Patents
Literature
90 results about "Metadata element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
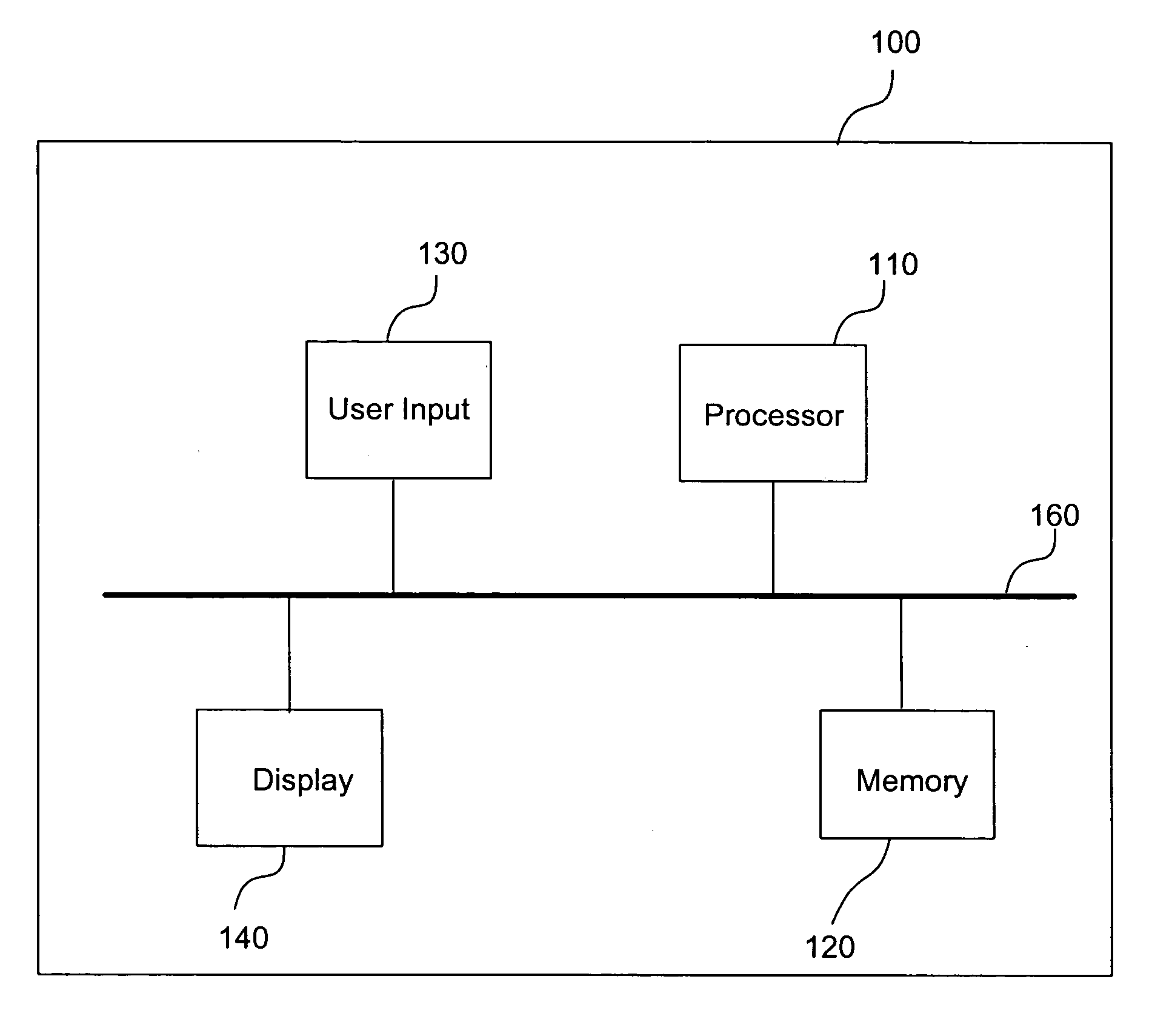
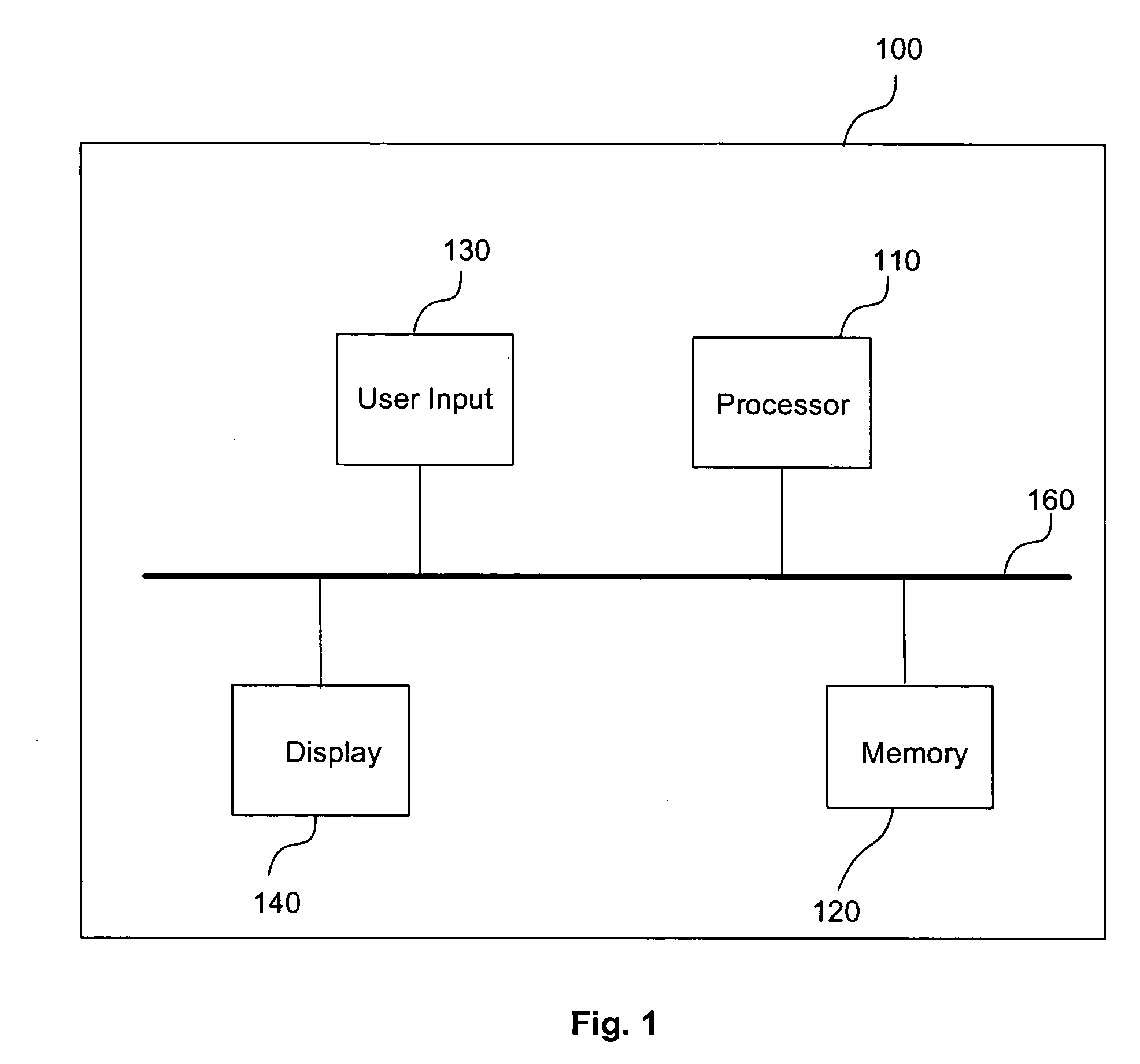
About Metadata Elements. Metadata elements are the logical objects derived from the physical objects in a data source. Metadata elements can be created when you create a data source connection or afterward. Metadata elements can also be created from other metadata that is already stored and cataloged for Essbase Studio use.
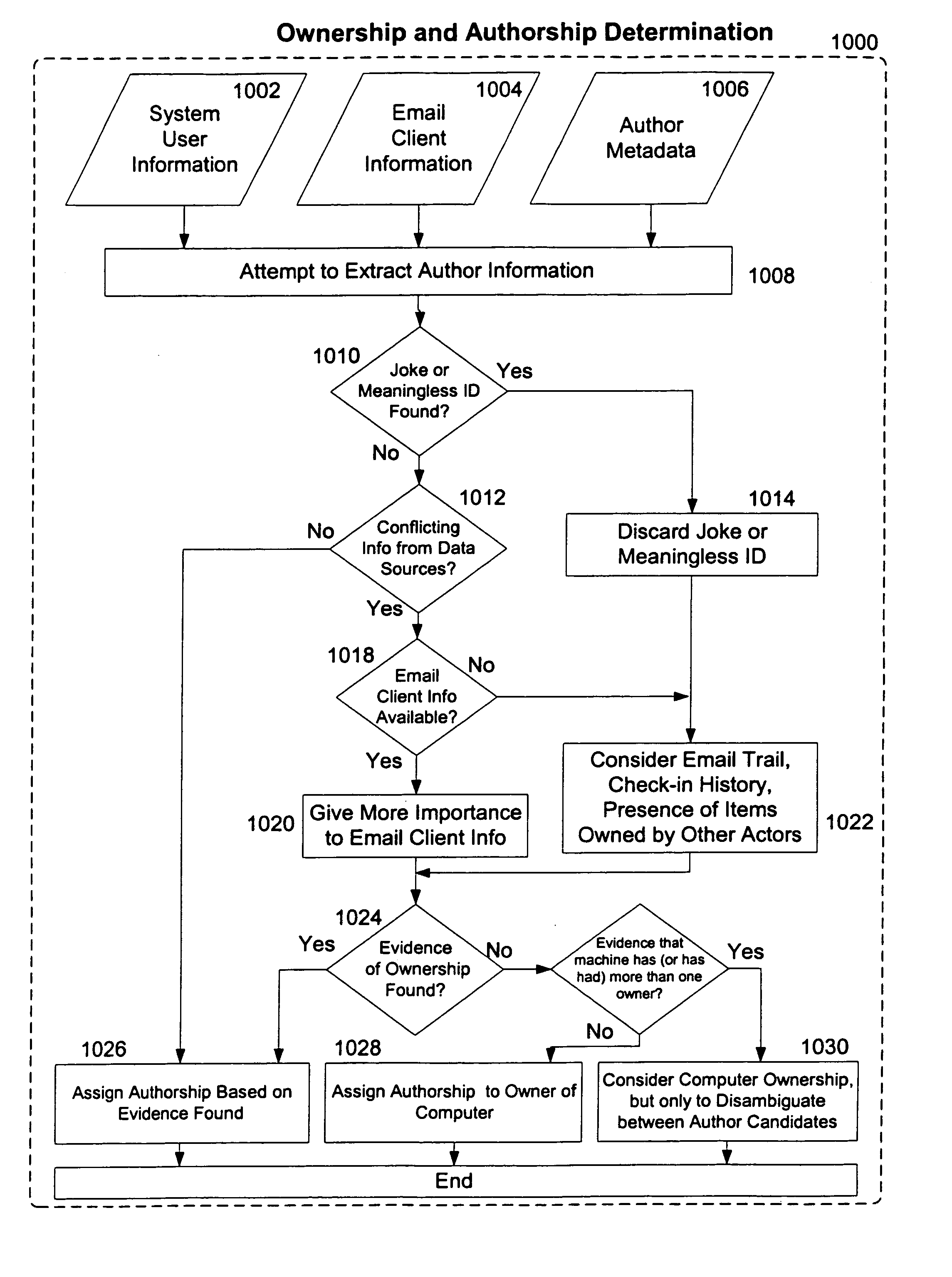
Method and apparatus for sociological data mining
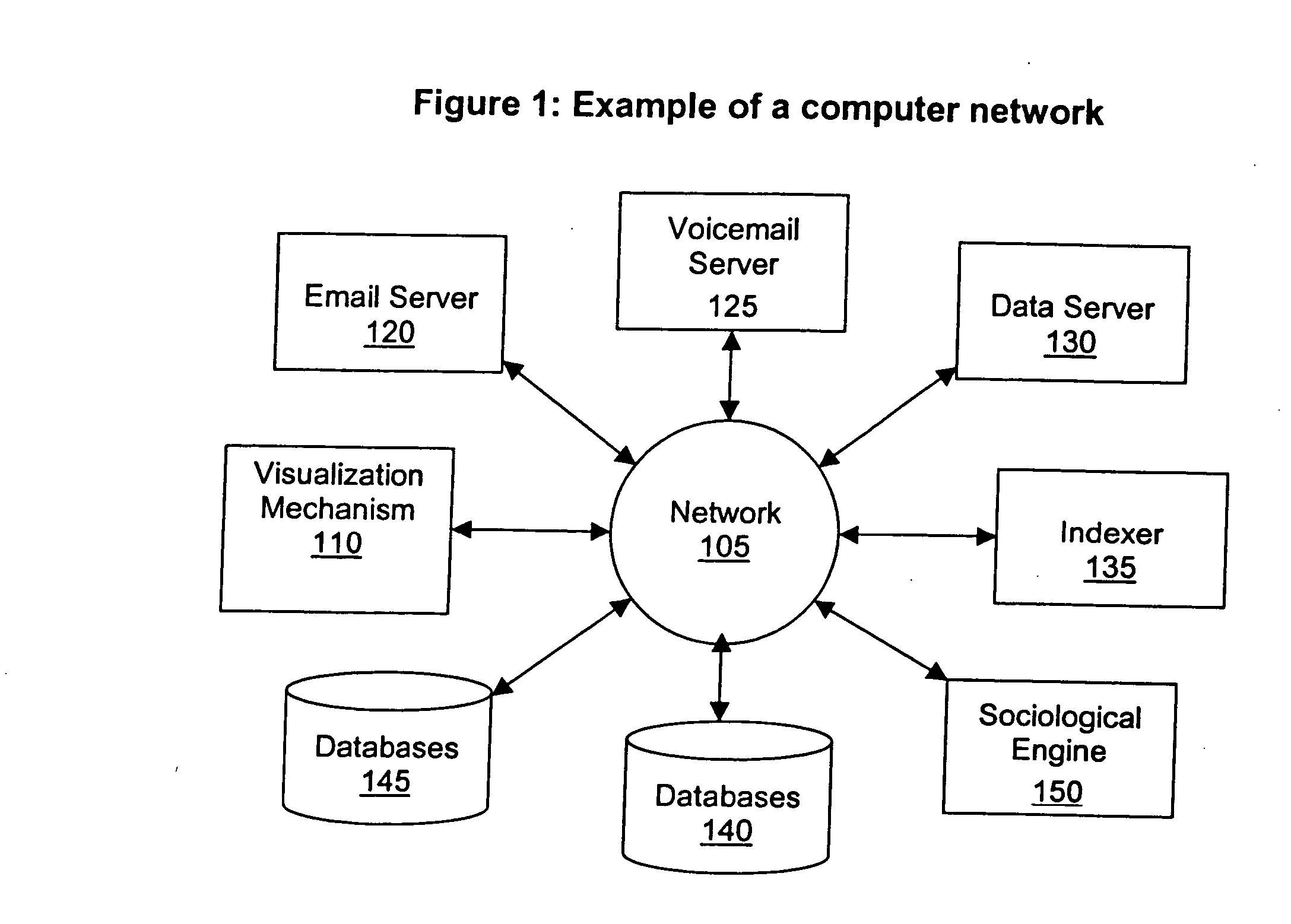
A processing system for retrieving interrelated documents is described. The system comprises a document repository for storing a plurality of documents, a metadata repository for storing a plurality of metadata elements to represent relations between the documents, and a sociological analysis engine to identify relationships between the documents using the metadata elements from the metadata repository.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Method and apparatus for sociological data mining
InactiveUS20060253418A1Metadata text retrievalDigital data processing detailsPaper documentDocument preparation
A processing system for retrieving interrelated documents is described. The system comprises a document repository for storing a plurality of documents, a metadata repository for storing a plurality of metadata elements to represent relations between the documents, and a sociological analysis engine to identify relationships between the documents using the metadata elements from the metadata repository.
