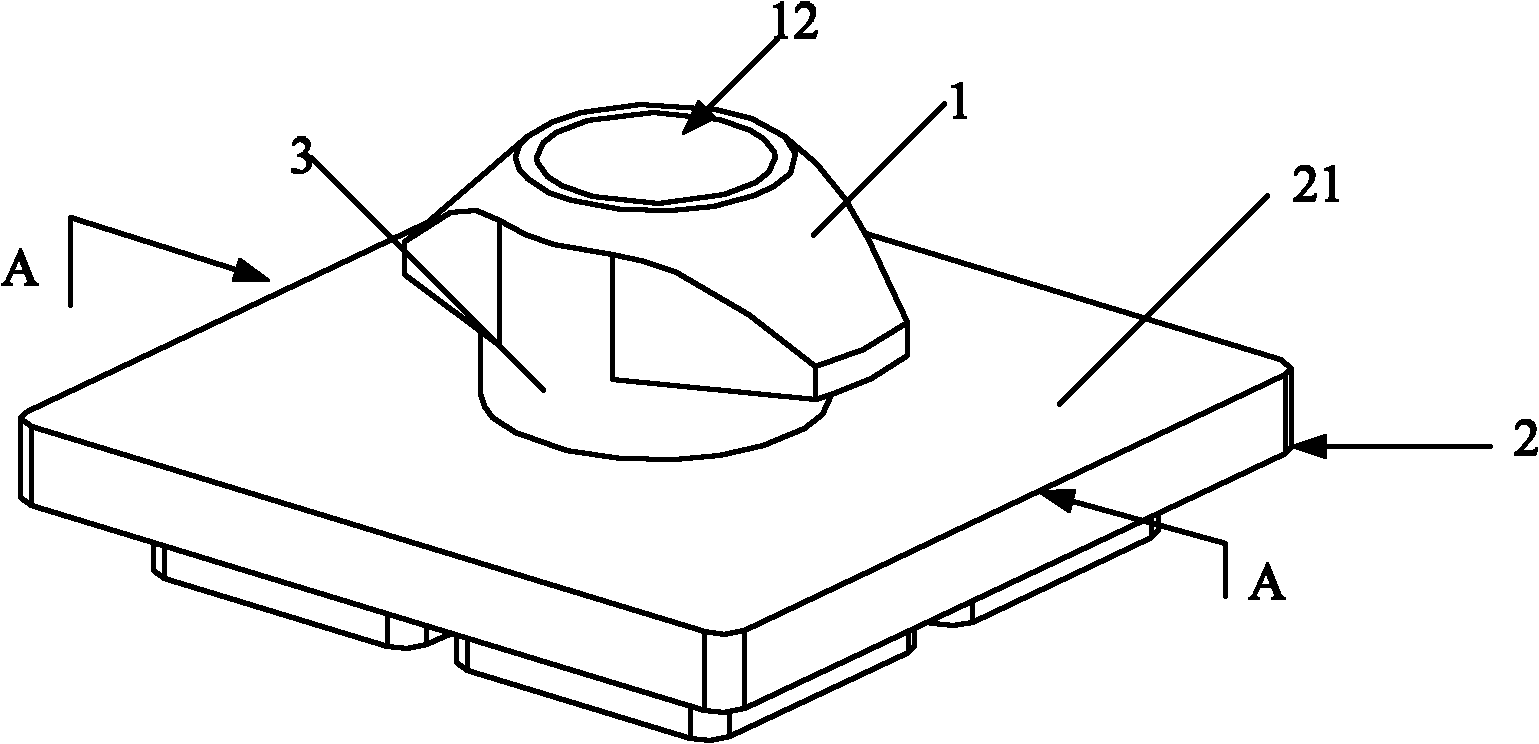
[0066] figure 1 It is a structural perspective view of Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
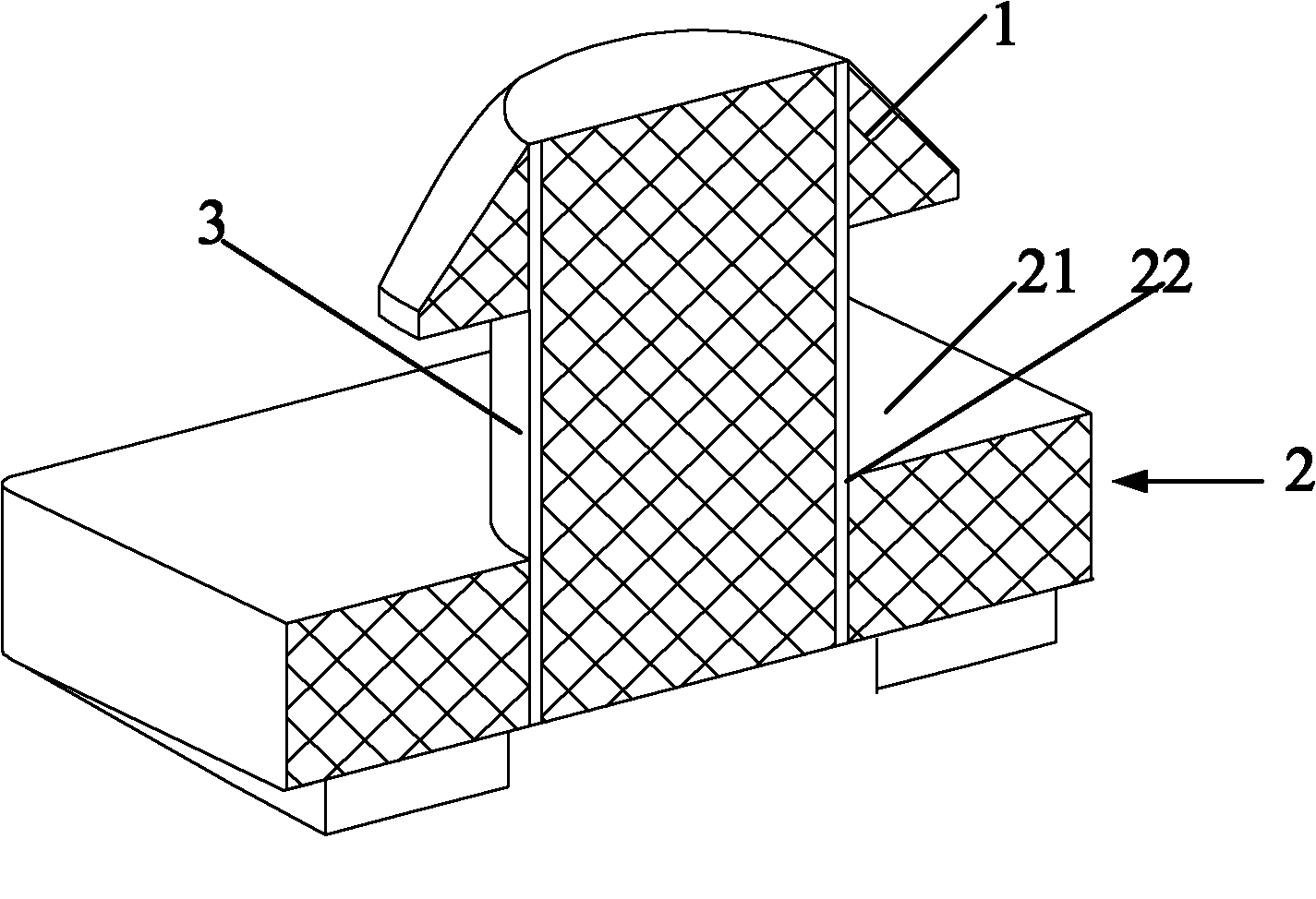
[0067] figure 2 for figure 1 Sectional view along line A-A.
[0068] like figure 1 As shown, the locking part includes a locking head 1 , a locking female part 2 with a bottom plate 21 and a locking column 3 . The locking column 3 is located between the locking head 1 and the bottom plate 21 of the locking female part 2, thereby forming a locking bayonet.
[0069] like figure 2 As shown, the locking head 1 and the locking column 3 are connected by threads, buckled or integrally formed. An appropriate connection method is selected according to the specific strength required by the locking member in actual use.
[0070] Further, the bottom plate 21 of the locking female part 2 is a flat bottom plate. Wherein, a connection hole 22 is provided on the surface of the bottom plate 21 , so that the diameter of the connection hole 22 matches the diameter of the locking post 3 . Th...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Figure 4 It is a front sectional view of Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0079] like Figure 4 As shown, the structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference being that a first stepped hole 12 is provided on the top surface of the locking head 1 . The first stepped hole 12 communicates from the top surface of the locking head 1 to the bottom surface of the locking post 3 , and the diameter of the upper hole is larger than the diameter of the lower hole 13 .
[0080] The locking part also includes a locking male part 5 . The locking male part 5 is provided with a through hole 51 penetrating from the top to the bottom, the diameter of which matches the diameter of the lower hole 13 of the first stepped hole 12 .
[0081] Further, the through hole 51 is a second stepped hole, and the diameter of the lower hole is larger than that of the upper hole.
