Graph similarity calculation system, method, and program
A similarity, computer technology, applied in the field of similarity, can solve problems such as difficult map comparison, and achieve the effect of high reliability and great effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
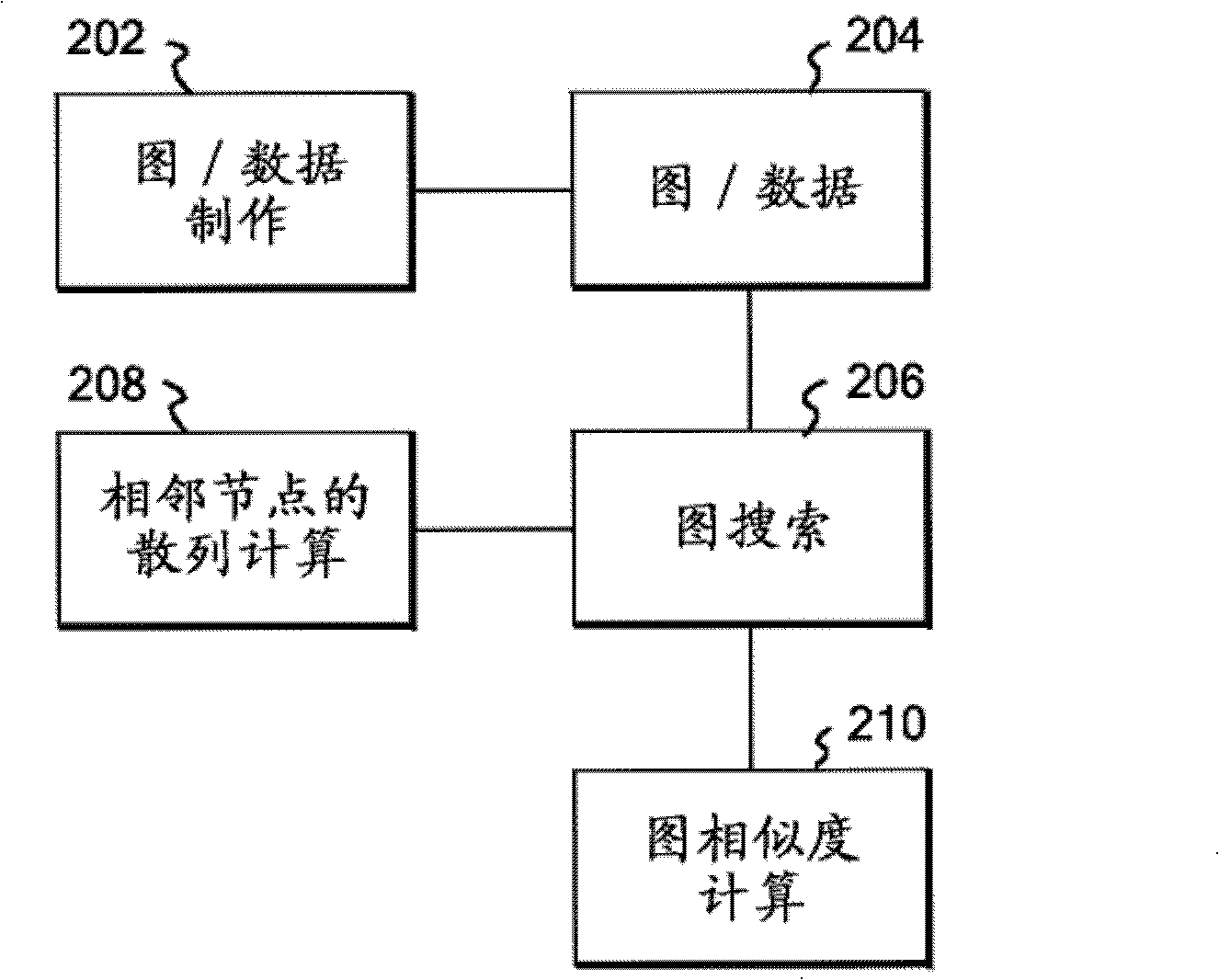
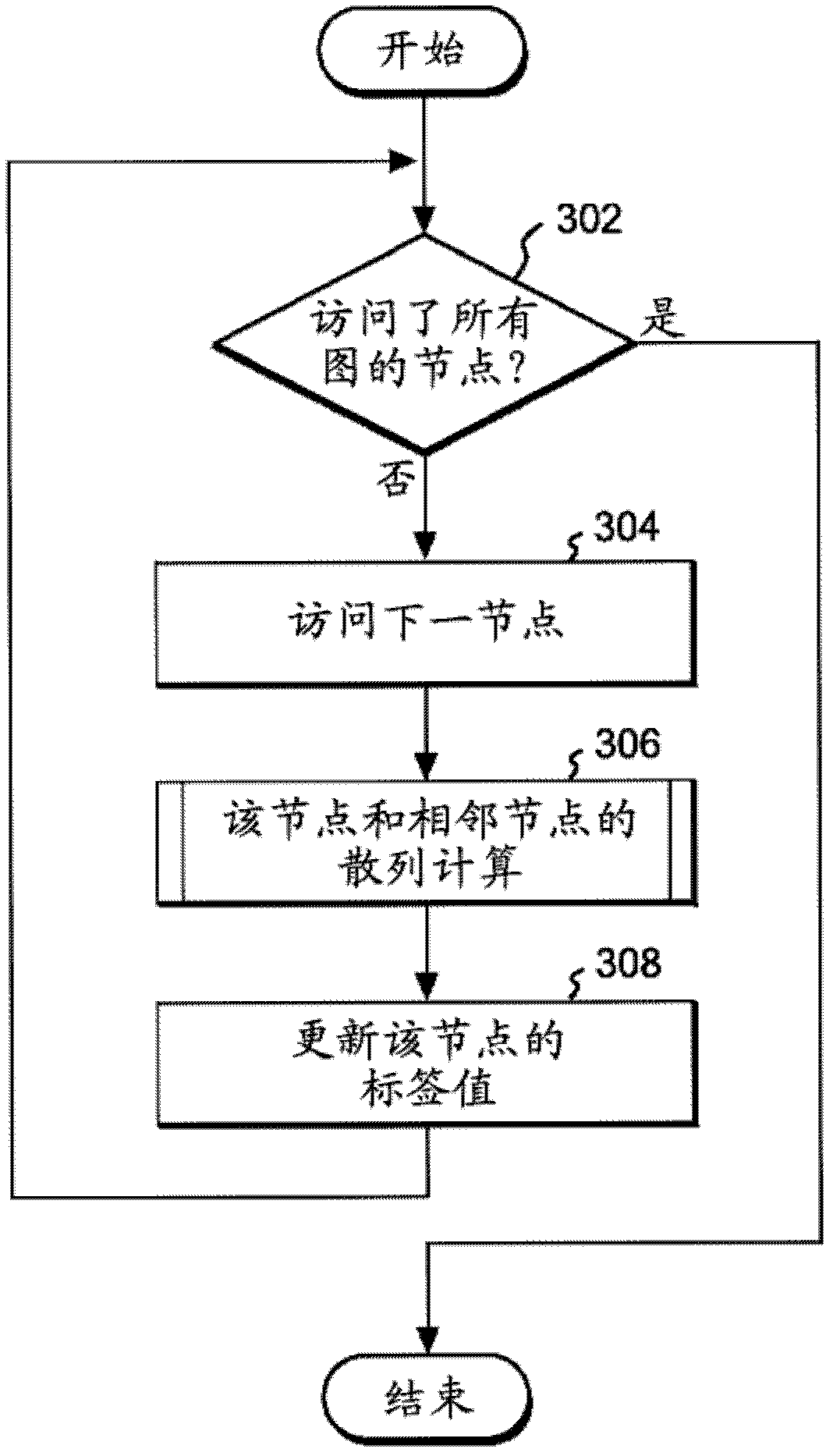
[0038] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described based on the drawings. Unless otherwise stated, the same reference numerals refer to the same objects throughout the drawings. One embodiment of the present invention will be described below, and it should be understood that the present invention is not intended to be limited to the content described in this example.