Owner:SUNRISE SERIES 54 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
System and method for accessing data in disparate information sources
InactiveUS7668798B2Metadata text retrievalData processing applicationsRelevant informationData field
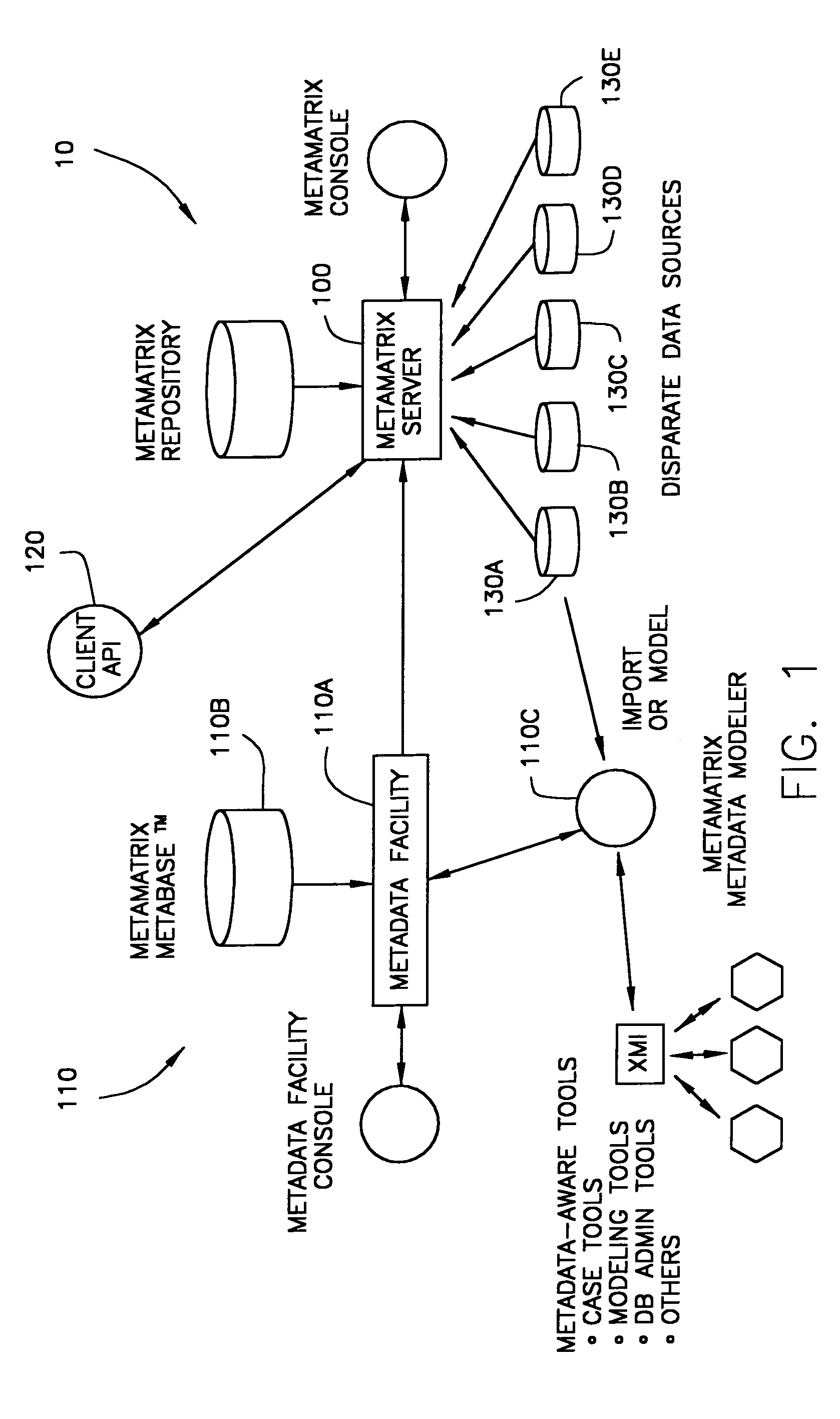
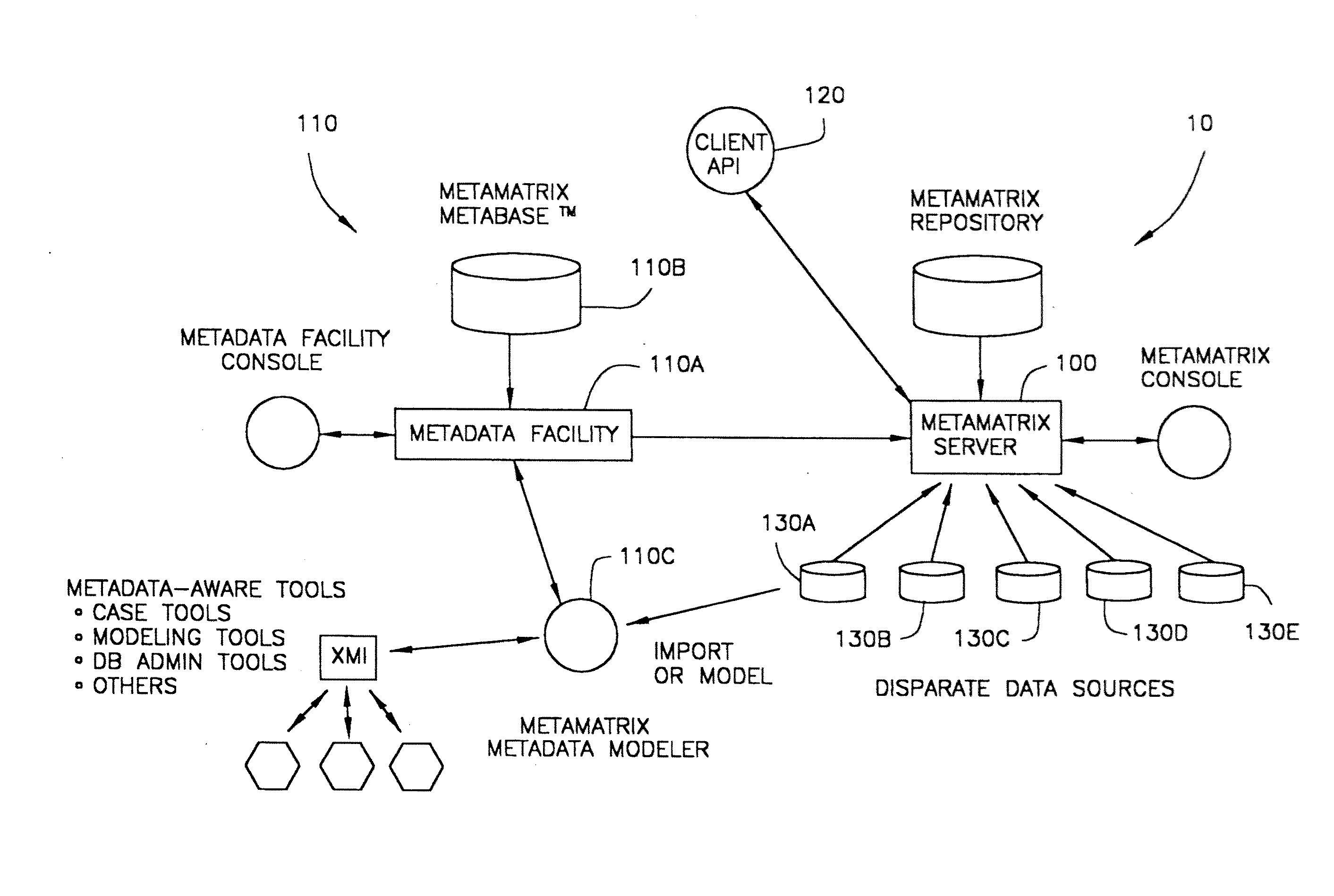
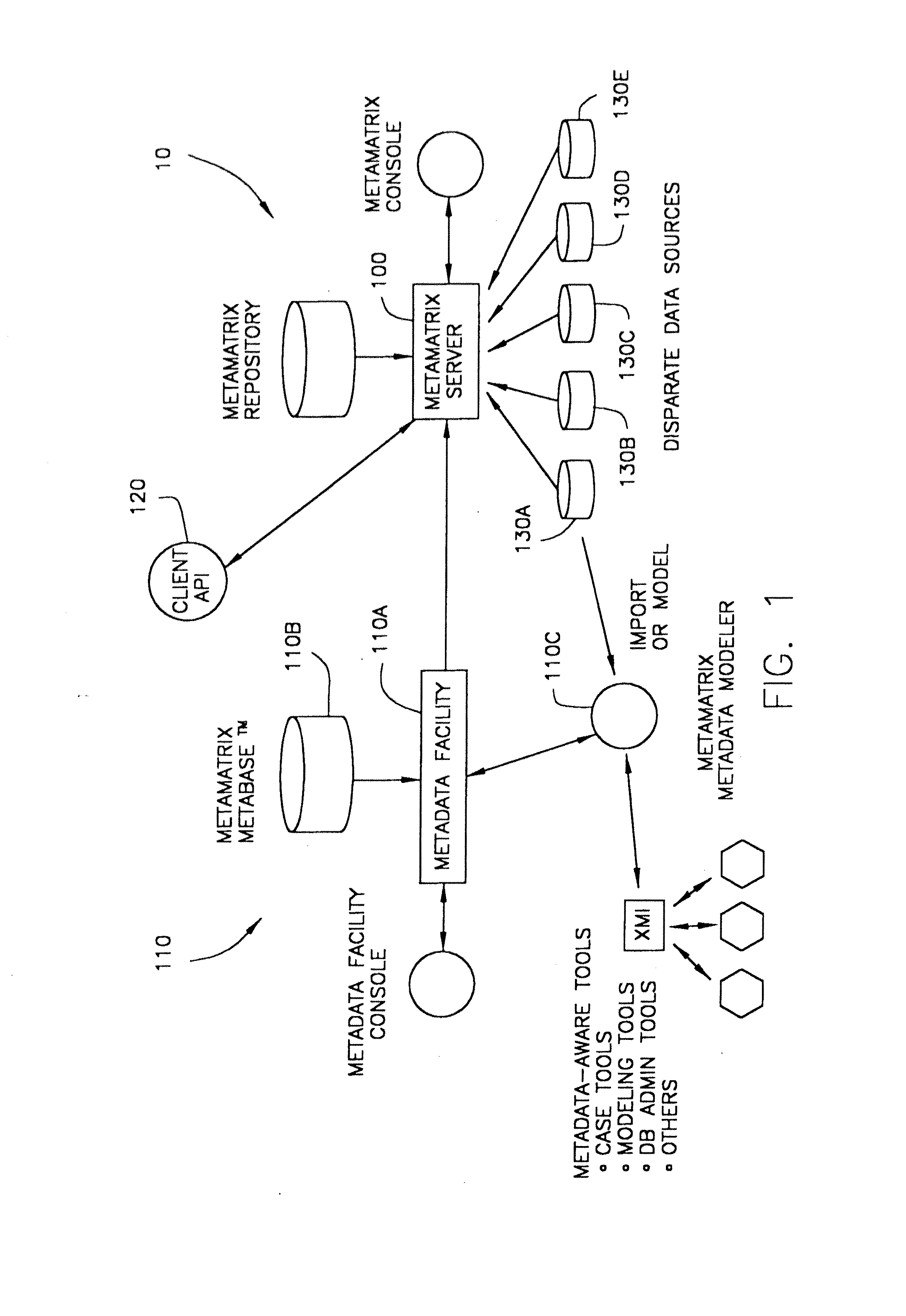
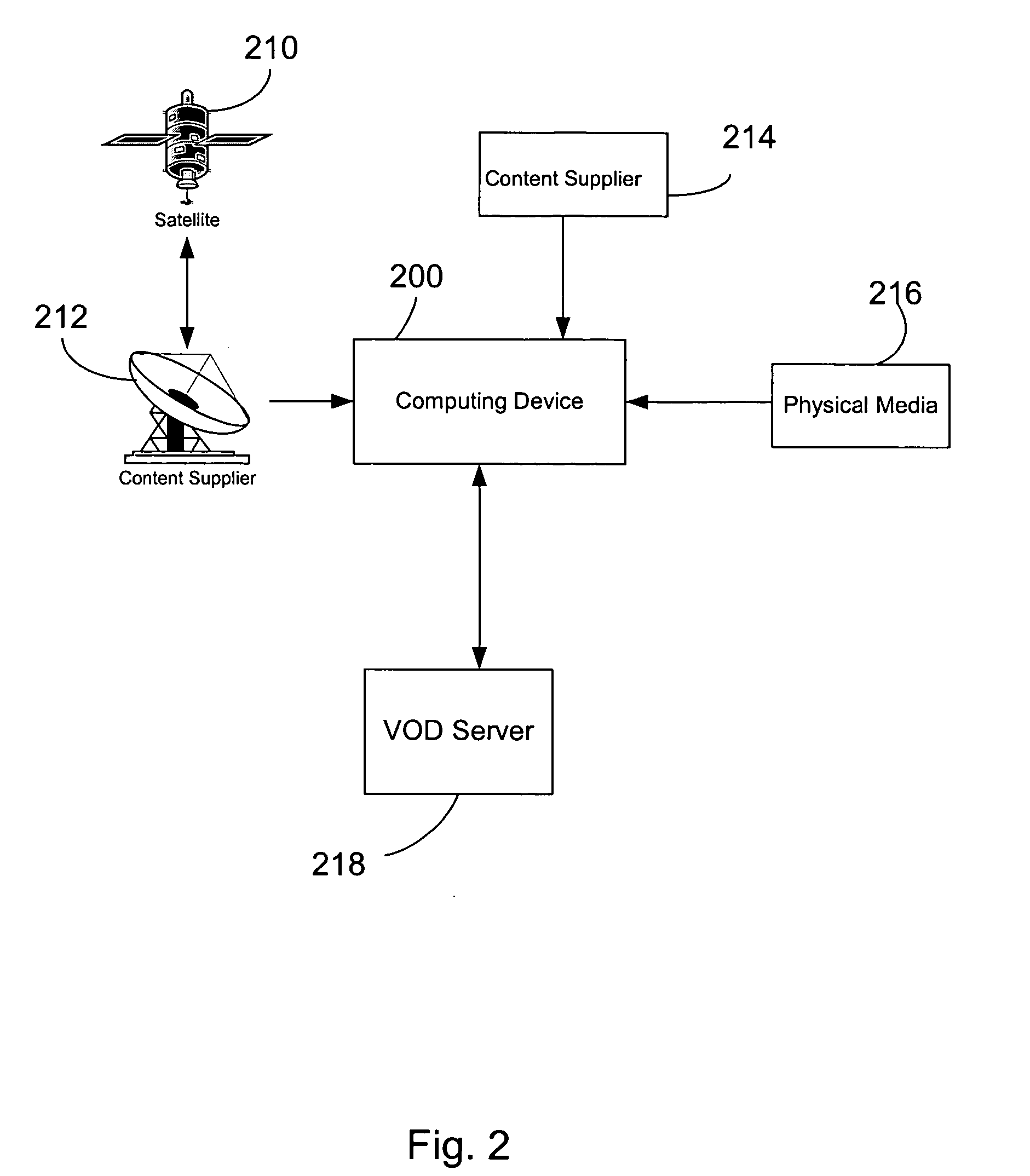
The present invention relates to a system (10) for generating and maintaining virtual and physical metadata layers in a MetaBase metadata repository (110b) in order to simplify and optimize the retrieval of data from a plurality of disparate information sources (130a-130c). The system stores in a physical metadata layer of a MetaBase metadata repository a plurality of physical metadata elements, wherein each one of the physical metadata elements corresponds to the metadata elements in the plurality of information sources. Logical metadata elements are stored in the virtual metadata layer and are linked to the physical metadata elements in order to maintain the relationships therebetween. By maintaining the relationships between the physical metadata elements, users can initiate a data query request for data corresponding to a logical metadata element, and the system is configurated to retrieve the desired data from the relevant information sources, even in the event that relevant information sources maintain the data in fields having different data field names, that the information sources employ incompatible data formats, and that the relevant information sources employ different query languages.
Owner:RED HAT
Role-based access to image metadata
InactiveUS6871231B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsMetadataMetadata element
A system and method for controlling access to image metadata is disclosed, where metadata elements are defined for an image. The method and system include associating users who will access the image with roles, and associating the roles with individual metadata elements. In response to receiving a request for access to the metadata by a particular user, the user's role is determined from the request and the user's role is compared to the roles associated with the metadata elements to determine which metadata elements to make available to the user.
Owner:IPAC SUB
Document/message management
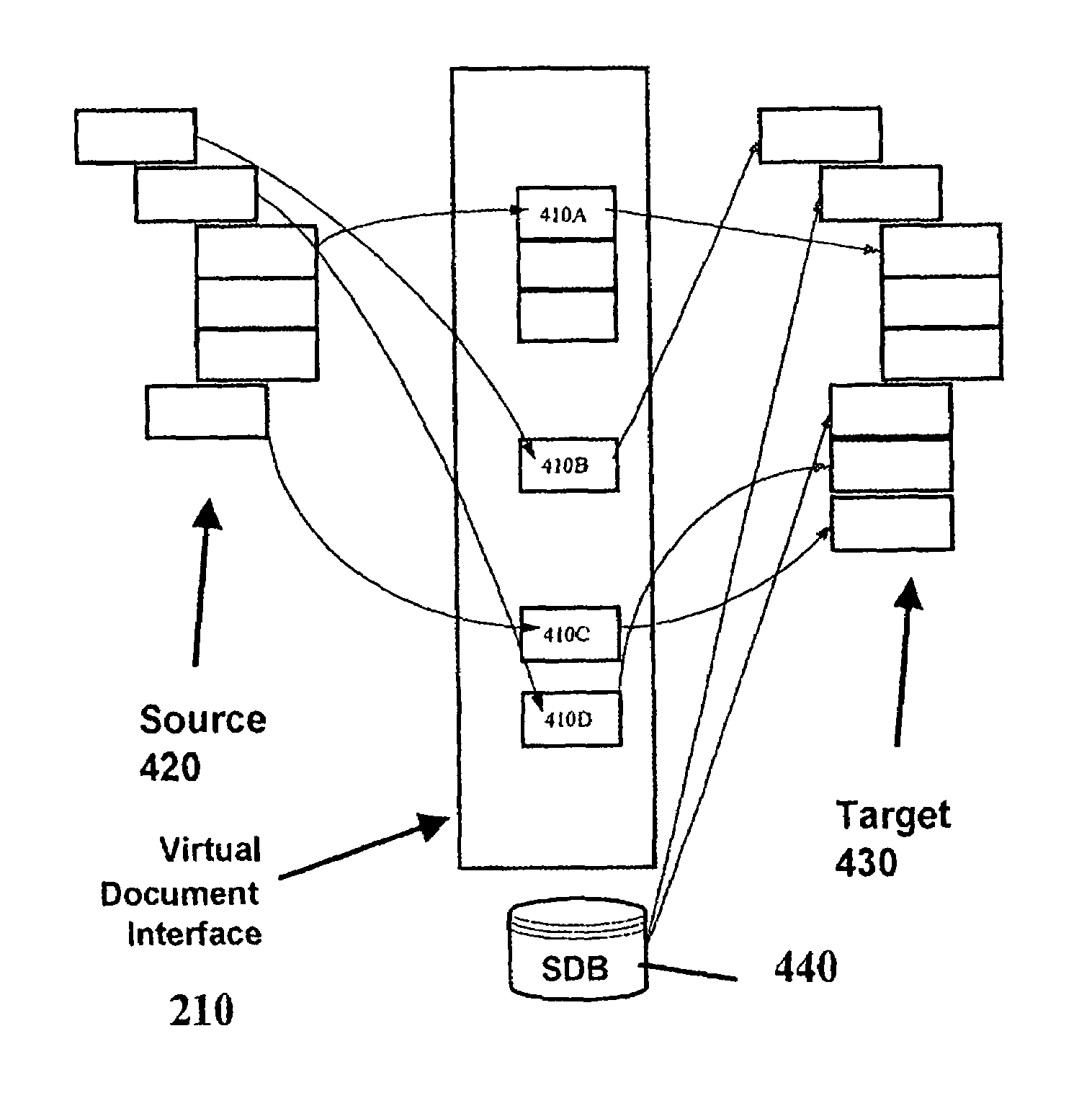
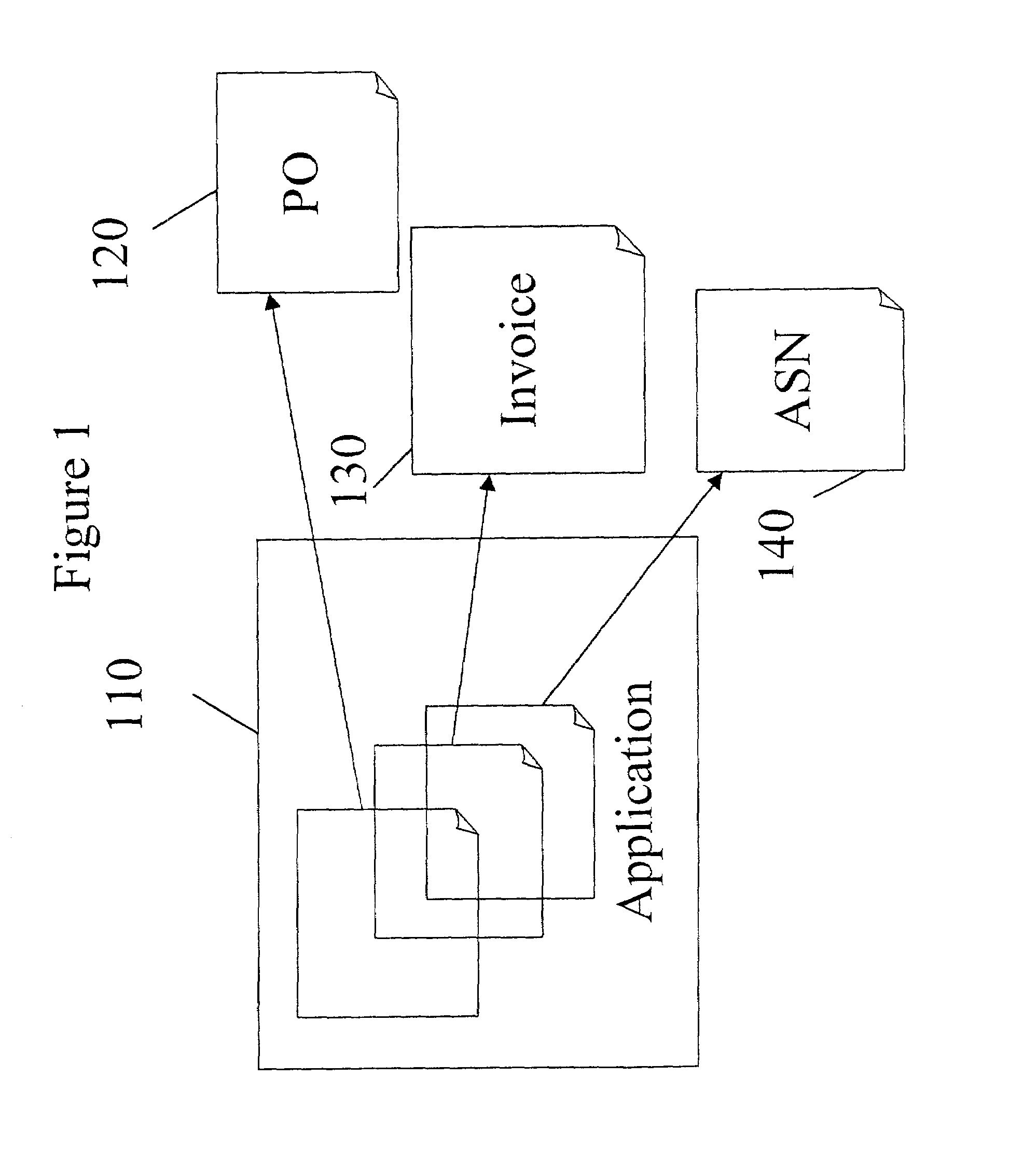
A computer implemented method, apparatus and software for automatically transforming data between Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) formats. For generating EDI documents or messages, a source data model with EDI related data is received. Data is transferred from metadata elements of the source data model to variables of a virtual document, based on a mapping that has been previously made. Data assigned to the variables of the virtual document are then transferred to metadata elements of a target data model. An EDI document or message corresponding to the target data model is automatically created as a result, which includes data from the source document or message.
