Clostridium difficile exotoxin A carboxy-terminal gene sequence with optimized codon and nucleic acid vaccine thereof
A codon-optimized, Clostridium difficile technology, applied in the field of Clostridium difficile exotoxin A carboxy-terminal gene fragment and its nucleic acid vaccine, can solve the problems of ineffective expression of foreign genes and low immunogenicity of nucleic acid vaccines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1. Design and synthesis of codon-optimized Clostridium difficile exotoxin A carboxy-terminal gene sequence
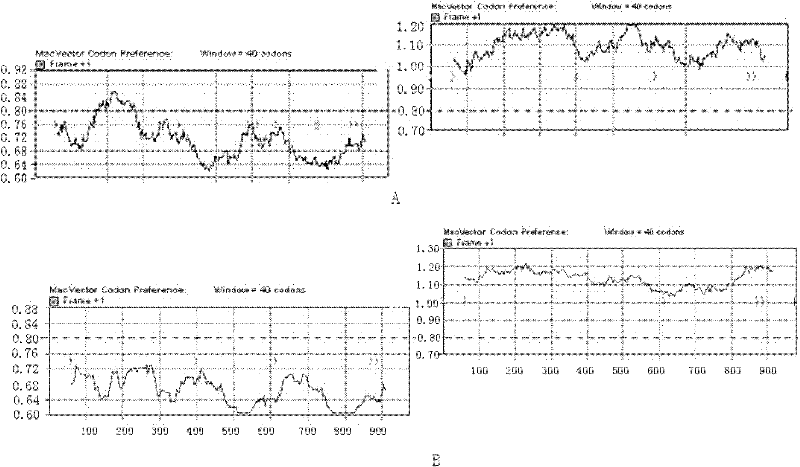
[0041] First, the software MacVector 7.2 was used to analyze the carboxy-terminal gene sequence encoding Clostridium difficile exotoxin A to find out its codon usage bias and the sites that differ from mammalian and Escherichia coli codon usage bias. For the codon sites with different usage preferences, codons preferred by both mammalian cells and Escherichia coli were substituted, and a codon-optimized C-terminal gene sequence of Clostridium difficile exotoxin A was designed. The protein amino acid sequence encoded by the codon-optimized gene sequence is consistent with its original amino acid sequence. The designed sequence was synthesized by American GENEART Company, loaded into vector pMK-RQ, and constructed into recombinant plasmid pMK-RQ-TcdA-C. The synthesized sequence was confirmed to be correct by sequencing.
[0042] In order to clearly show t...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2. Construction of eukaryotic expression vector pJW4303-TcdA-C
[0066] (1) Obtaining the TcdA-C fragment and the large linear fragment of the plasmid pJW4303: the plasmids pJW4303 and pMK-RQ-TcdA-C (synthesized by GENEART, USA) were double-digested with Pst I and BamH I, respectively. The enzyme digestion reaction system is: 10×BufferTango TM 4 μl, plasmid (pJW4303, pMK-RQ-TcdA-C) 10 μl, Pst I 1.5 μl, BamHI 1.5 μl, water up to 40 μl, 37°C, 2h.
[0067] (2) Purification of digested products: The digested products were subjected to 10 g / L agarose gel electrophoresis, placed under a UV detector, and purified according to the gel recovery kit (Agarose Gel DNA Purification Kit Ver. Company) instructions, cut out the gel containing the target fragment, weigh the mass of the gel block with an analytical balance, and calculate the volume of the gel block according to 1 mg=1 μl. Add 4 times the volume of DR-I Buffer, place in a 75°C water bath to heat and melt the ge...
Embodiment 3
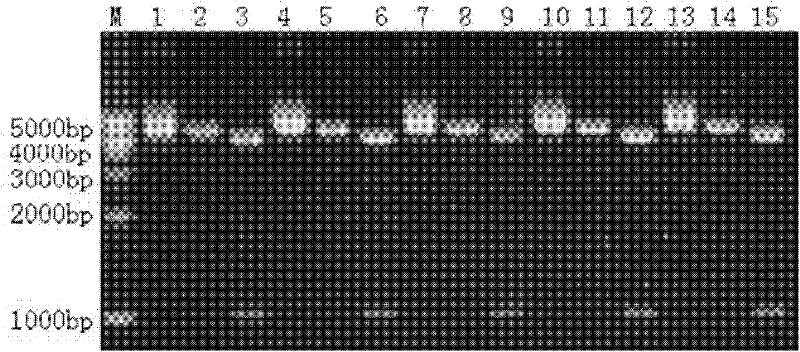
[0069] Example 3. Identification of recombinant plasmid pJW4303-TcdA-C
[0070] 3.1 pJW4303-TcdA-C respectively transformed HB101 competent cells
[0071] 1) Add 10 μl of the linker to an Ep tube containing 100 μl of HB101 competent cells, gently tap the tube wall several times, mix well, and place on ice for 30 minutes.
[0072] 2) Place the Ep tube in a 42°C water bath for 90s.
[0073] 3) Slowly add 0.5 mL of LB medium to the Ep tube, shake at 37°C, 80 rpm, for 45 min.
[0074] 4) Spread the bacterial solution on an LB plate containing ampicillin (0.1 g / L), and culture overnight at 37°C.
[0075] 3.2 Screening positive clones
[0076] Pick 5 single colonies at random, inoculate them in 5 culture test tubes (LB medium containing 0.1 g / L ampicillin), shake at 200 rpm at 37°C, and culture overnight.
[0077] 3.3 Small extraction of recombinant plasmid pJW4303-TcdA-C (Plasmid small extraction kit: TaKaRa MiniBEST PlasmidPurification Kit Ver.2.0, TaKaRa Company)
[0078] 1)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com