Heat-dissipation structure for LED (Light Emitting Diode) light
A technology of LED lamps and heat dissipation structures, which is applied to lighting and heating equipment, cooling/heating devices of lighting devices, lighting devices, etc., can solve the problems of high junction temperature, insufficient service life, and low luminous efficiency of LED lamps. , to achieve the effect of improving reliability and service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
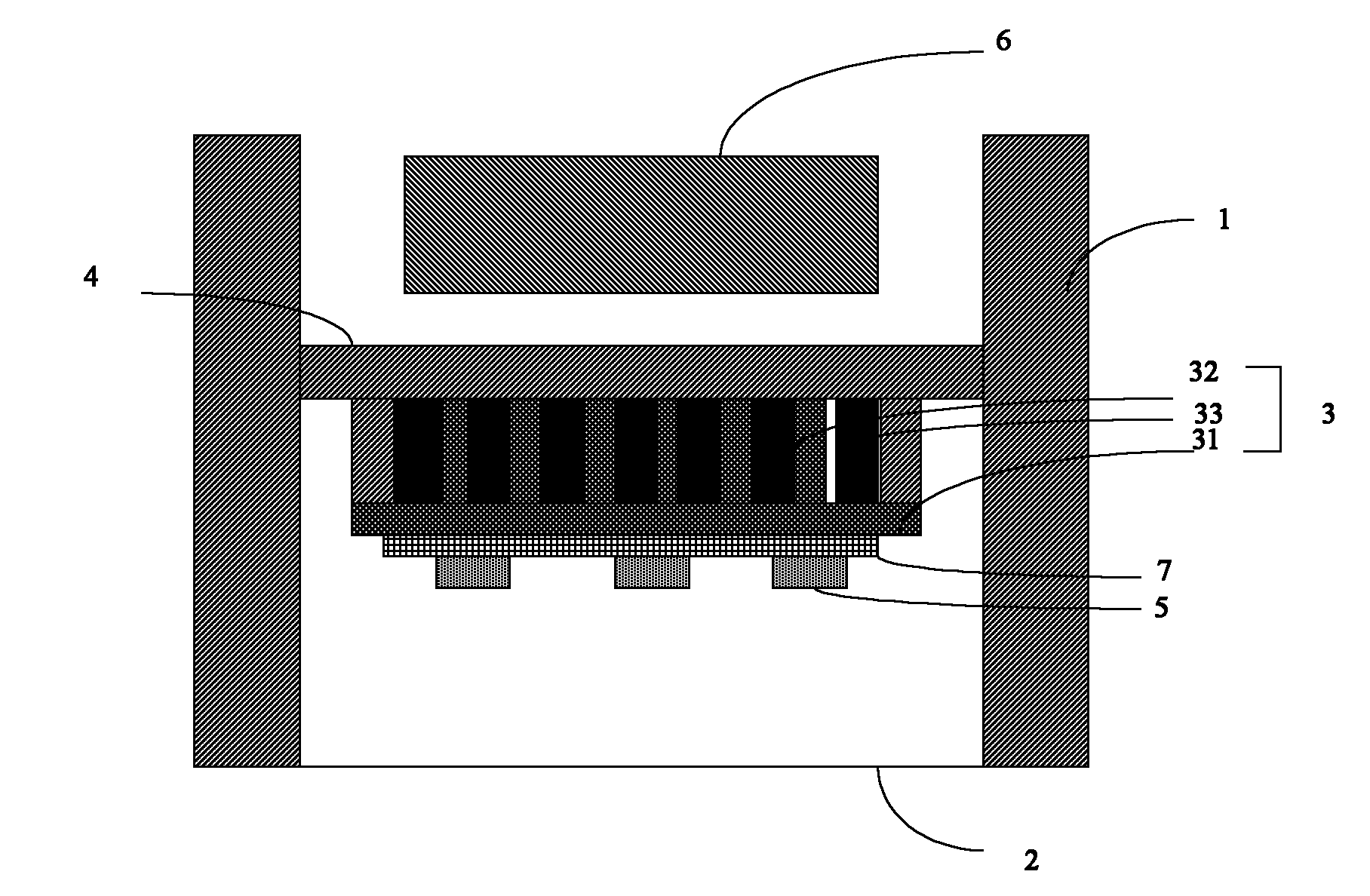
[0018] see figure 2 The heat dissipation structure of an LED lamp is shown, which includes a cavity surrounded by an LED lamp housing 1 and a lens 2 and a driving power source 6 accommodated in the cavity; the cavity is provided with an energy storage cavity 3, The housing bottom plate 4 forming a sealed cavity with the energy storage cavity, the PCB board 7 connected with the energy storage cavity 3 and the LED particles 5 on the PCB board 7 . The energy storage cavity 3 cooperates with the housing bottom plate 4 to form several sealed cavities, and the sealed cavities are used to fill the phase change material 33 to form a phase change material layer.