Owner:FOOTHILL CAPITAL A CA +1
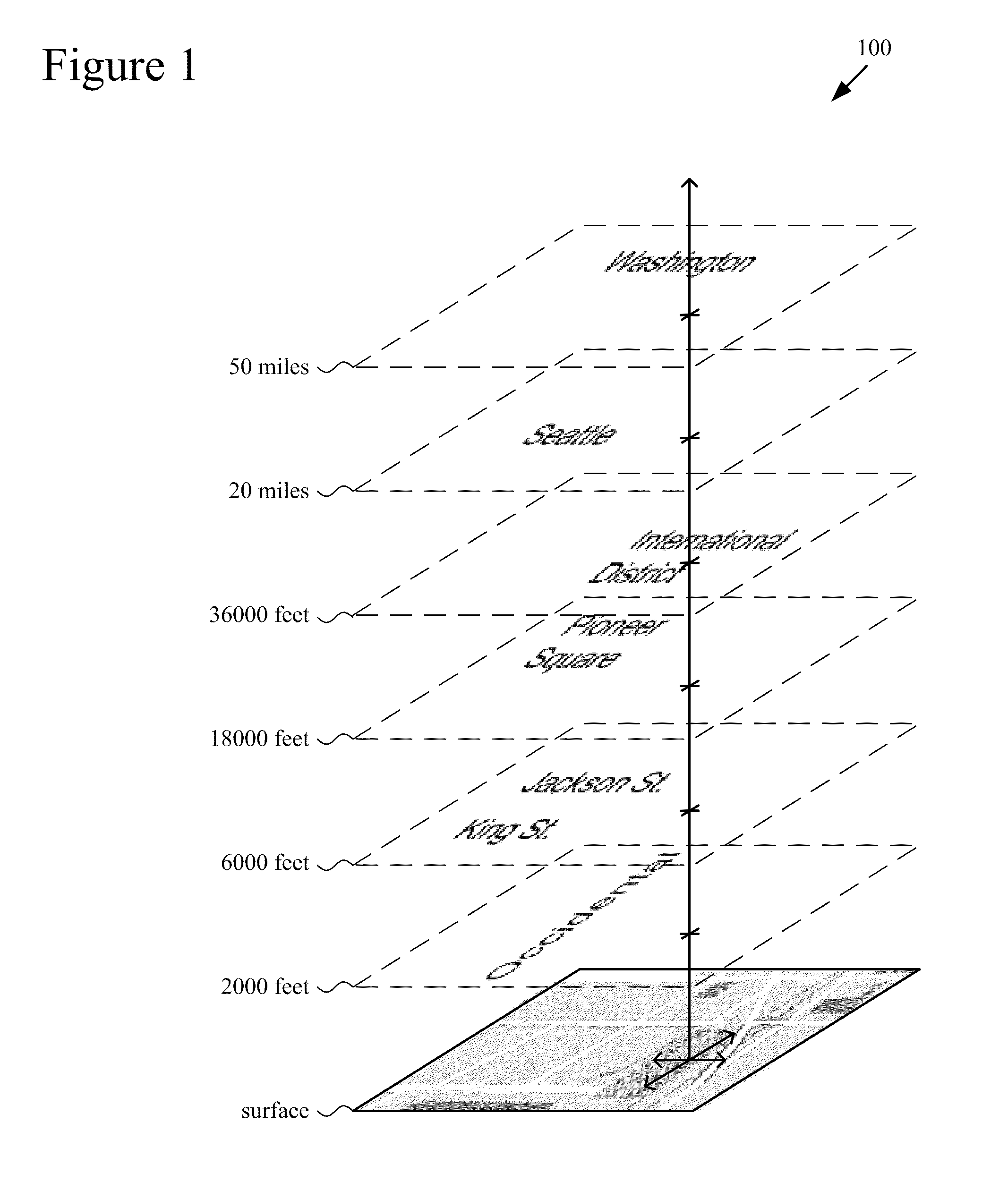
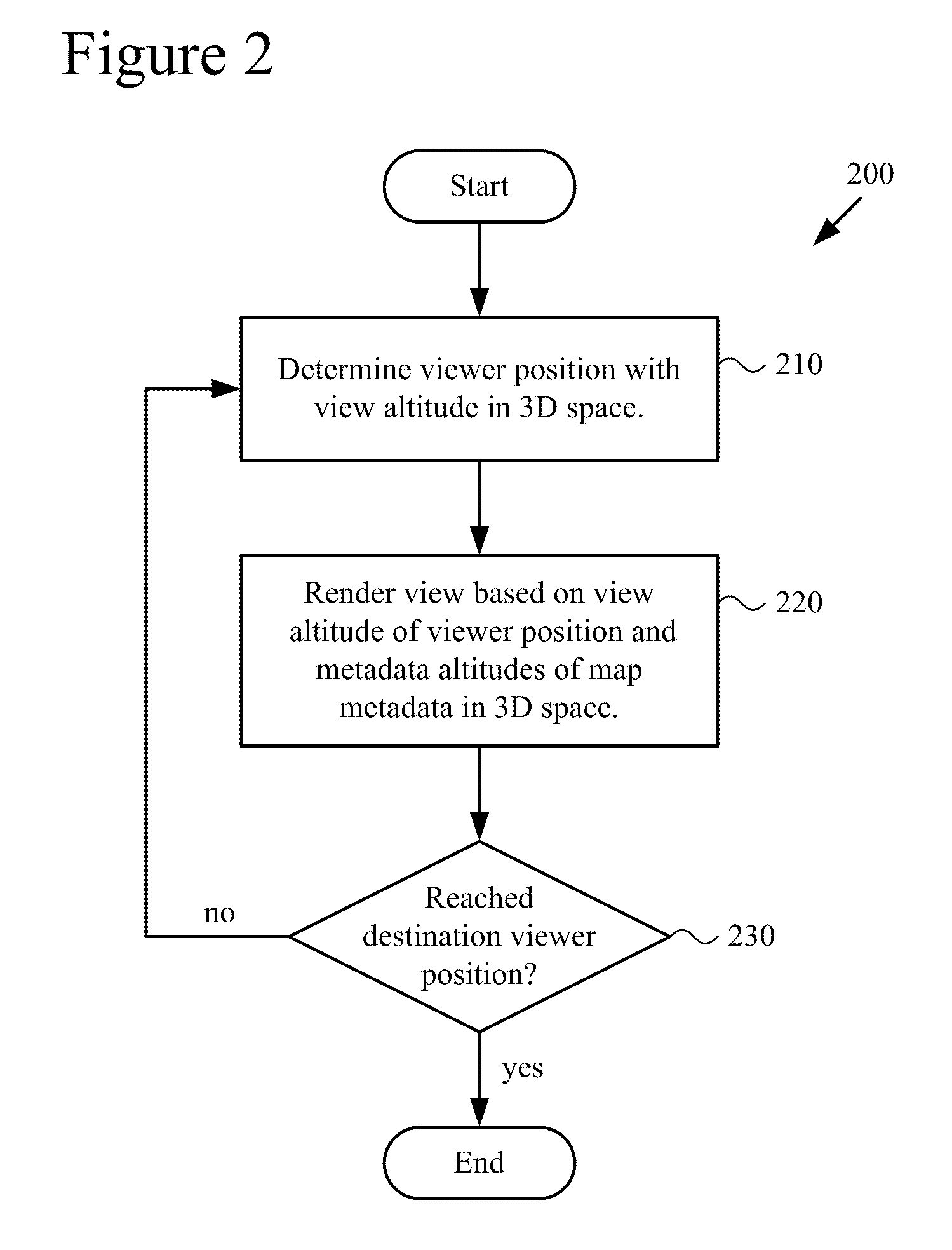
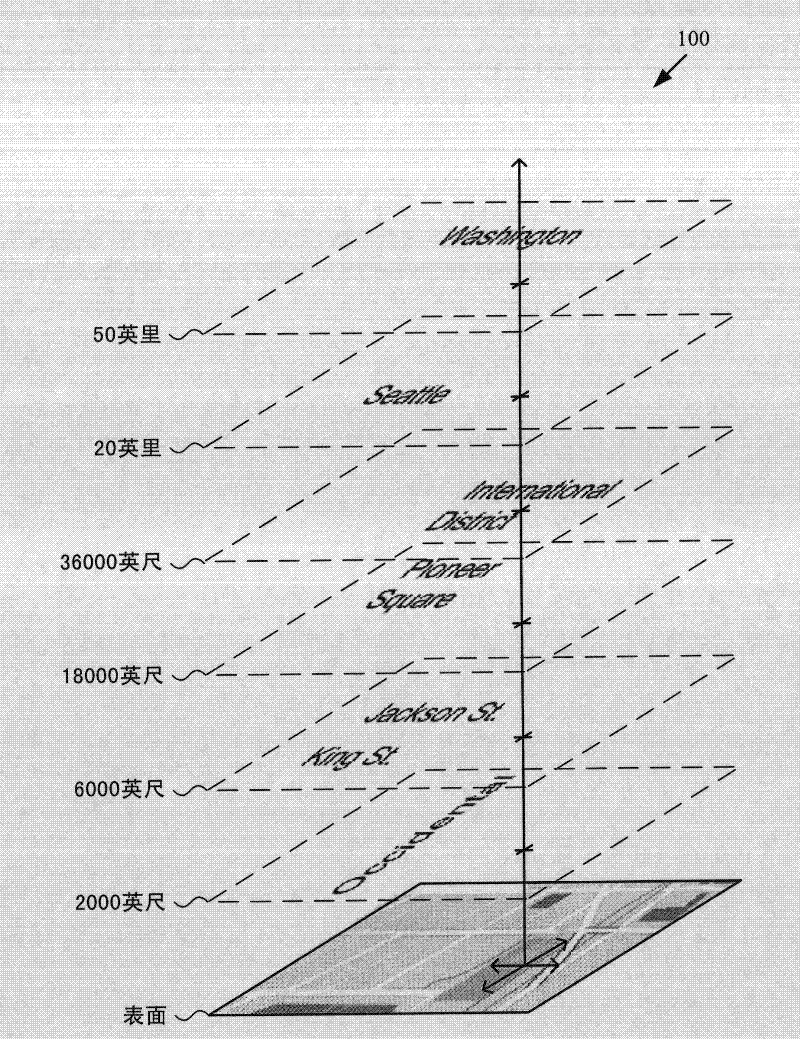
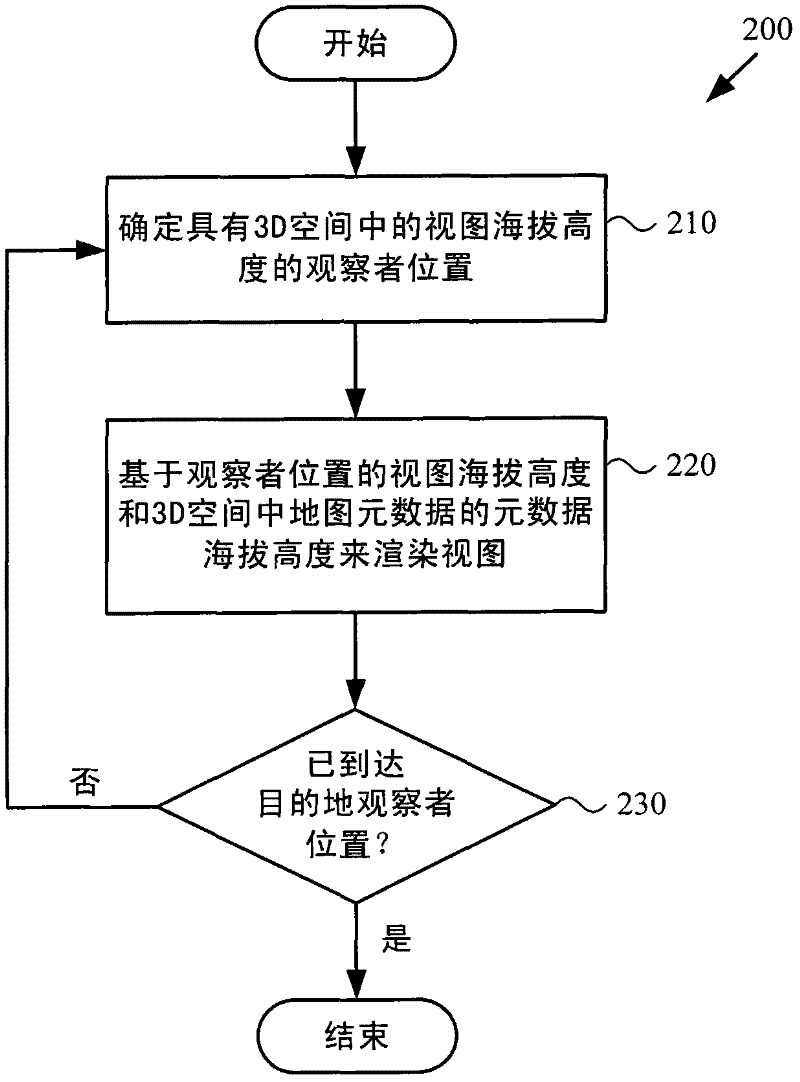
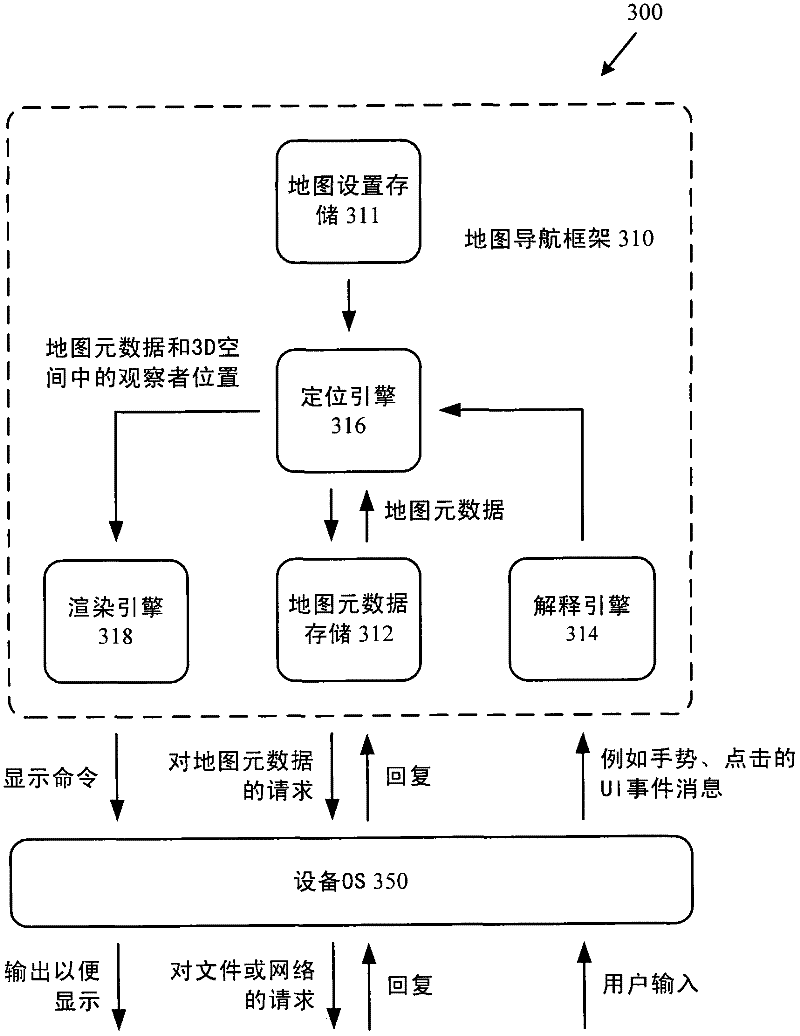
3D layering of map metadata
ActiveUS20120019513A1Good effectImprove experienceMaps/plans/chartsVehicle position indicationParallaxSurface layer
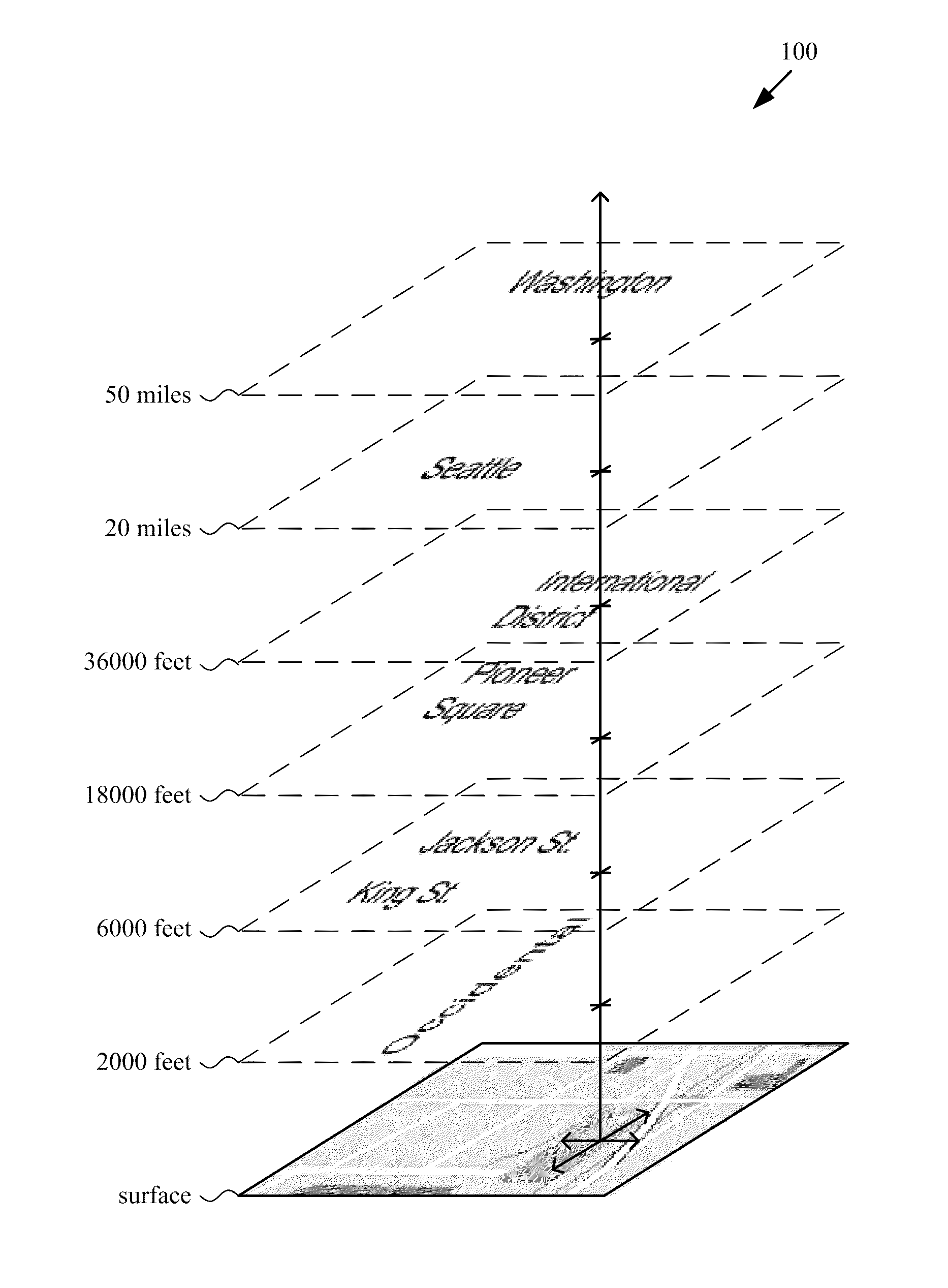
Techniques and tools are described for rendering views of a map in which map metadata elements are layered in 3D space through which a viewer navigates. Layering of metadata elements such as text labels in 3D space facilitates parallax and smooth motion effects for zoom-in, zoom-out and scrolling operations during map navigation. A computing device can determine a viewer position that is associated with a view altitude in 3D space, then render for display a map view based upon the viewer position and metadata elements layered at different metadata altitudes in 3D space. For example, the computing device places text labels in 3D space above features associated with the respective labels, at the metadata altitudes indicated for the respective labels. The computing device creates a map view from points of the placed labels and points of a surface layer of the map that are visible from the viewer position.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
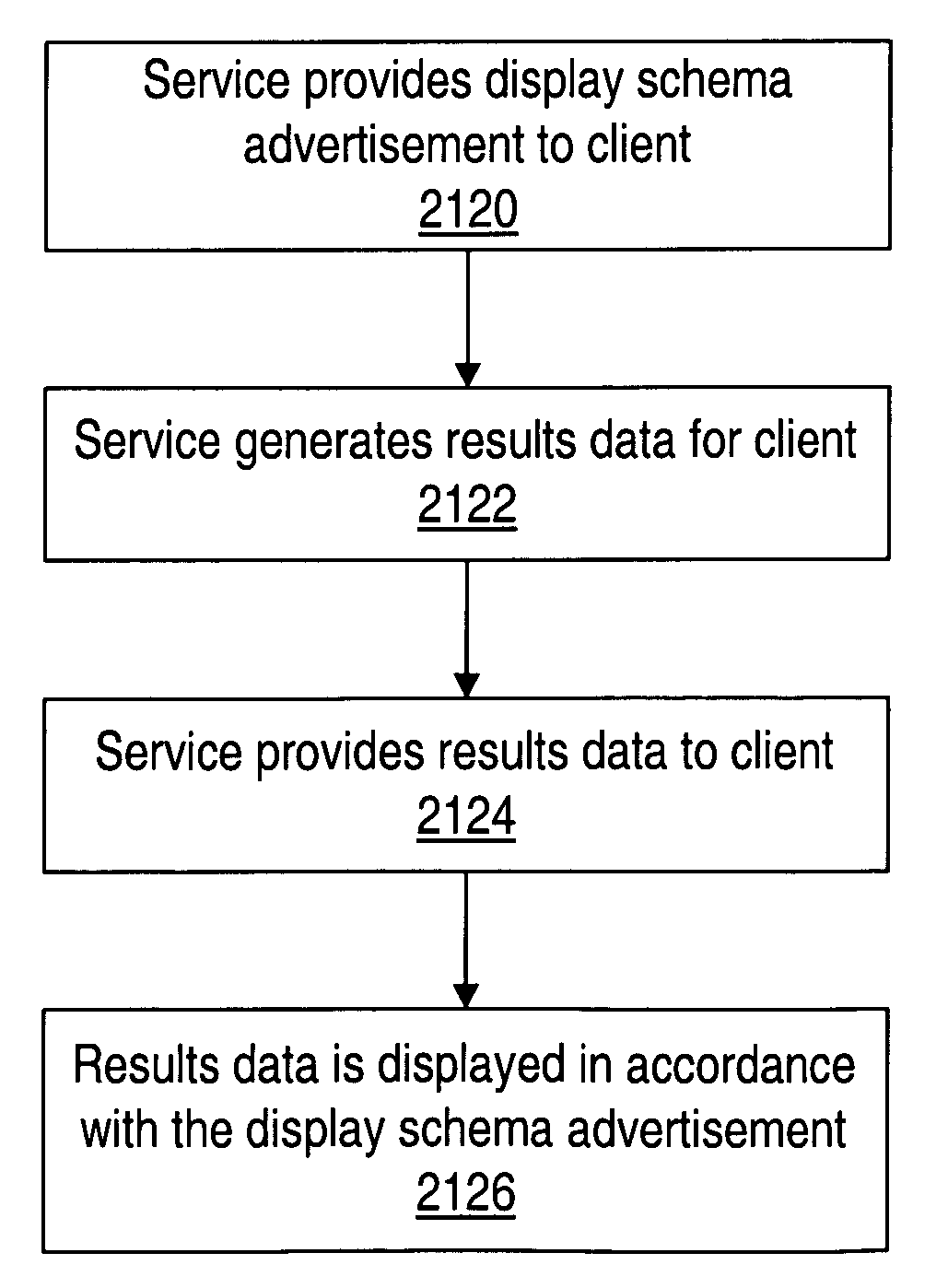
Dynamic displays in a distributed computing environment
ActiveUS8082491B1Application behavior may be alteredWeb data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed Computing EnvironmentClient-side
A mechanism for describing dynamic display objects in a distributed computing environment is described. A service in a distributed computing environment may generate results data for a client in response to client requests. The service may provide schemas describing the presentation characteristics of results data. The schemas may include information for use in presenting the results data. The results data may include data elements, and the presentation schema may include presentation elements each including information describing the presentation characteristics of one or more of the data elements. The client may map data elements to corresponding presentation elements from the schema, and may use the element corresponding to a data element to present the data element. Using the dynamic display objects, display behavior may be altered without having to rebuild code.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for generating consistent user interfaces