[0082] When it is necessary to change the gap size of the locking ba...
Embodiment 3
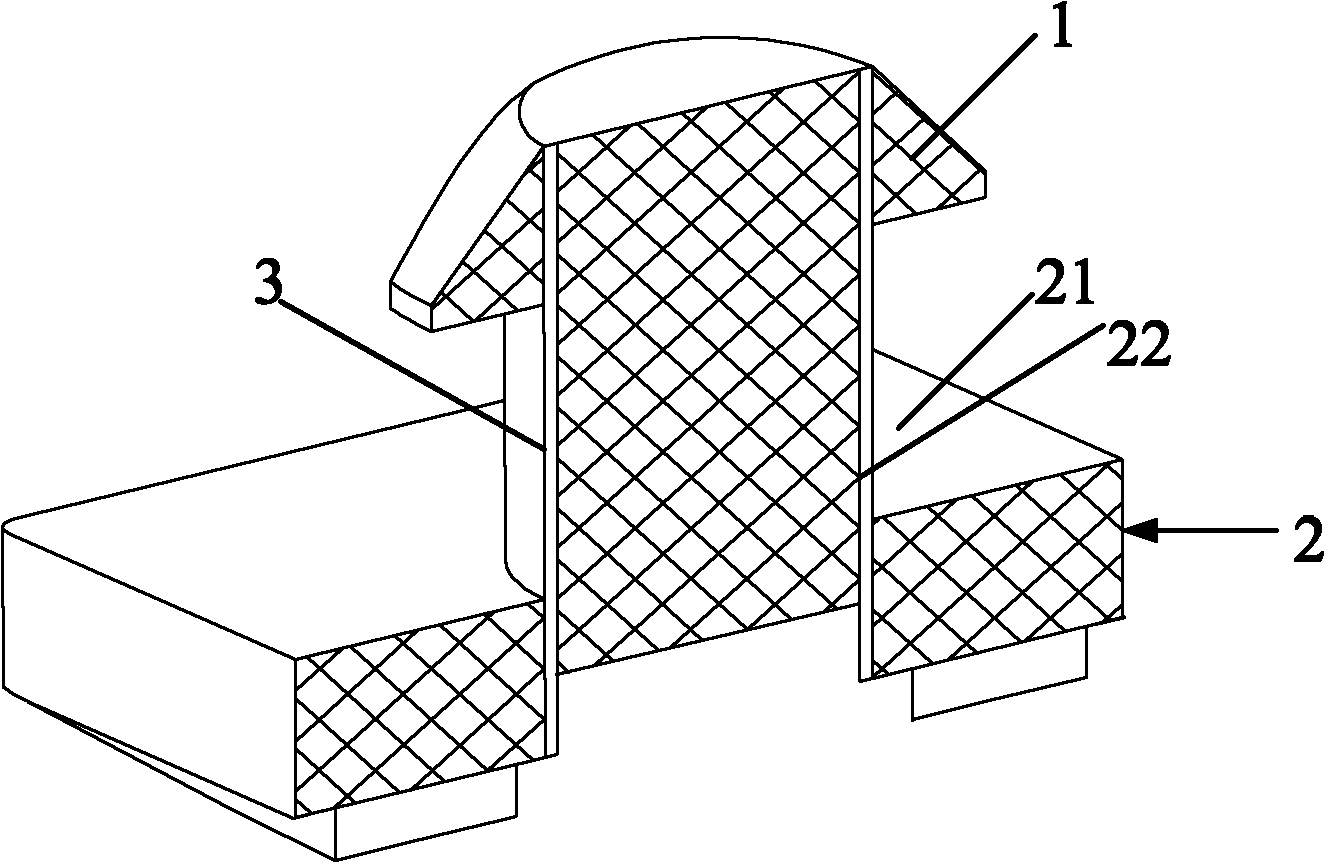
[0086] Image 6 It is a structural perspective view of Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0087] Figure 7 It is a front sectional view of Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0088] like Image 6 and Figure 7 As shown, the structure of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the second embodiment, the difference being that the lower part of the bottom plate 21 of the locking female part 2 is a through space 23 . The locking male part 5 is embedded in the space 23 . The shape of the locking male part 5 matches the space 23, so that the outer walls around the locking male part 5 cooperate with the inner walls of the space 23 to produce frictional locking. The function of this structure is to make the locking male part 5 more firm through frictional locking, so that the locking column 3 will not loosen, and it is convenient to fix and form the required locking bayonet gap. In addition, it is also convenient to connect the locking element to the connecti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com