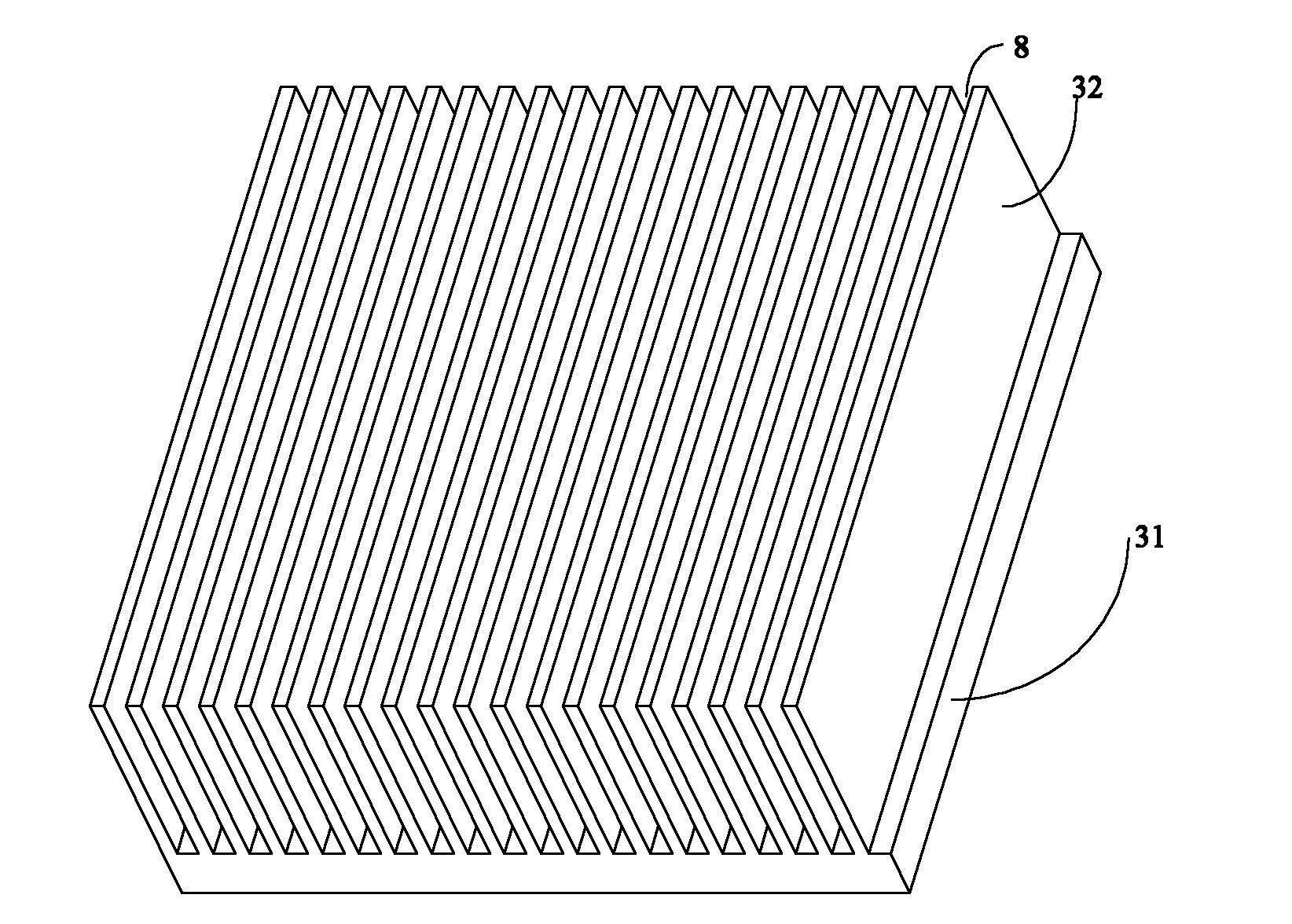
[0019] Please continue to refer to image 3 As shown, the energy storage cavity 3 includes a substrate 31 , a fin array 32 located on the substrate 31 , and a phase change material layer 33 accommodated in the fin array 32 . The fin array 32 and the casing bottom plate 4 form a sealed cavity for accommodating the phase cha...