InactiveUS7873908B1Software engineeringInput/output processes for data processingData validationSource Data Verification
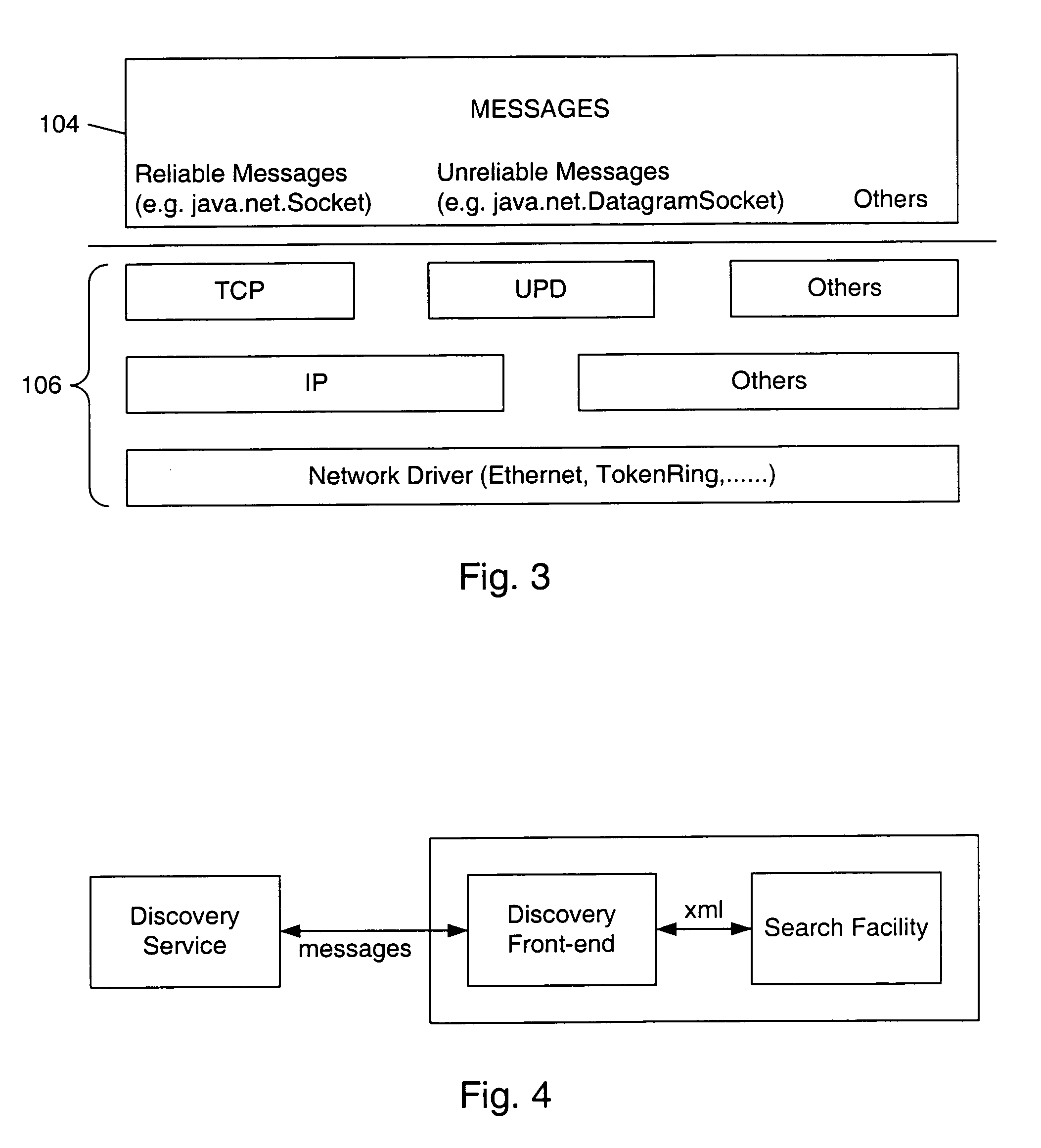
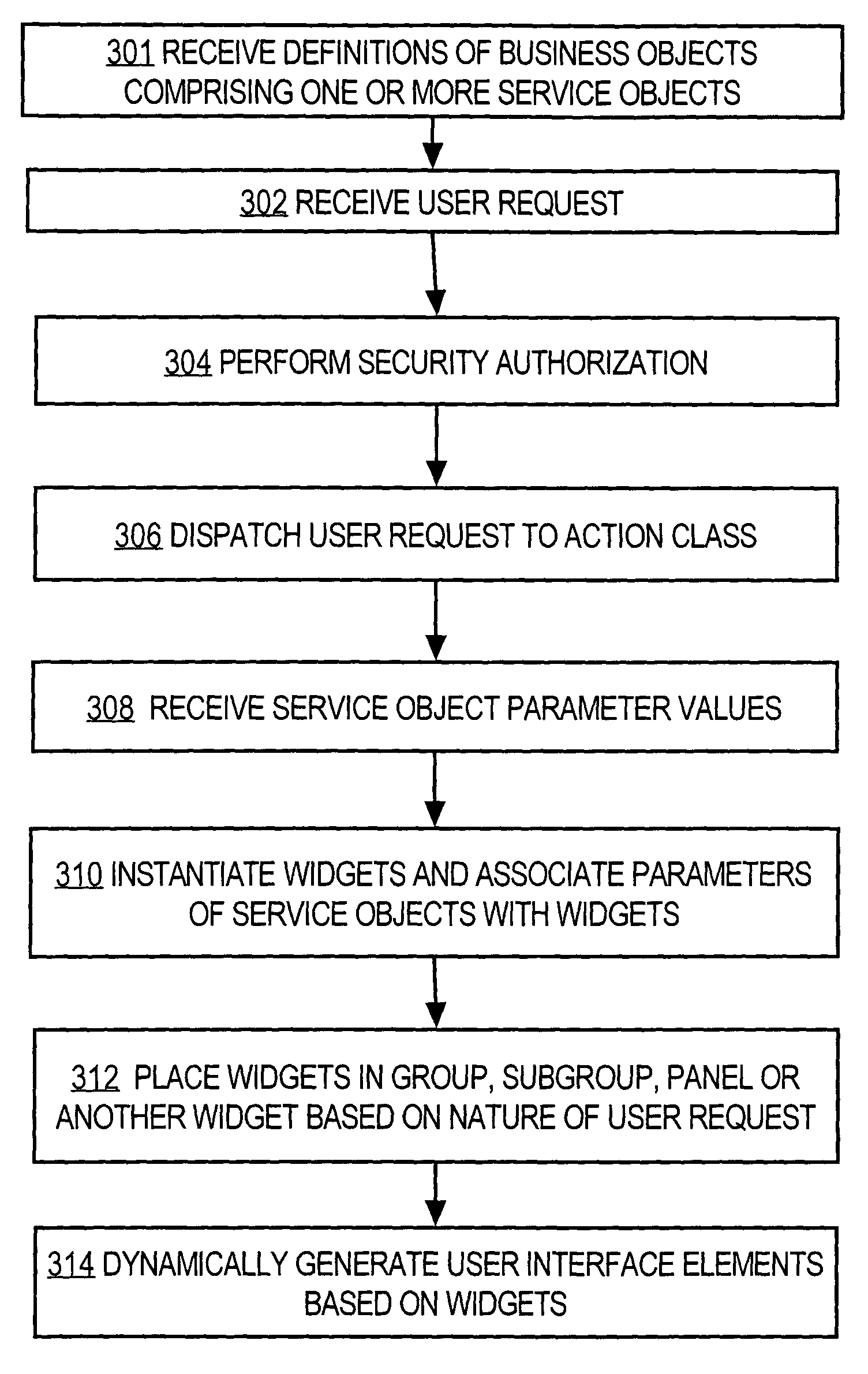
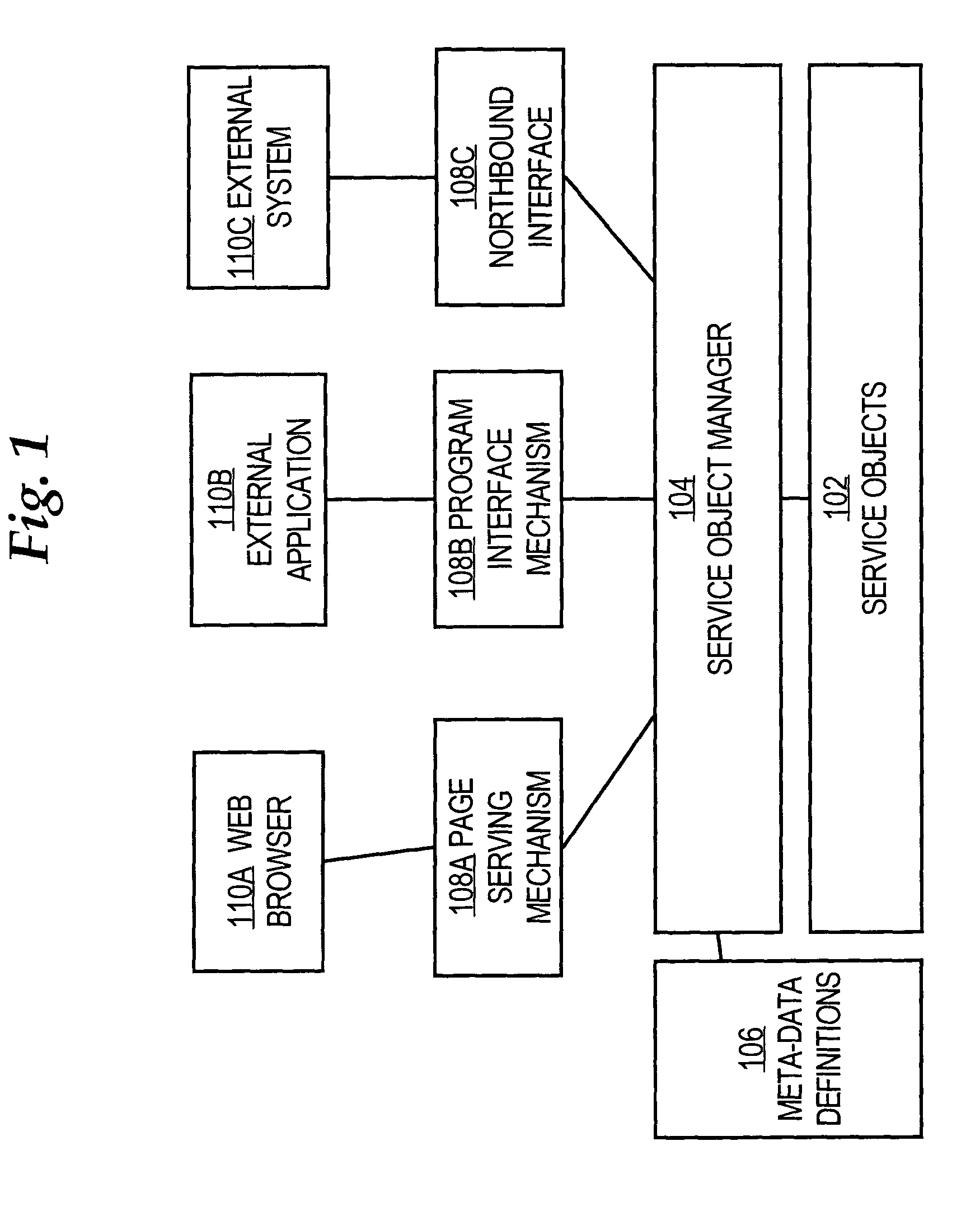
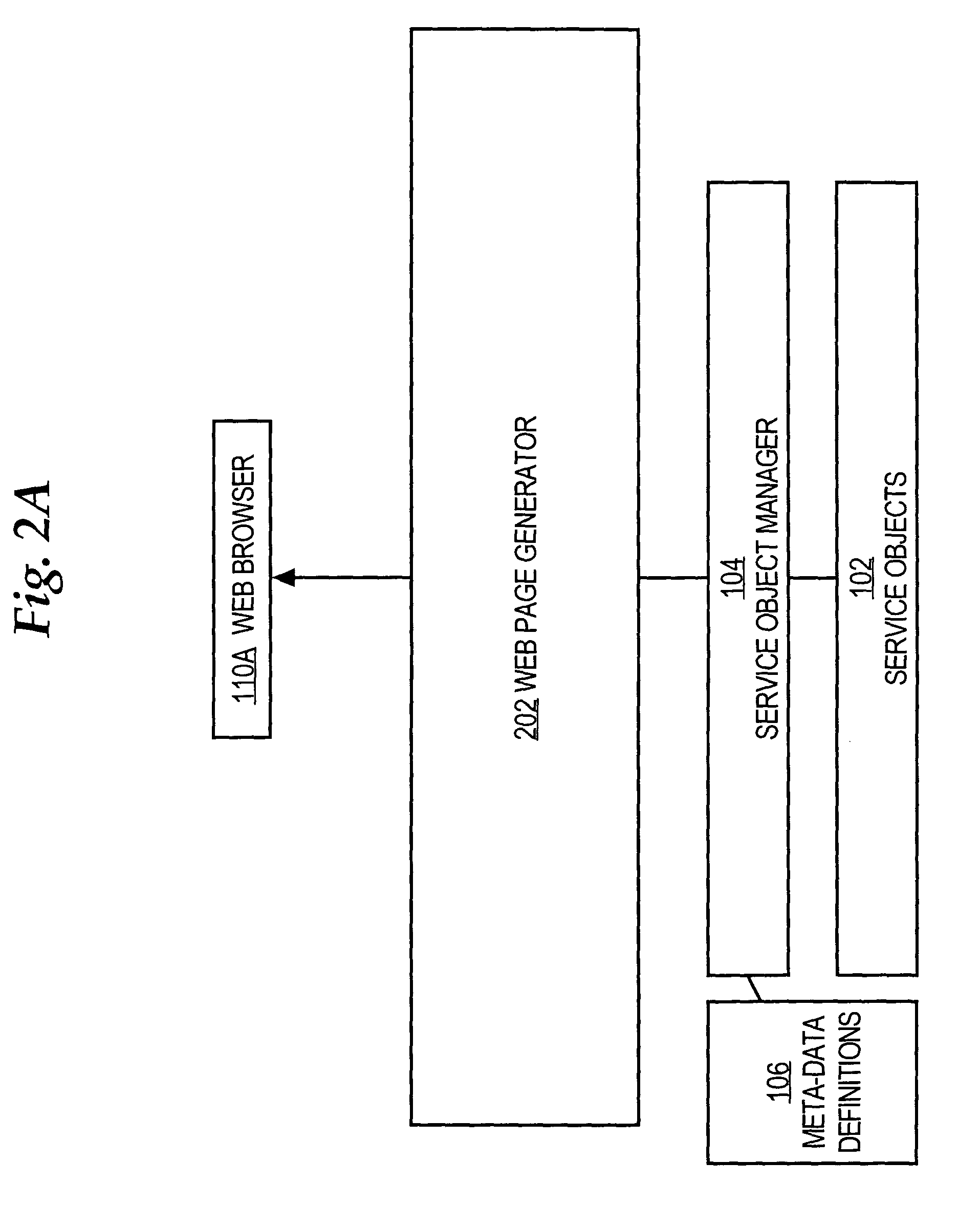
A method is disclosed for generating a consistent user interface for an HTML-based application program, without extensive coding of Java Server Pages and other elements. In one approach, business objects each define a user action for the application program, and metadata elements defining parameters for the user actions of the business object. A controller is communicatively coupled to one or more actions, widgets, and panels. A user request is received from a browser and dispatched to one or the actions. Using the actions, one or more parameter values are obtained from the business objects. The business object parameter values are associated with a widget selected from among the one or more widgets. The selected widget is associated with a panel selected from the one or more panels. An HTML user interface page that includes the selected panel is generated. The widgets represent properties of the business objects as HTML elements, automatically generate client-side executable code for performing data validation, and convert values received in users requests into programmatic objects of appropriate data types for use by the application program.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
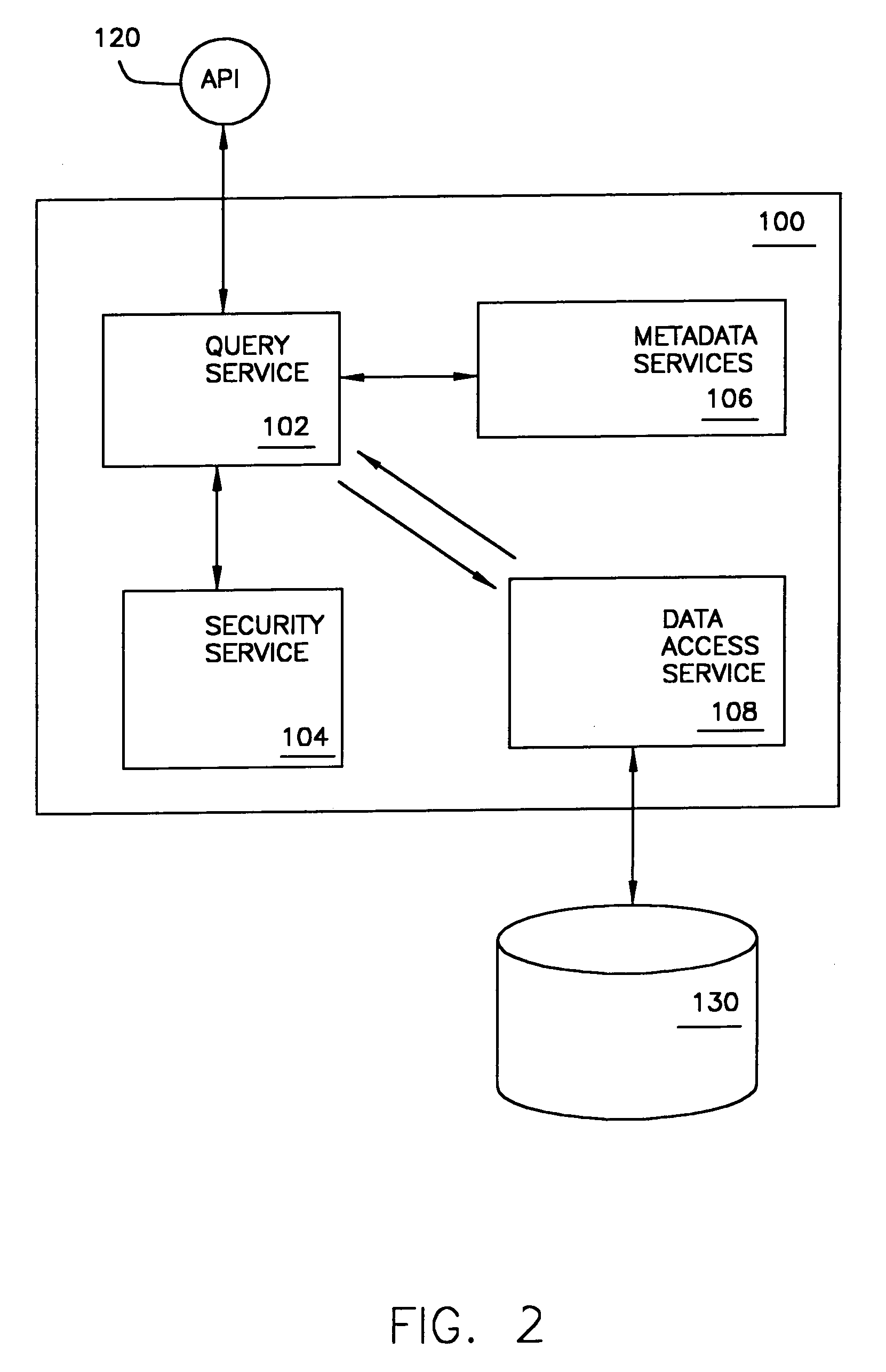
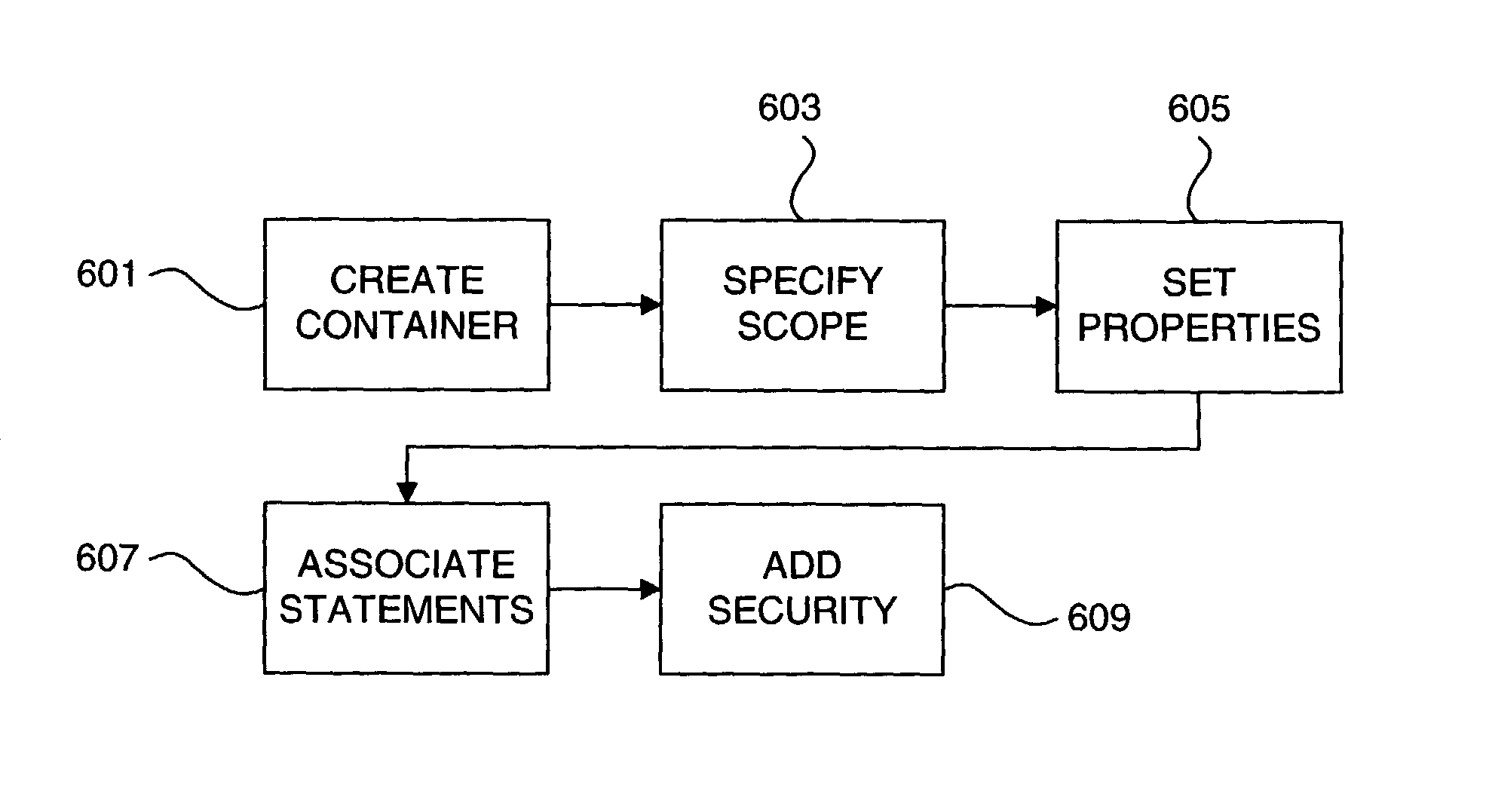
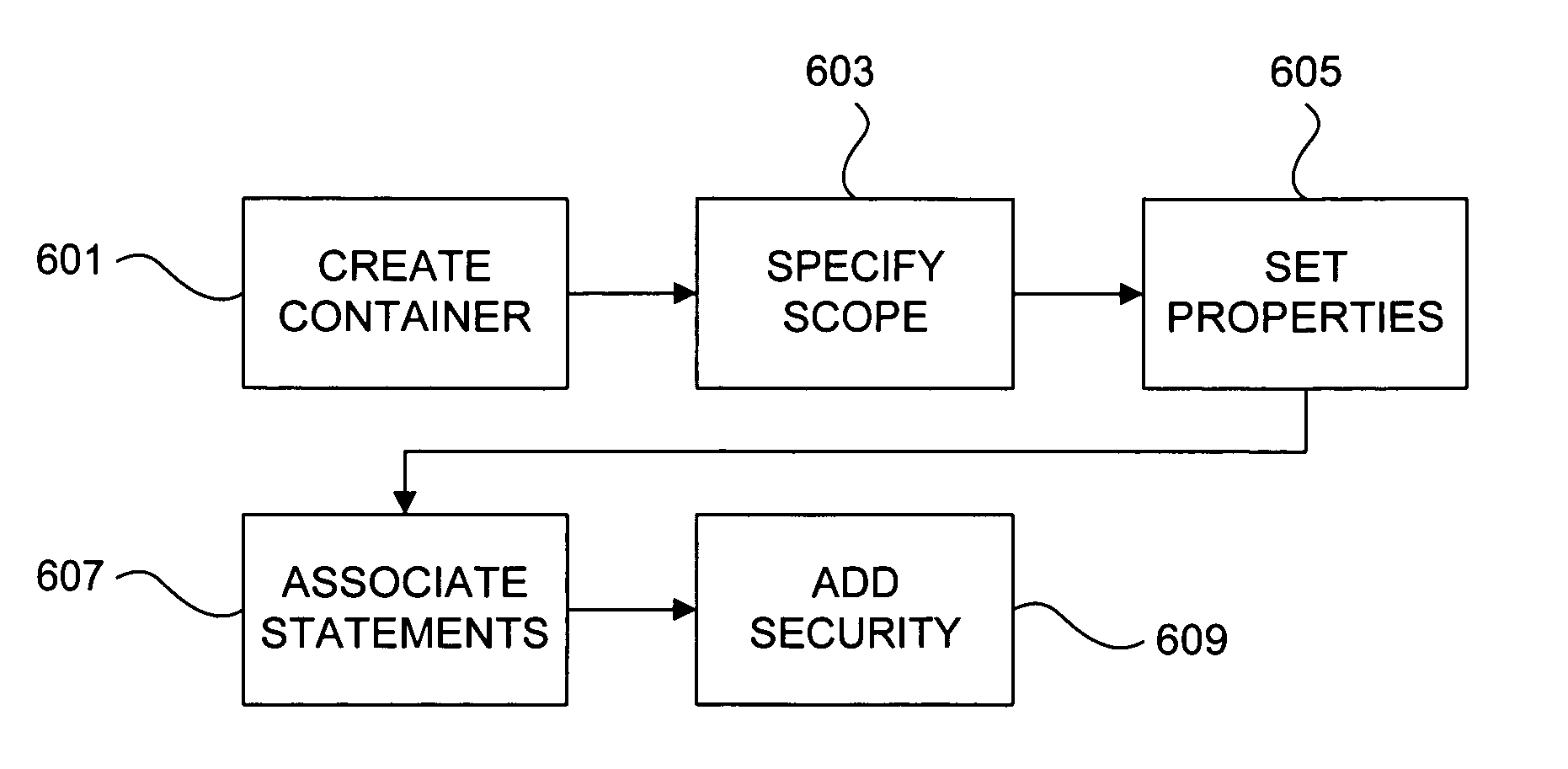
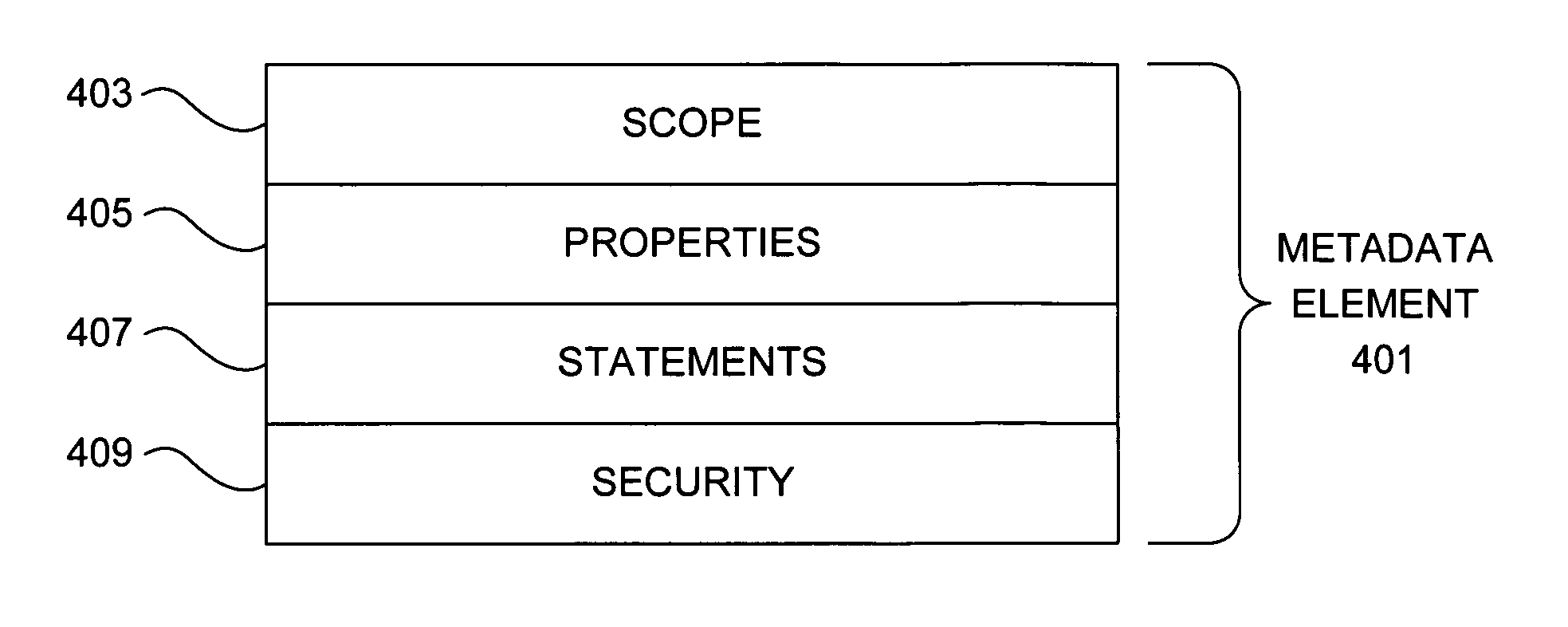
Scoped access control metadata element
