Solid-state imaging device and camera system
A solid-state imaging device and device technology, which can be used in TV system components, electrical components, image communication, etc., and can solve problems such as image quality degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0045] 1. First embodiment (first exemplary configuration of CMOS image sensor (solid-state imaging device))
[0046] 2. Second embodiment (second exemplary configuration of CMOS image sensor (solid-state imaging device))
no. 3 example
[0047] 3. Third embodiment (third exemplary configuration of CMOS image sensor (solid-state imaging device))
[0048] 4. Fourth Embodiment (Exemplary Configuration of Camera System)
[0049]
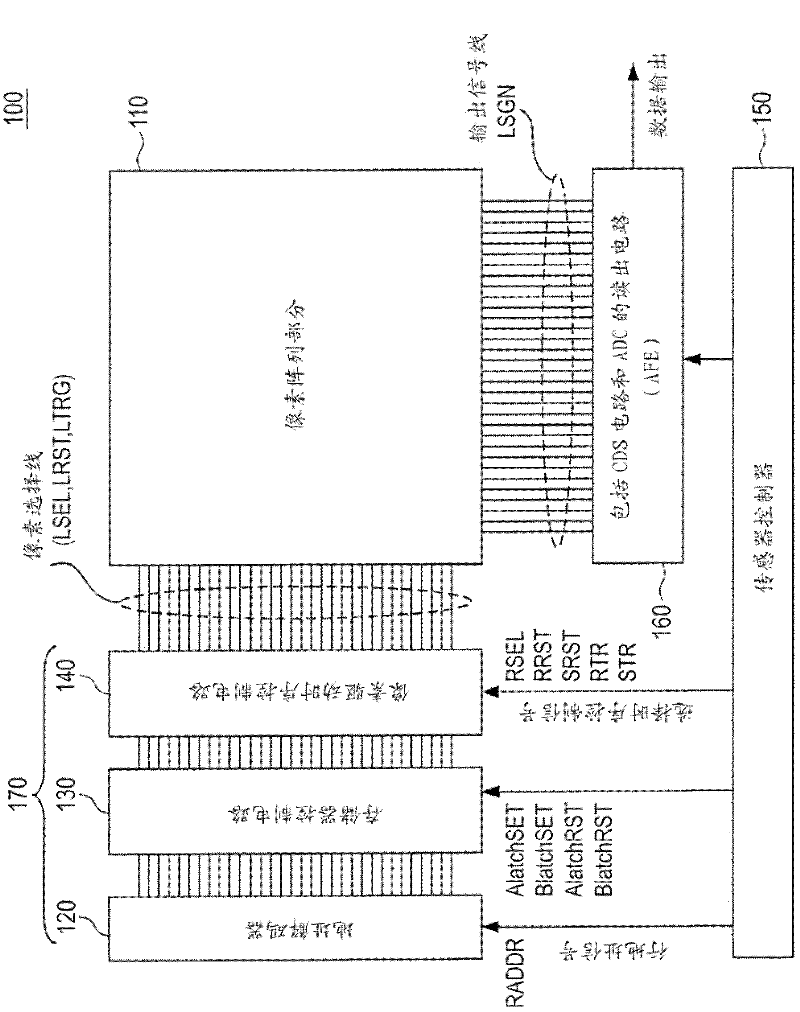
[0050] figure 1 Is a diagram illustrating an exemplary configuration of a CMOS image sensor (solid-state imaging device) according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure.
[0051] The CMOS image sensor 100 has a pixel portion 110, an address decoder 120, a latch (memory) control circuit 130, a pixel drive timing control circuit 140, a sensor controller 150, and a readout circuit (AFE) 160.
[0052] The address decoder 120, the memory control circuit 130, the pixel driving timing control circuit 140, and the sensor controller 150 constitute a pixel driving part.
[0053] In this embodiment, the address decoder 120, the memory control circuit 130, and the pixel drive timing control circuit 140 constitute a row (vertical) selection circuit 170.
[0054] The vertical selection circuit 170 is...
no. 2 example
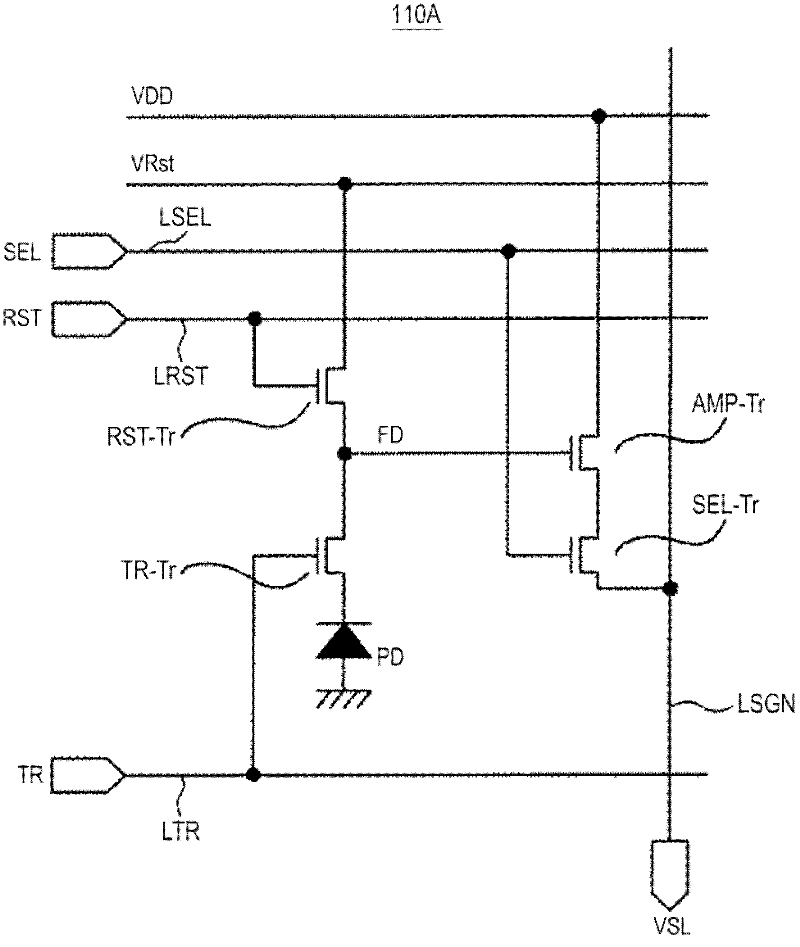
[0187] Picture 11 It is a diagram illustrating an example of a pixel drive timing control circuit and a memory control circuit of the vertical (row) selection circuit of the CMOS image sensor (solid-state imaging device) according to the second embodiment.
[0188] In the second embodiment, the circuit configuration is basically the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0189] Therefore, pixel drivers and other Figure 7 Or the same configuration as those of 8.
[0190] The second embodiment differs from the above-mentioned first embodiment in the following points. Such as Picture 11 As shown, the second memory (B memory) 132 of each row is reset as a whole by the B memory (latch) reset control signal BLatchRST.
[0191] in Picture 11 In the memory control circuit 130C, the AND gate AG134 is not arranged at the input stage of the reset terminal R of the second memory (B memory) 132, and directly provides the B memory (latch) reset control signal BLatchRST.
[0192] In the case of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com