Embodiment 2
[0023] see Figure 4 As shown, the energy storage cavity can also be Figure 4 In the structure shown, the energy storage cavity includes a substrate 31 ′, a fin array 32 ′ located on the substrate 31 ′, and a phase change material layer 33 ′ accommodated in the fin array 32 ′. The fin array 32 ′ and the bottom plate of the casing form a sealed cavity for accommodating the phase change material layer. The fin array 32 ′ is perpendicular to the base plate 31 ′, and is roughly a plurality of spaced cylinders, and spaced slots are formed between the cylinders. The bottom plate of the housing also includes the bottom plate and the sides perpendicular to the bottom plate and distributed around the bottom plate. Wall; the housing bottom plate surrounds the fin array 32', thereby forming several sealed cavities. The material of the energy storage cavity is mainly metal, such as aluminum and the like.
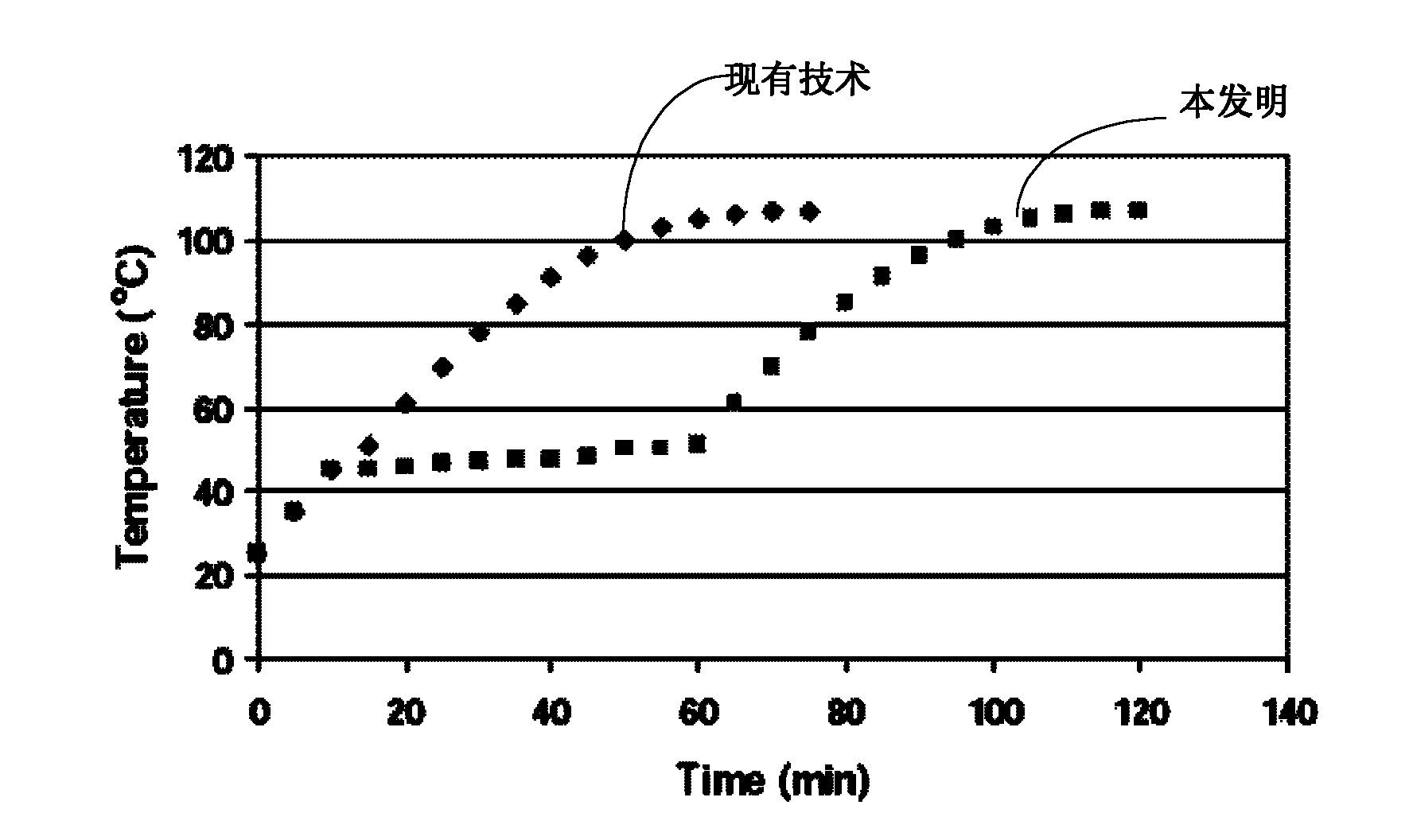
[0024] The principle of the present invention is: the service time of the indoo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com