Methods, systems, and data structures for communicating object metadata are provided. A generic metadata container is presented that allows object metadata to be described in an extensible manner using protocol-neutral and platform-independent methodologies. A metadata scope refers to a dynamic universe of targets to which the included metadata statements correspond. Metadata properties provide a mechanism to describe the metadata itself, and metadata security can be used to ensure authentic metadata is sent and received. Mechanisms are also provided to allow refinement and replacement of metadata statements. The generic metadata container can be adapted to dynamically define access control rights to a range of objects by a range of users, including granted and denied access rights.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
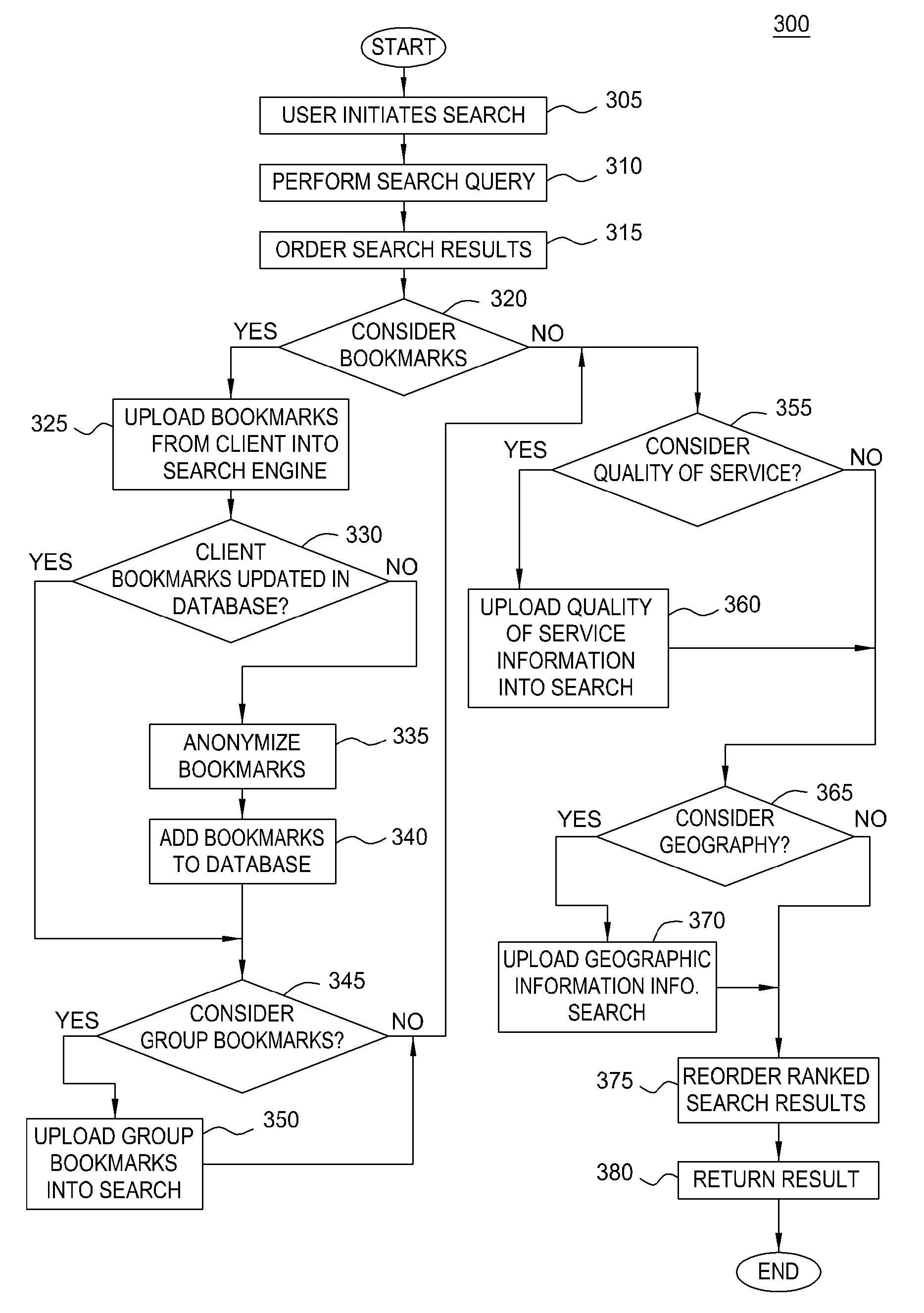
Enhancing and optimizing enterprise search
ActiveUS20090132516A1Increase heightDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsWeb siteRanking
Embodiments of the invention improve the quality of search results returned for a given set of search terms based on metadata associated with the user performing the search. A search query may specify metadata elements to consider in ranking the search results. The metadata used may include bookmarks set by the user (either locally or at a social bookmaking site), group bookmarks, etc. In such a case, search results may be reordered to improve the ranking of websites that are both in the search results and in the bookmarks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mapping binary objects in extended relational database management systems with relational registry
InactiveUS6502086B2Small footprintReduce maintenanceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData processing systemAutomated data processing
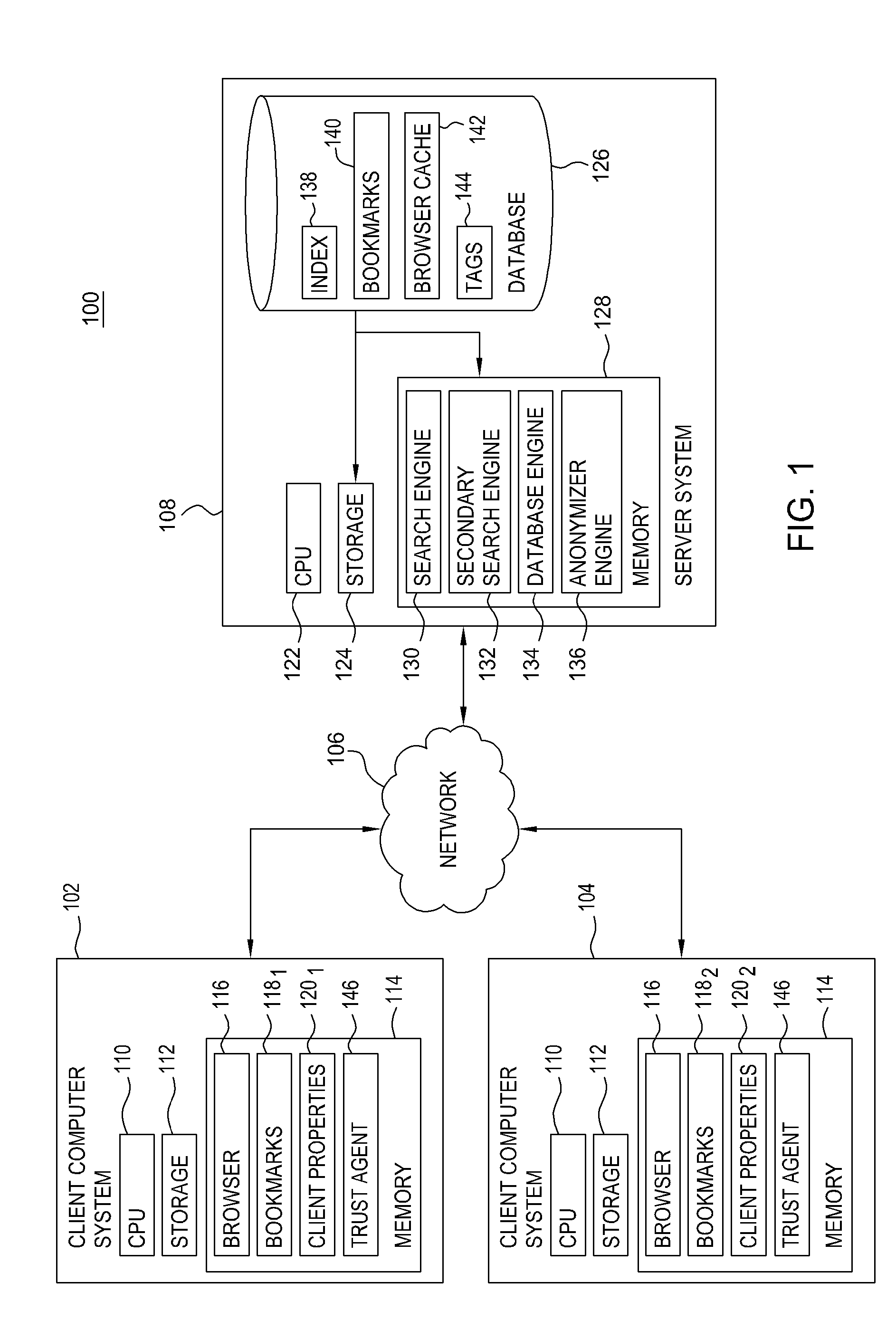
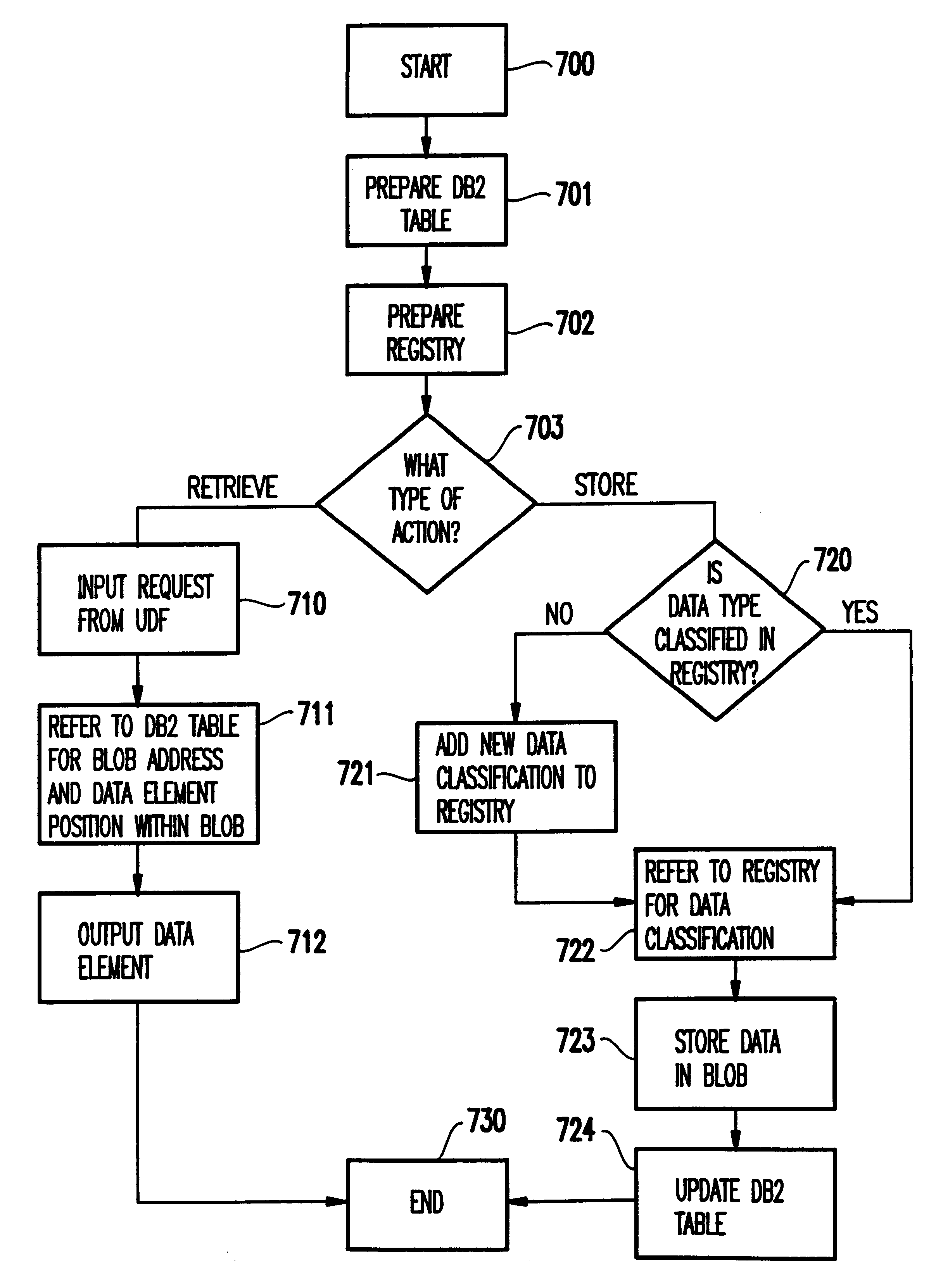
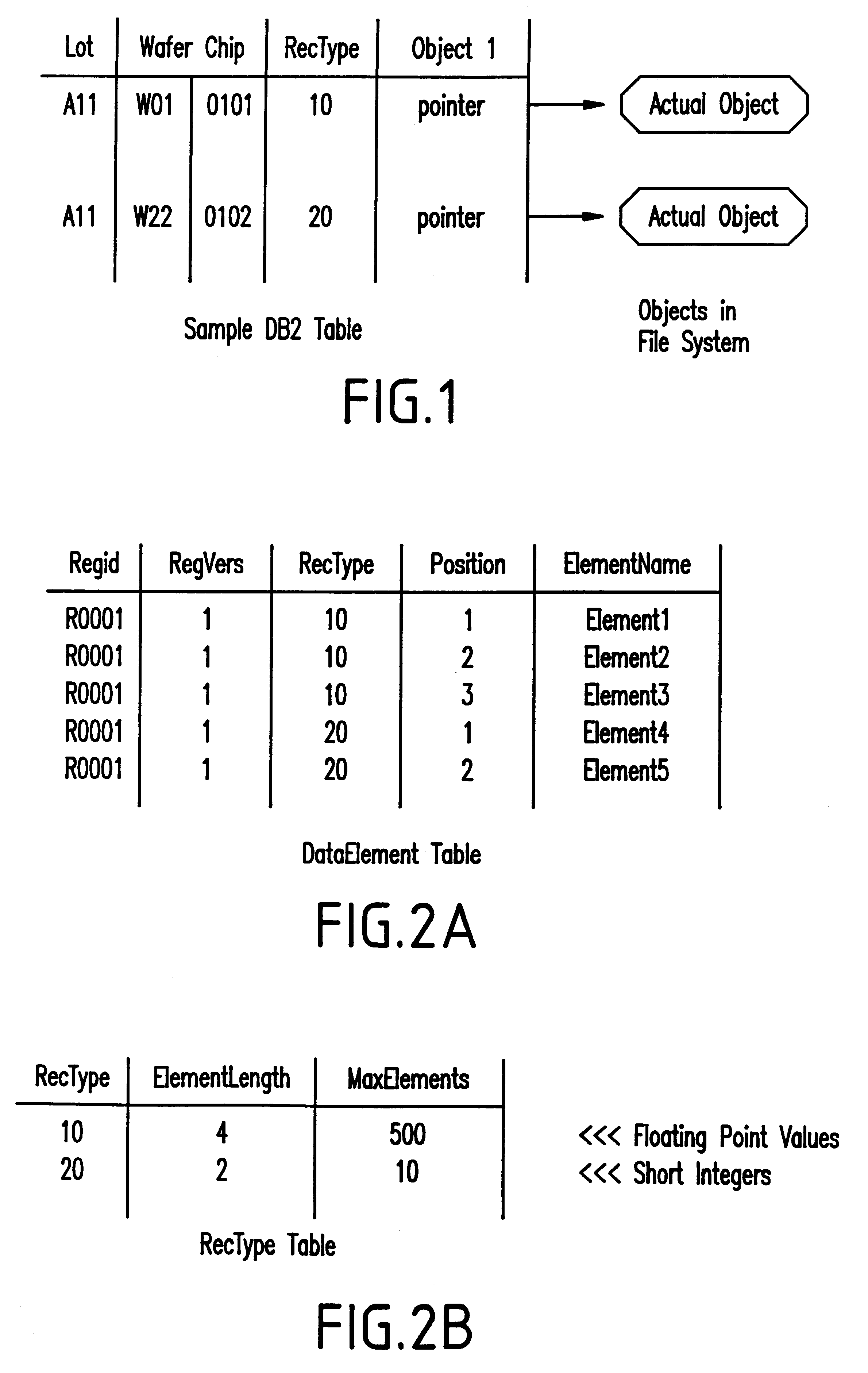
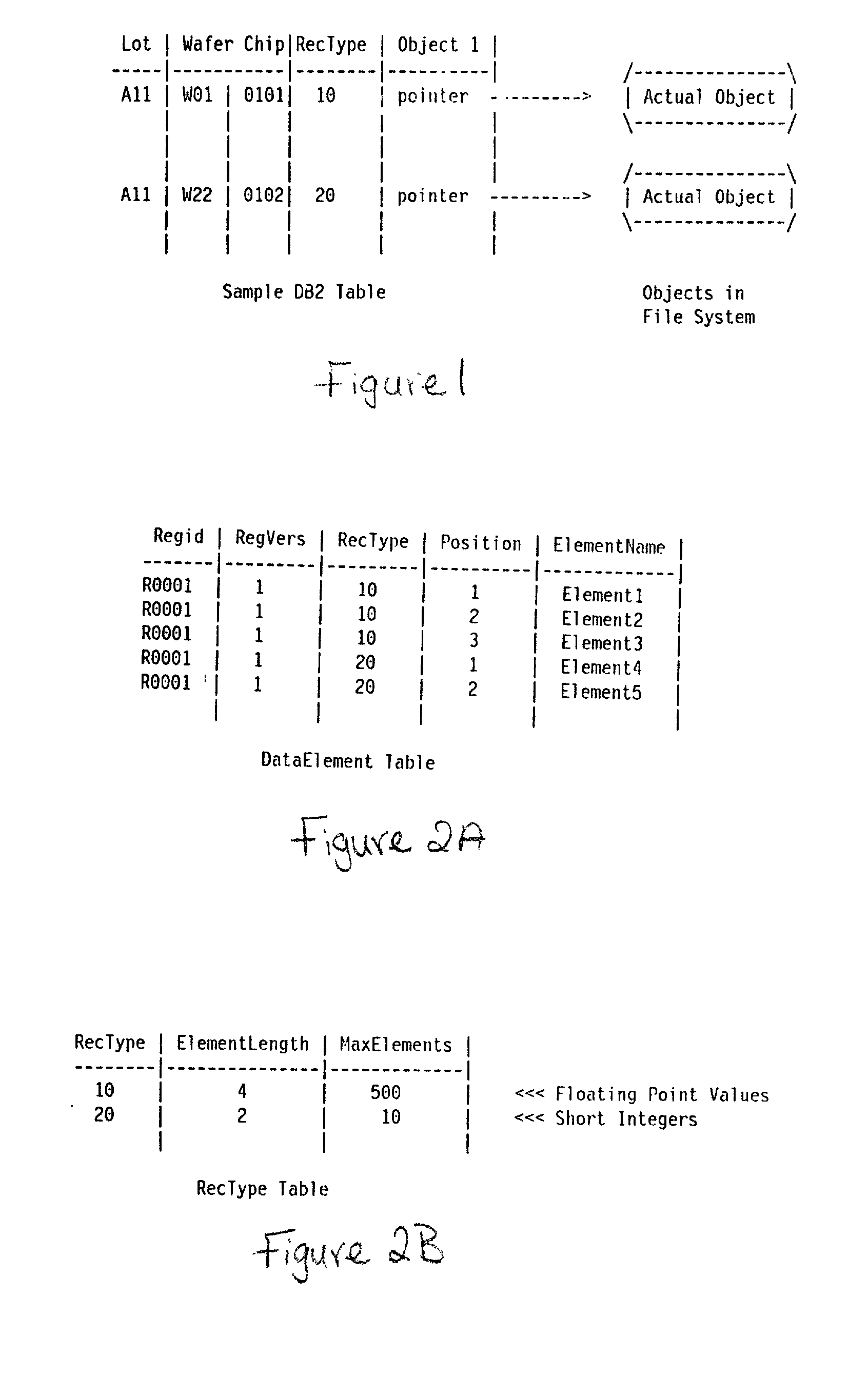
An automated data processing system includes a relational database engine, storage devices having a database table, registry and binary large objects created and updated by the relational database engine and a user defined function engine retrieving data elements stored in the binary large objects. The registry includes data element classifications. The database table includes relational information of the data elements, the data element classifications and pointers to the binary large objects, and the relational database engine creates and updates the binary large objects based on the database table and the registry.
