Non-rigid medical image registration method based on finite element model
A medical image, finite element technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of registration time process, low accuracy, segmentation accuracy, etc., and achieve the effect of enhancing robustness, accuracy and speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below. This embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following implementation example.
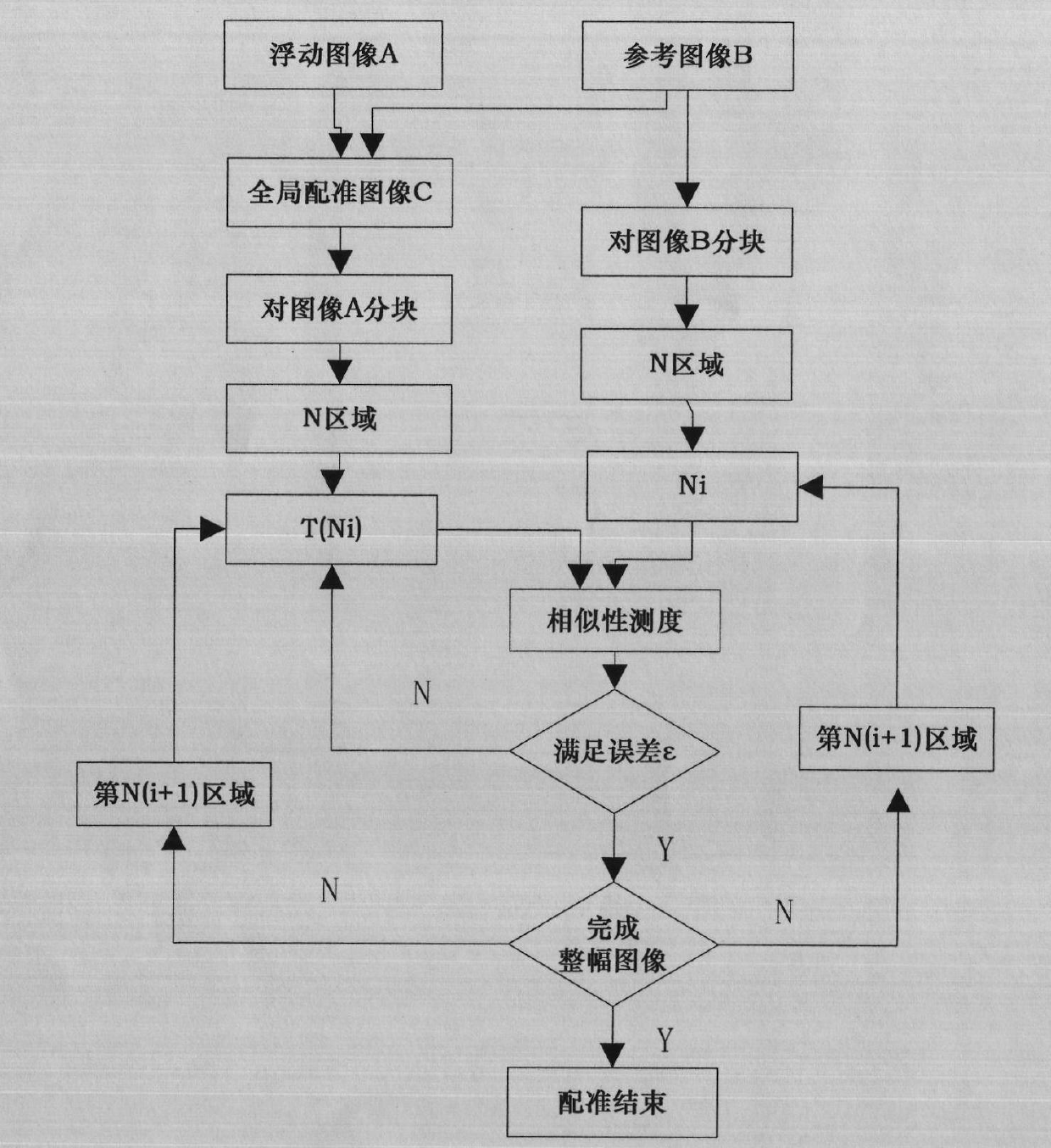
[0024] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0025] Step 1: Globally register the two images to be registered
[0026] First, find the centroid of the two images of the floating image and the reference image through the first-order moment, and then find the angle between the main axis and the coordinate system of the floating image and the reference image through the second-order central moment, and use the position difference of the centroid of the two images as the translation Component, and then calculate the respective axis directions and rotate and align the two images accor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com