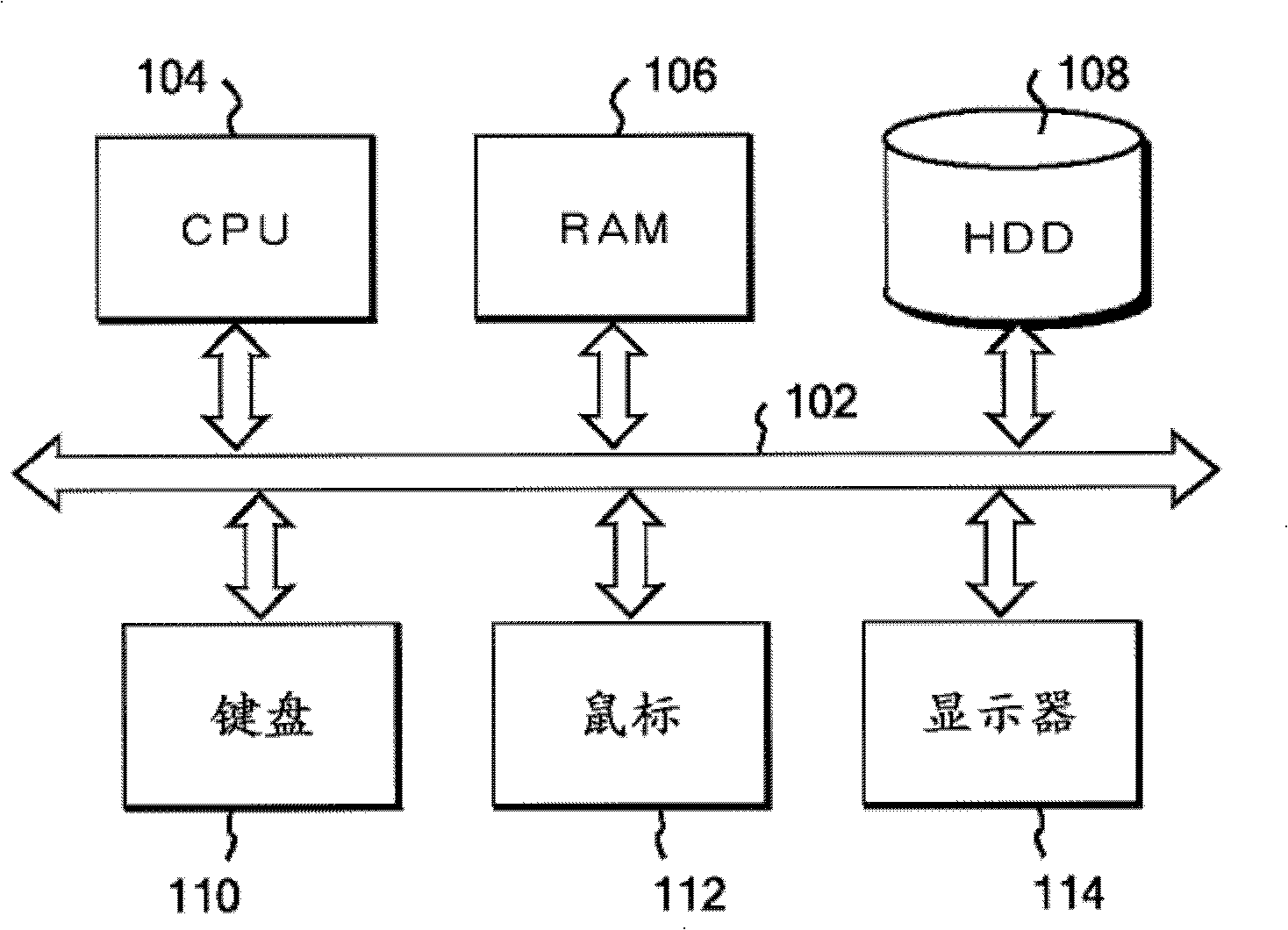
[0039] refer to figure 1 , is a block diagram showing computer hardware for implementing the structures and processes involved in one embodiment of the present invention. figure 1 Among them, CPU 104 , main storage (RAM) 106 , hard disk drive (HDD) 108 , keyboard 110 , mouse 112 , and display 114 are connected to system bus 102 . Preferably, the CPU 104 is based on a 32-bit or 64-bit design, for example, Intel's Pentium (trademark) 4, Core (trademark) 2Duo, Xeon (trademark), AMD's Athlon (trademark), etc. can be used. The main storage 106 preferably has a capacity of 2 GB or more. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com