Owner:IBM CORP
Document archiving system
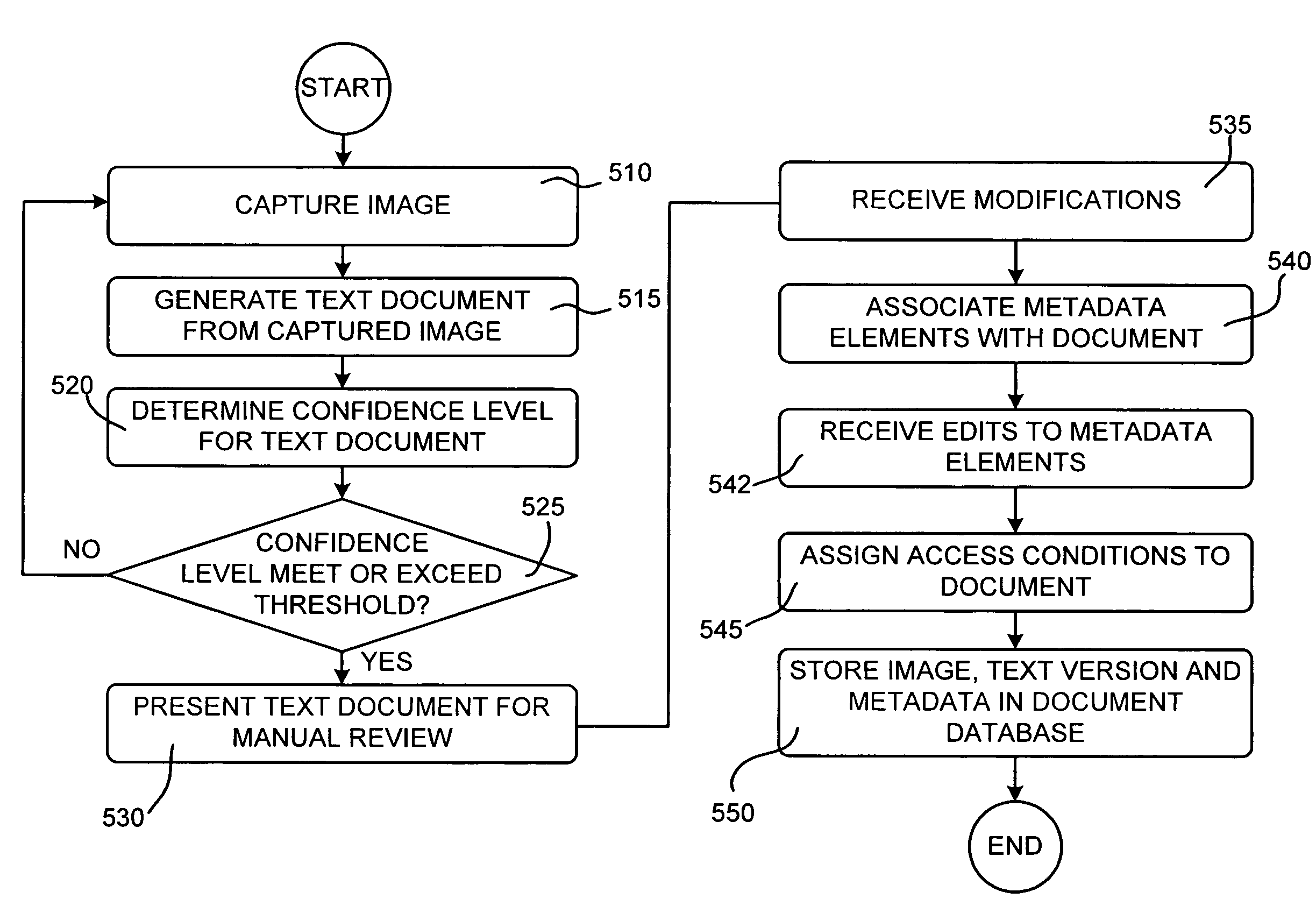
InactiveUS20080162603A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsDocument preparationDocumentation
A system generates a text document from a received document image. Metadata elements may be assigned to all or part of the text document by a user or by a template used to generate the text document. The text document and the associated metadata elements may be stored to facilitate subsequent searching and retrieval of the text document or the document image based on contents of the text document and / or its associated metadata elements.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Scoped access control metadata element
Methods, systems, and data structures for communicating object metadata are provided. A generic metadata container is presented that allows object metadata to be described in an extensible manner using protocol-neutral and platform-independent methodologies. A metadata scope refers to a dynamic universe of targets to which the included metadata statements correspond. Metadata properties provide a mechanism to describe the metadata itself, and metadata security can be used to ensure authentic metadata is sent and received. Mechanisms are also provided to allow refinement and replacement of metadata statements. The generic metadata container can be adapted to dynamically define access control rights to a range of objects by a range of users, including granted and denied access rights.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Dynamic Displays in a Distributed Computing Environment
InactiveUS20120079368A1Application behavior may be alteredWeb data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed Computing EnvironmentClient-side
A mechanism for describing dynamic display objects in a distributed computing environment is described. A service in a distributed computing environment may generate results data for a client in response to client requests. The service may provide schemas describing the presentation characteristics of results data. The schemas may include information for use in presenting the results data. The results data may include data elements, and the presentation schema may include presentation elements each including information describing the presentation characteristics of one or more of the data elements. The client may map data elements to corresponding presentation elements from the schema, and may use the element corresponding to a data element to present the data element. Using the dynamic display objects, display behavior may be altered without having to rebuild code.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for accessing data in disparate information sources
InactiveUS20100114952A1Metadata text retrievalData processing applicationsRelevant informationData retrieval
The present invention relates to a system (10) for generating and maintaining virtual and physical metadata layers in a MetaBase metadata repository (110b) in order to simplify and optimize the retrieval of data from a plurality of disparate information sources (130a-130c). The system stores in a physical metadata layer of a MetaBase metadata repository a plurality of physical metadata elements, wherein each one of the physical metadata elements corresponds to the metadata elements in the plurality of information sources. Logical metadata elements are stored in the virtual metadata layer and are linked to the physical metadata elements in order to maintain the