3D layering of map metadata
A metadata and map technology, applied in the field of 3D layering of map metadata, can solve problems such as losing context and unclear directions, and achieve the effect of improving the overall experience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
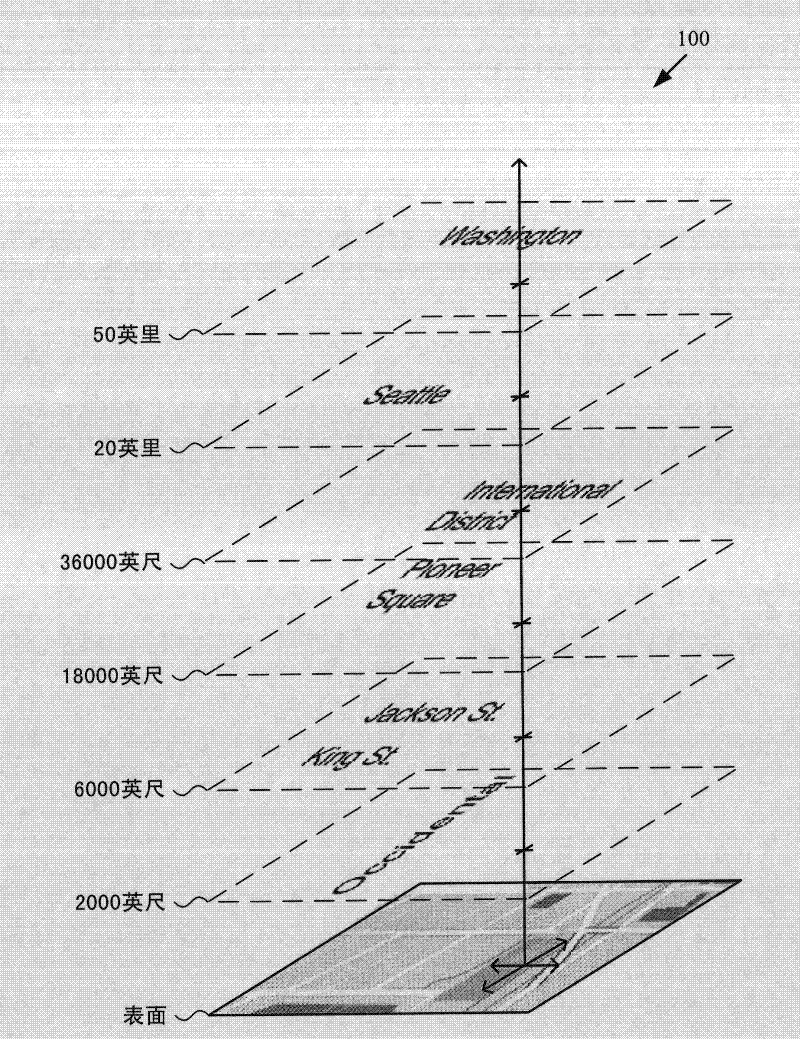
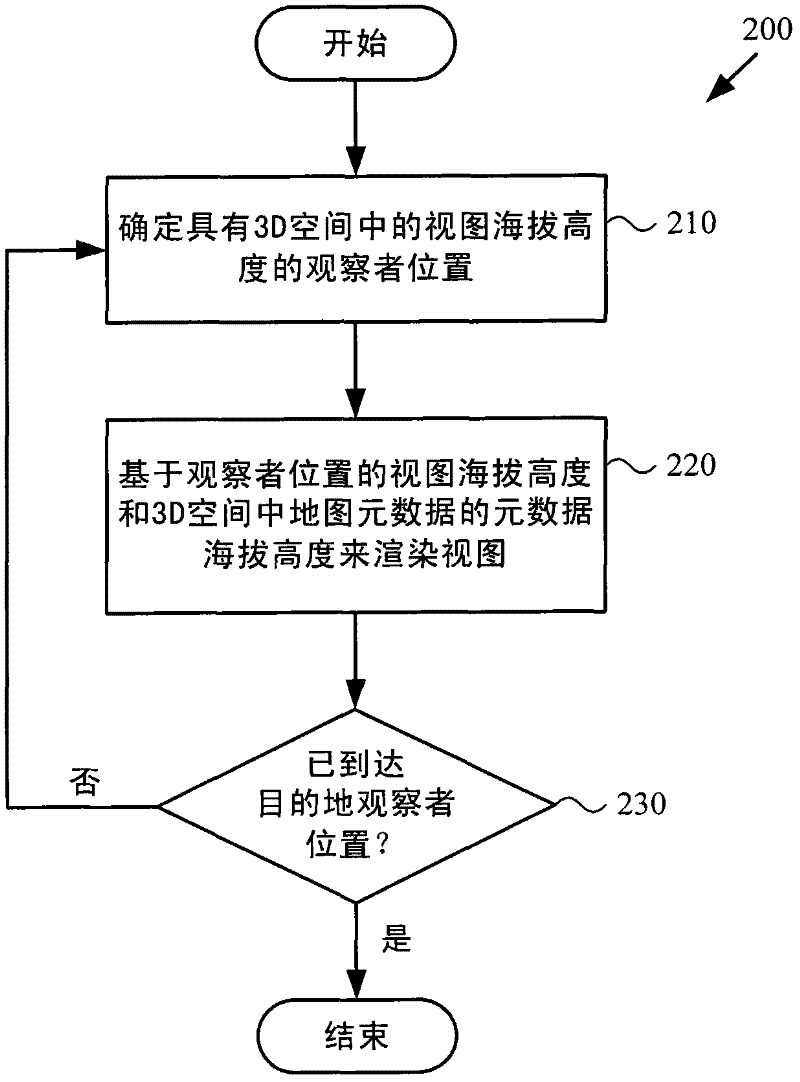
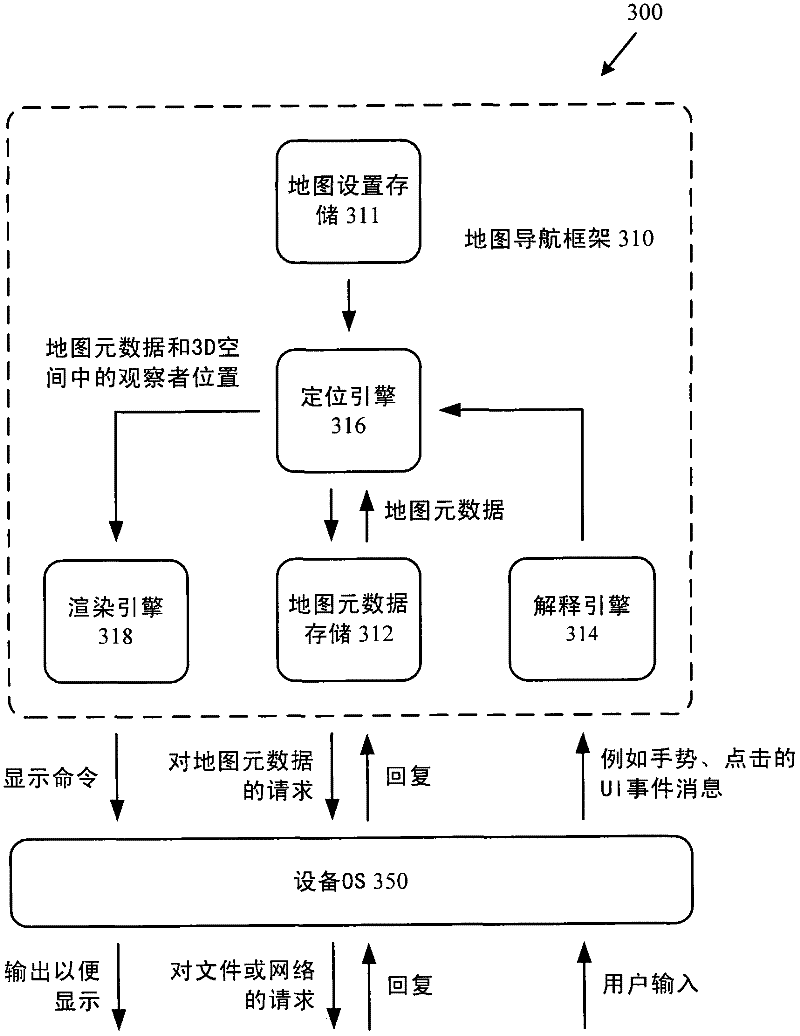
[0026] Techniques and tools for rendering views of maps in which map metadata elements are separated from the map base layer are described. Map metadata elements may be layered over the base layer of the map in 3D space. For example, map metadata elements are associated with features such as buildings, roads, towns, cities, states in the map, and map metadata elements are placed in 3D space depending on the altitude of the feature scale (for buildings and lower elevations for roads, higher elevations for cities, etc.) above the feature with which the map metadata element is associated. In various scenarios, the 3D layering of map metadata elements improves the overall experience of using map navigation tools.
[0027] Separating the map metadata elements from the base layer of the map and using 3D layering of the map metadata elements on the map simplifies the process of deciding which map metadata elements to show or hide for a given task. For example, depending on the search...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com