relationships therebetween. By maintaining the relationships between the physical metadata elements, users can initiate a data query request for data corresponding to a logical metadata element, and the system is configurated to retrieve the desired data from the relevant information sources, even in the event that relevant information sources maintain the data in fields having different data field names, that the information sources employ incompatible data formats, and that the relevant information sources employ different query languages.
Owner:RED HAT
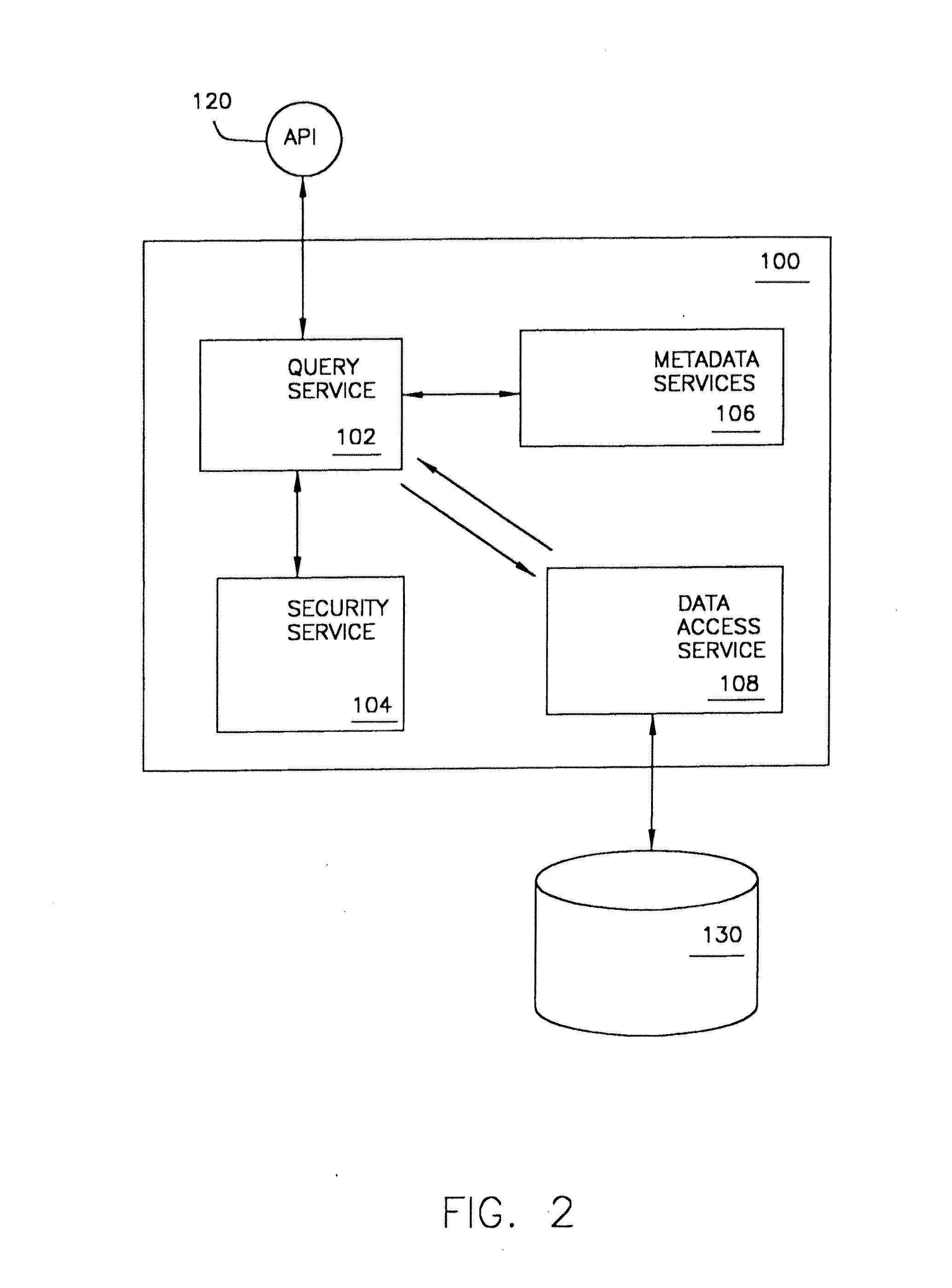
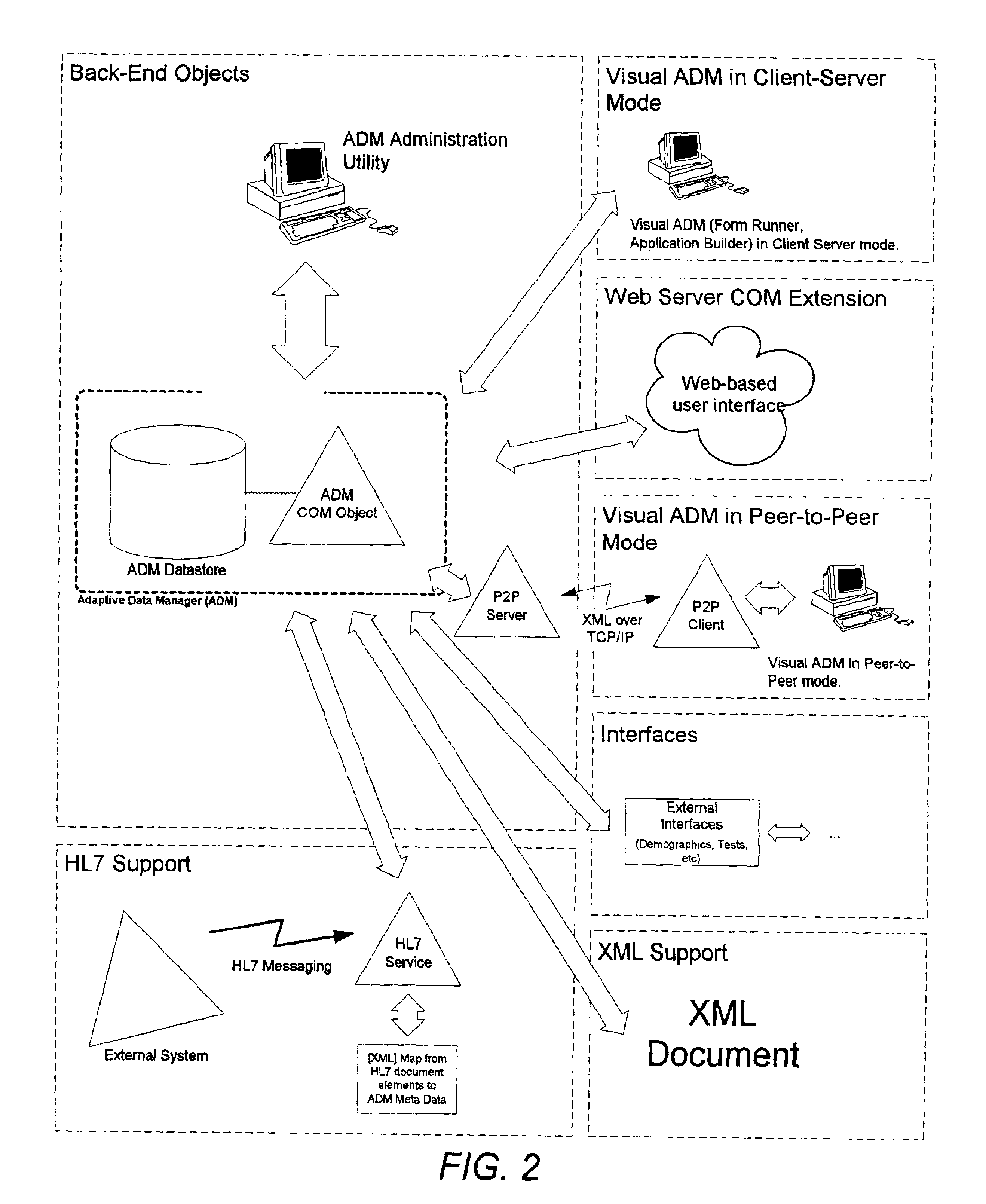
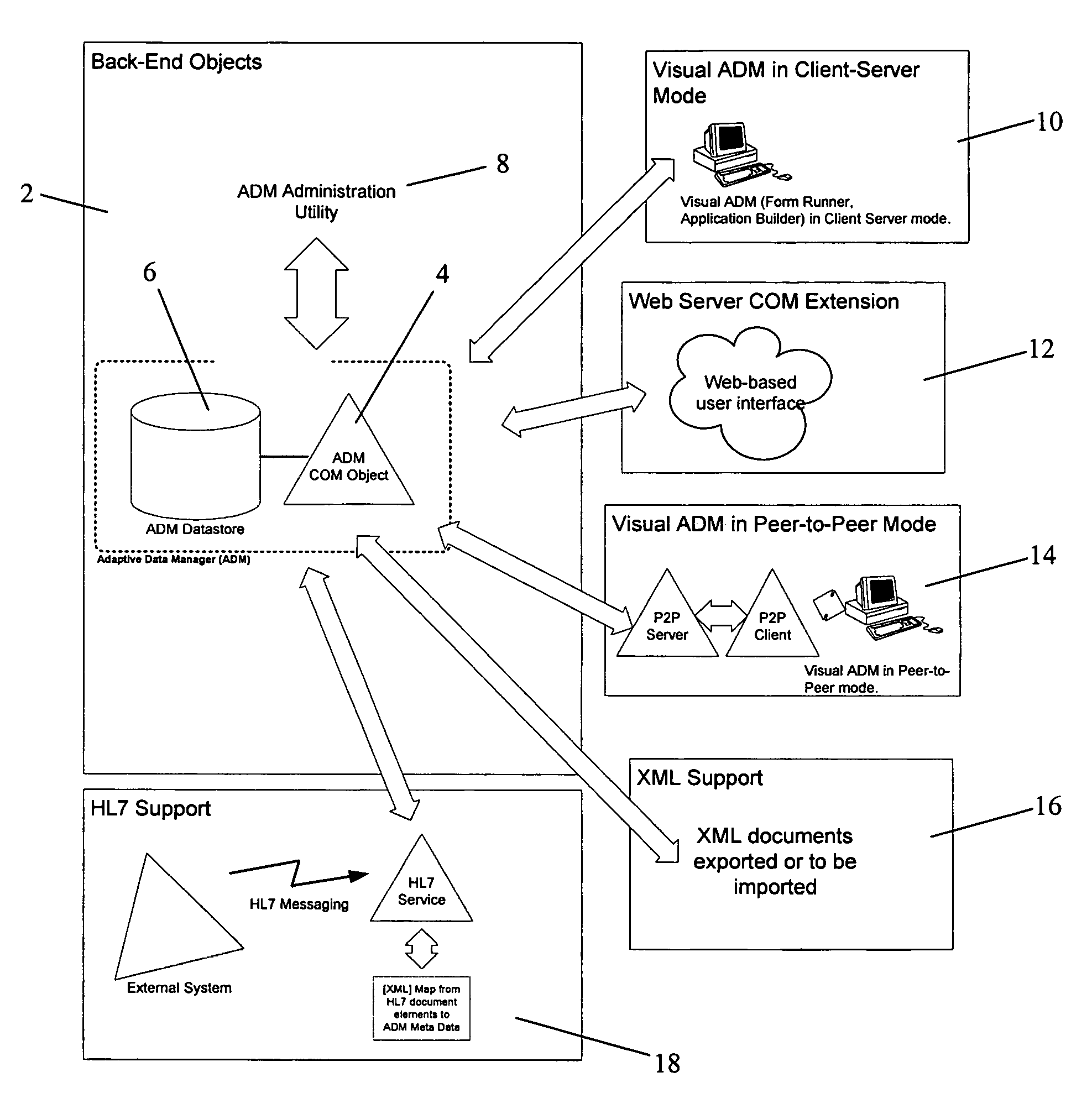
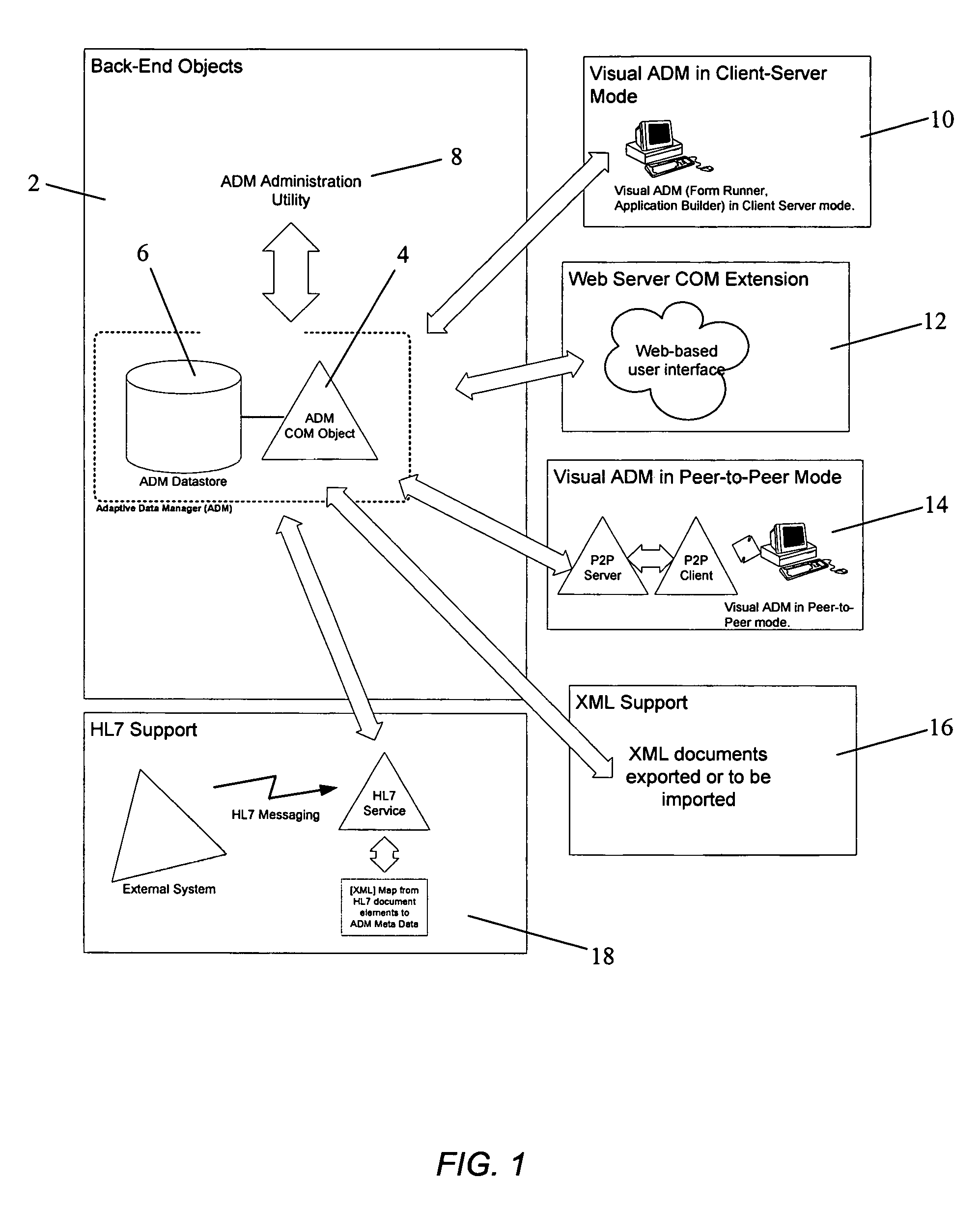
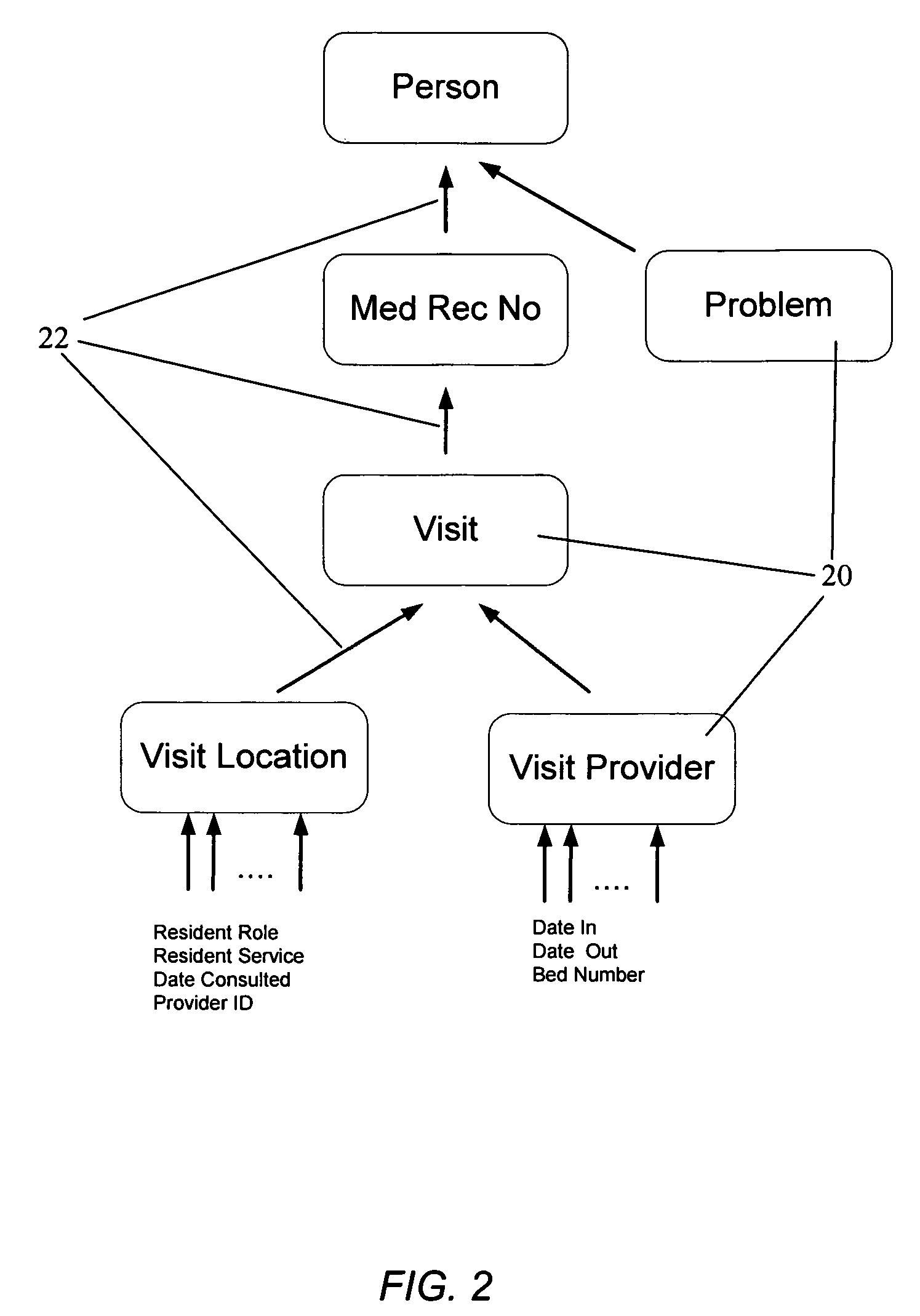
Adaptive data manager
ActiveUS6904432B2Simplify the development processSuitable for implementationData processing applicationsDatabase management systemsRelational databaseComputerized system
A method for managing a back-end information storage infrastructure and a flexible development environment for data storage using a computer system. The method includes managing system resources including a relational database. Meta data models are created to model processes and to define meta data elements and their relationships by using trees and graphs. The method manages access to the data by authenticating users through a directory describing user rights, while providing management of multi-user access and concurrency. The method includes running the processes that generate instance data, storing the instance data following the meta data model, and transforming the instance data into physical views.
Owner:INTELLIGENT MEDICAL OBJECTS
Method, system, and program for transferring data from an application engine
InactiveUS20030023472A1Improve network performanceAvoid the needData processing applicationsResource allocationApplication softwareCollection Object
Provided is a method, system, and program for enabling access to resource objects in an application engine. A request is received from a calling entity for resource objects of a specified type in the application engine. A request to the application engine is generated for information on available resource objects of the specified type. In response to receiving the information from the application engine, a collection object is generated including one metadata element for each resource object of the specified type in the application engine. The generated collection object is returned to the calling entity.
Owner:IBM CORP
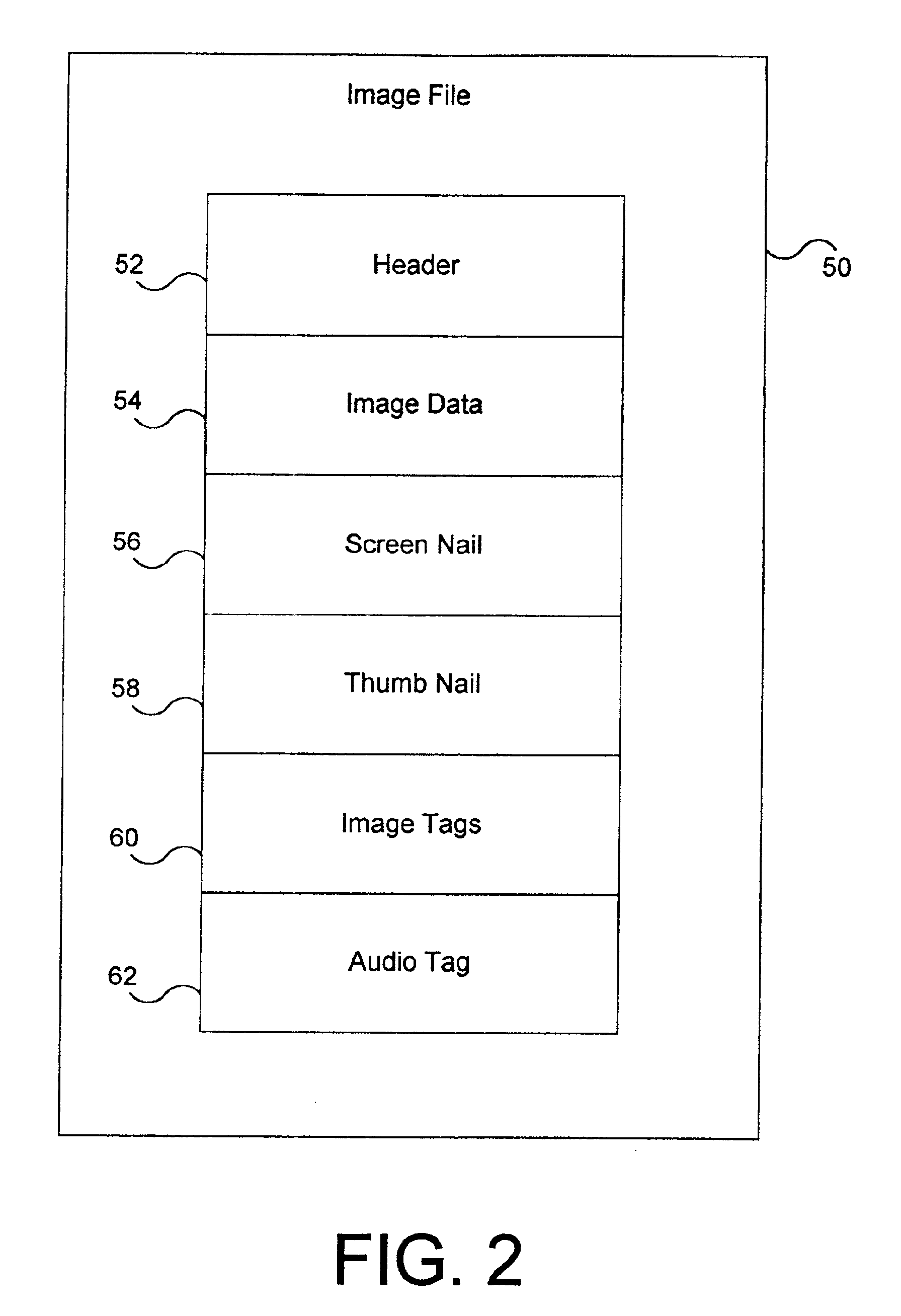
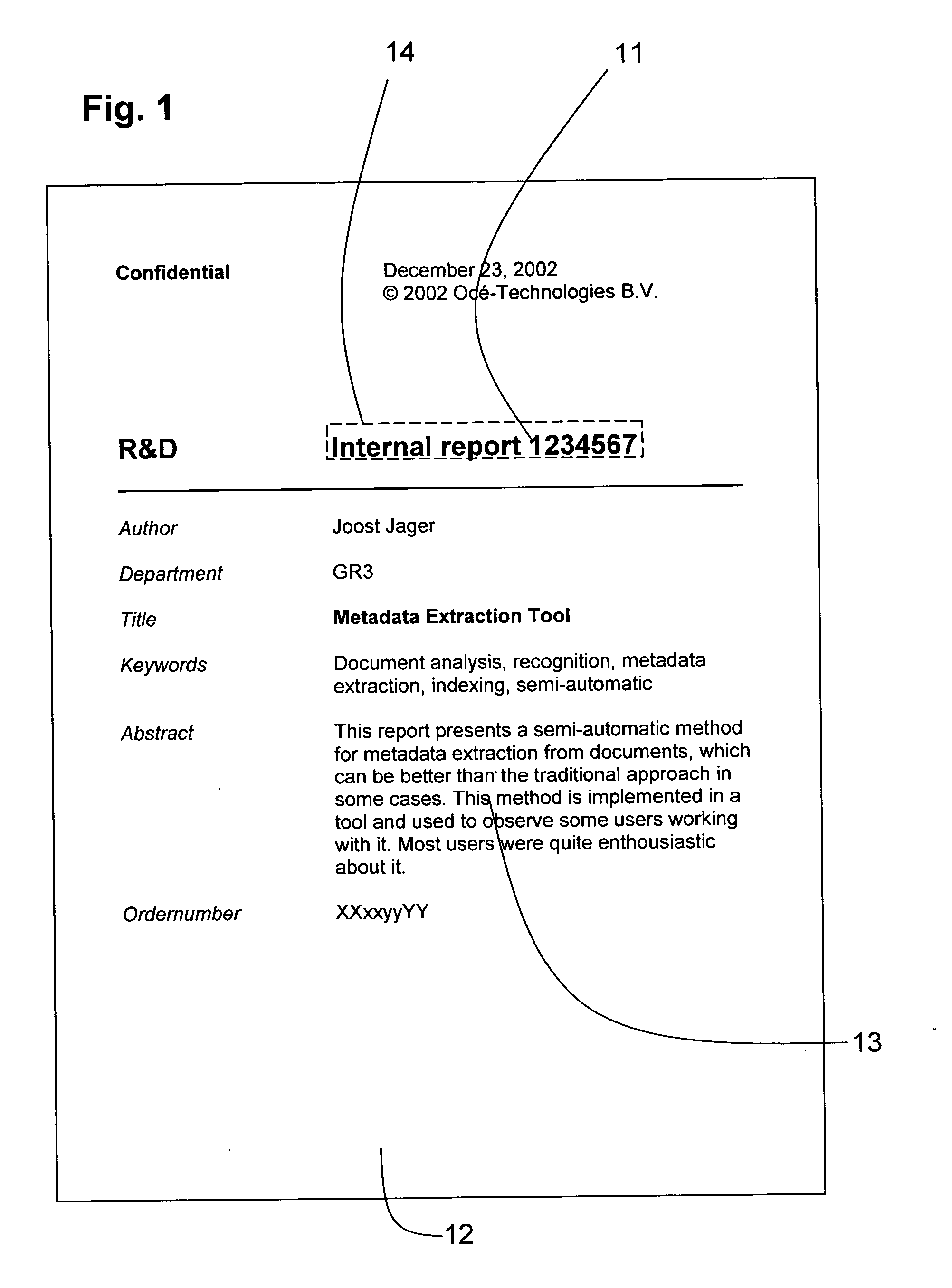
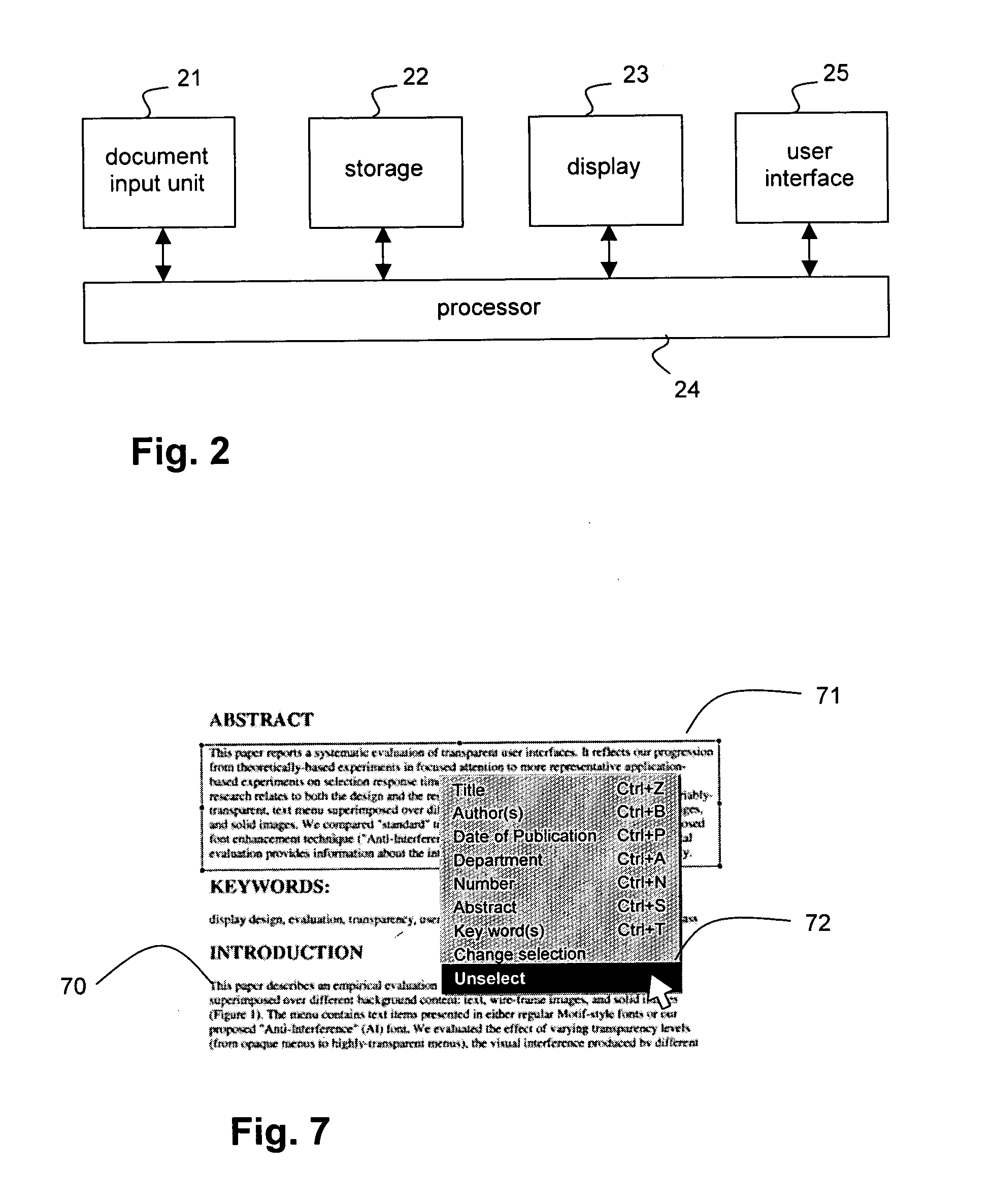
Metadata extraction from designated document areas
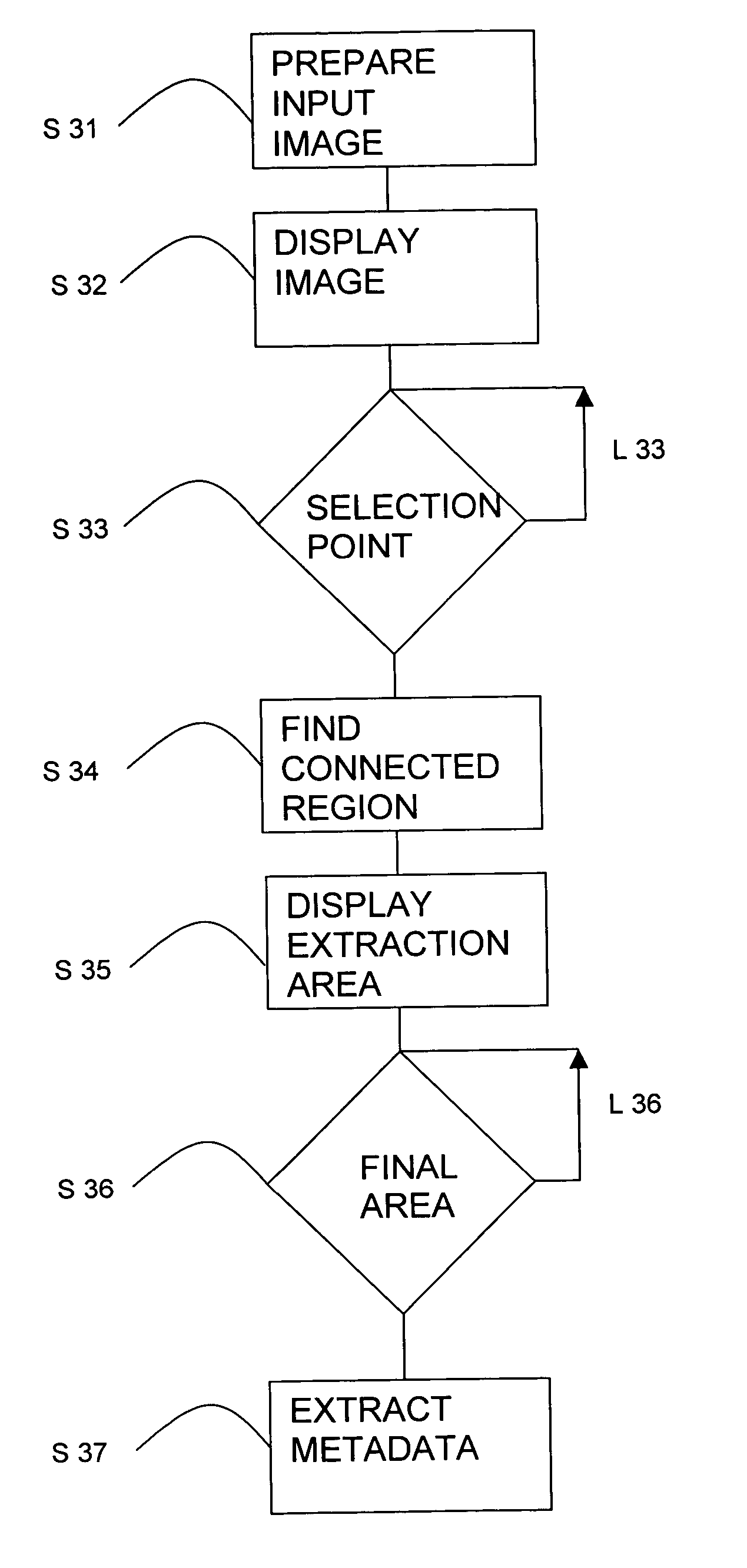
InactiveUS20050041860A1Robust and easy wayEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsDisplay deviceTouchscreen
A method and device are described for extracting metadata from an image of pixels, such as a title or author of a document. At least part of the image is shown on a display for a user. A pointing control element in a user interface, such as a mouse or a touch screen, is operated by a user to generate a selection command. The selection command includes a selection point in a metadata element in the image. A region of foreground pixels is determined, the region containing pixels that are connected to the selection point. An extraction area is constructed around the region. Finally metadata is extracted by processing pixels in the extraction area.
Owner:OCE TECH
Scoped access control metadata element
InactiveUS20050278390A1Overcome problemsData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMetadataDynamic range
Methods, systems, and data structures for communicating object metadata are provided. A generic metadata container is presented that allows object metadata to be described in an extensible manner using protocol-neutral and platform-independent methodologies. A metadata scope refers to a dynamic universe of targets to which the included metadata statements correspond. Metadata properties provide a mechanism to describe the metadata itself, and metadata security can be used to ensure authentic metadata is sent and received. Mechanisms are also provided to allow refinement and replacement of metadata statements. The generic metadata container can be adapted to dynamically define access control rights to a range of objects by a range of users, including granted and denied access rights.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
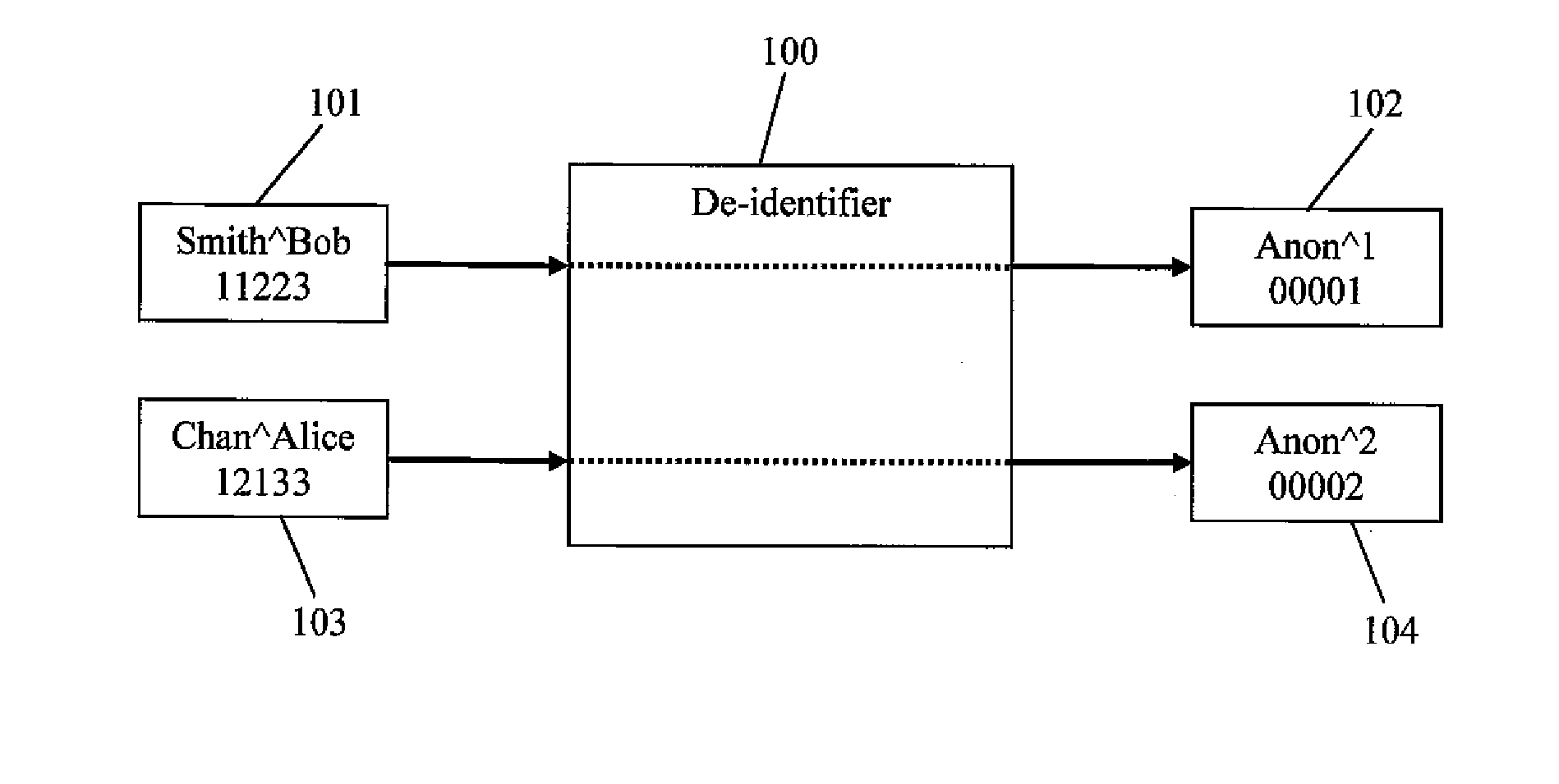
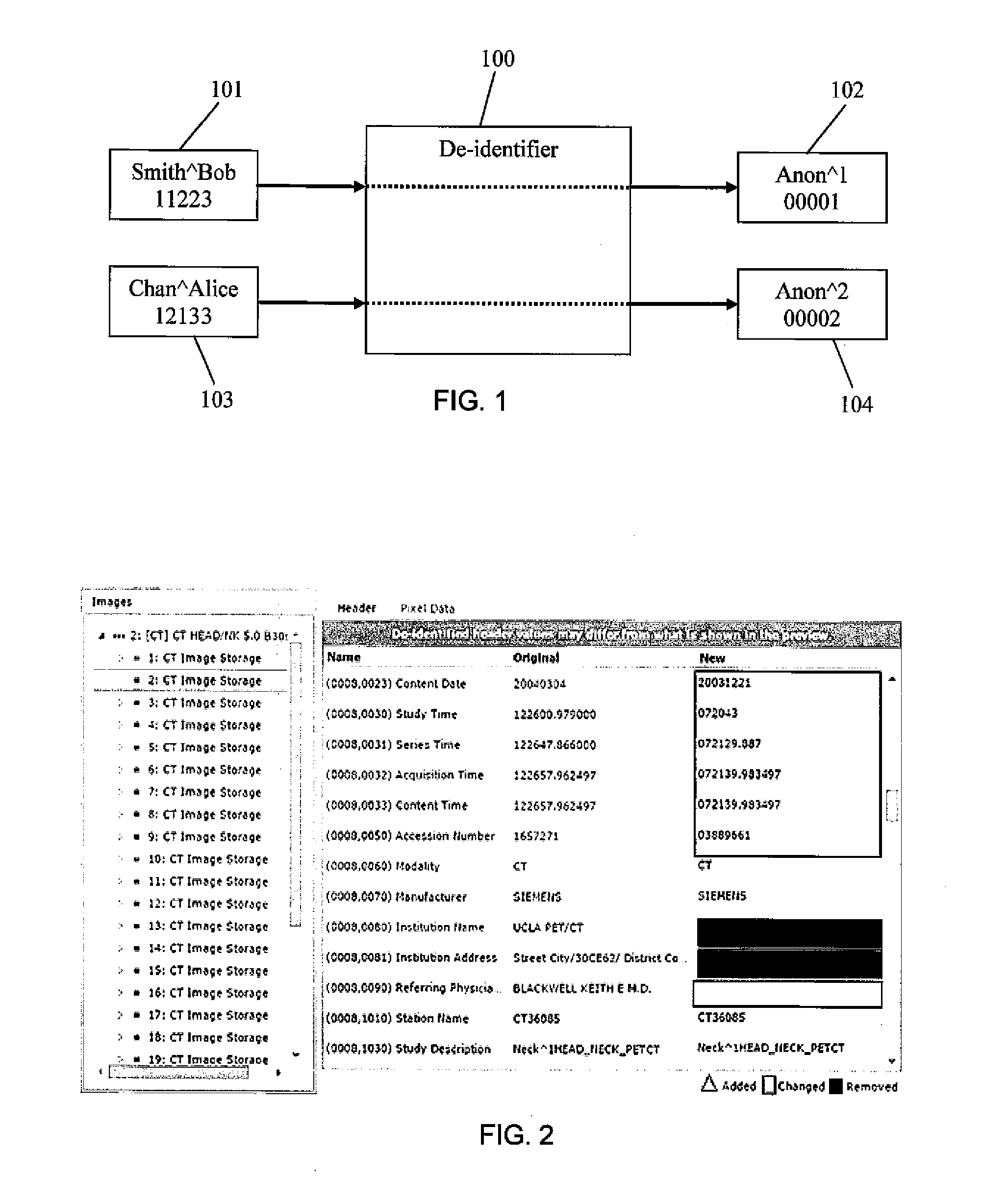
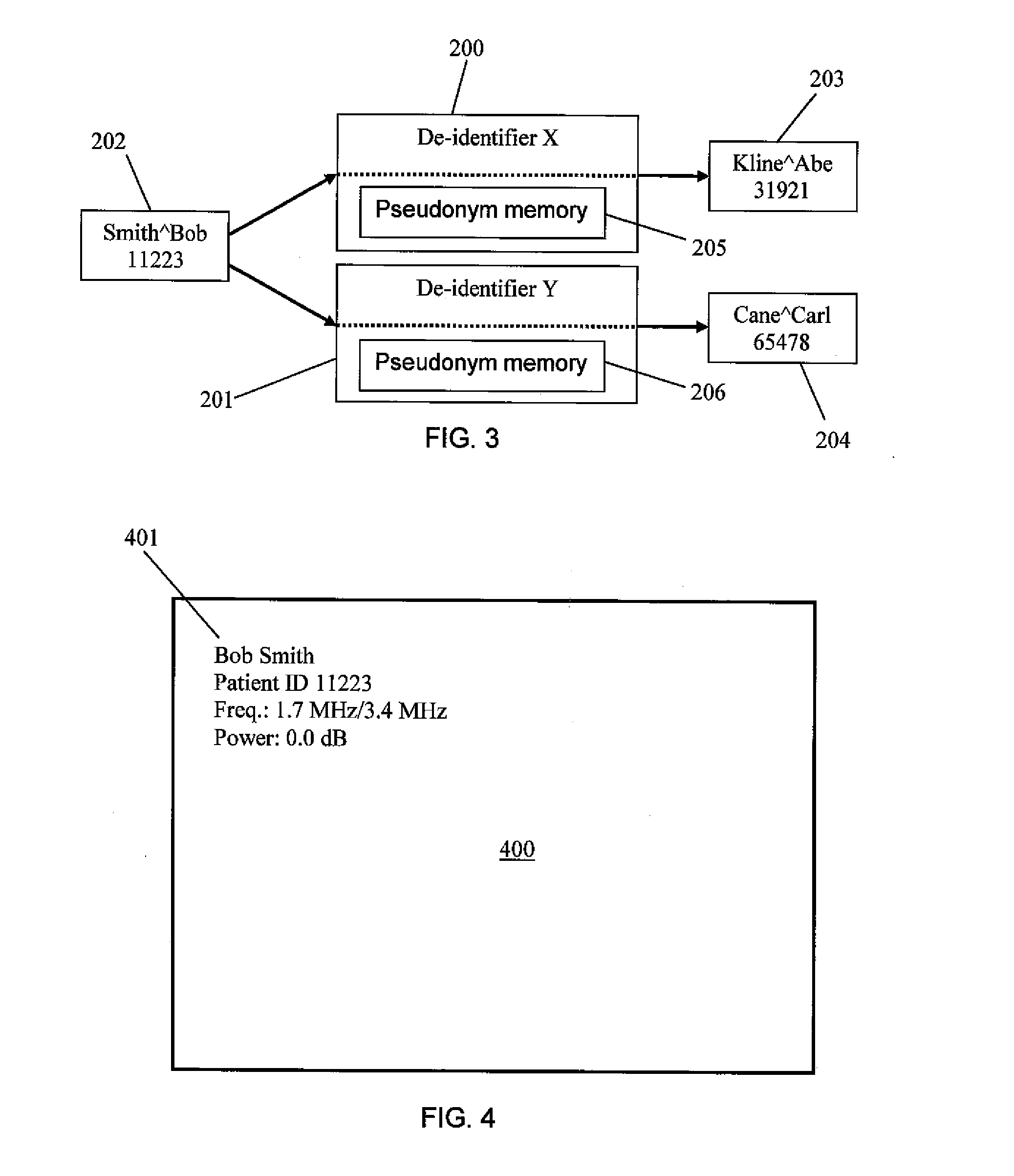
Dicom de-identification system and method
A system for creating de-identification programs for de-identifying DICOM image files containing DICOM images and metadata. The system provides a user interface that allows users to create de-identification programs. Each program has redaction rules specifying redaction regions in normalized coordinates defining a region of a DICOM image to be redacted to obfuscate content in the redaction region, and metadata substitution rules specifying metadata elements to be substituted with pseudonyms. The user may modify the redaction rules and metadata substitution rules, and preview the effect of the de-identification program by applying the de-identification program to DICOM images and associated metadata and displaying the resulting modified DICOM image and associated metadata. The system maintains a pseudonym memory to determine if a pseudonym has been stored for each metadata element specified by the substitution rule so that the same pseudonym is consistently used for the same element values.
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL INC
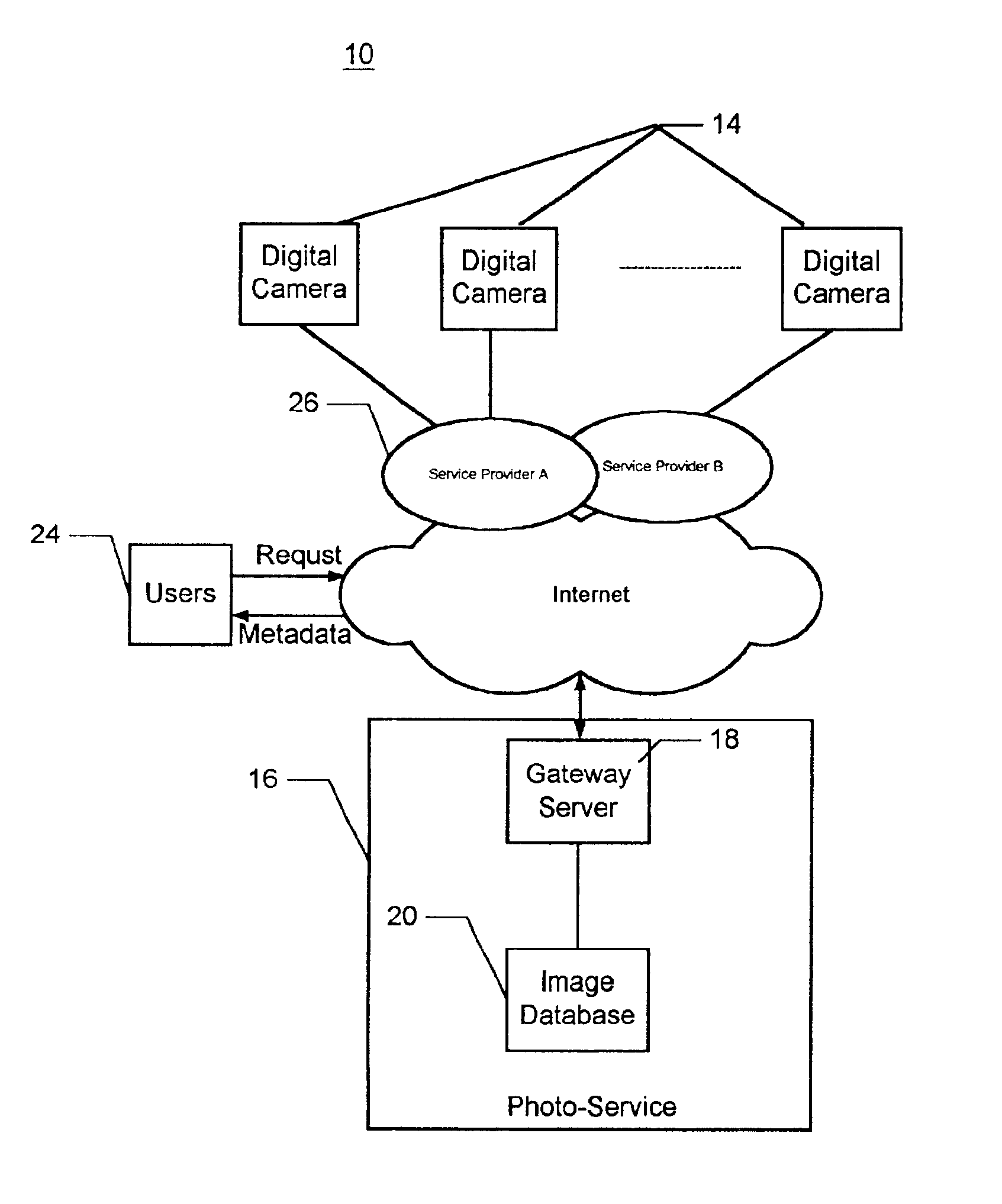
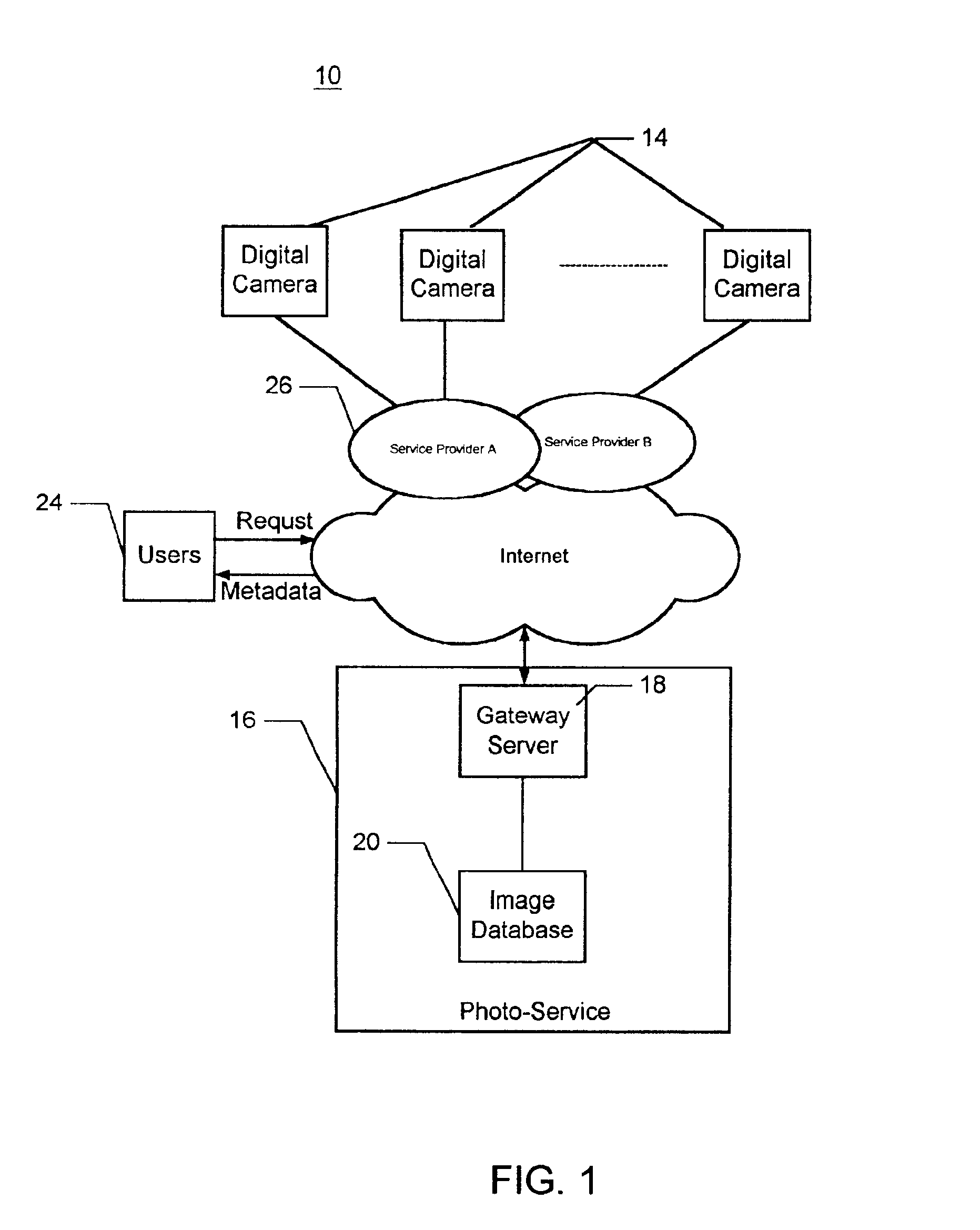
Asset management system and associated methods
InactiveUS20050278375A1Digital data processing detailsMetadata video data retrievalDatabaseManagement system
A method and apparatus prepare an asset for placement on a server, the asset including a media file and corresponding metadata elements. The media file is received, and it is automatically determined whether all required metadata elements are associated with the received media file. If all of the required metadata elements are not associated with the received media file, it is determined which of the required metadata elements are missing, and the missing metadata elements are required to be added before the asset is placed on the server.
Owner:CSC HLDG
Mapping binary objects in extended relational database management systems with relational registry
InactiveUS20010049693A1Small footprintReduce maintenanceDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsData processing systemAutomated data processing
An automated data processing system includes a relational database engine, storage devices having a database table, registry and binary large objects created and updated by the relational database engine and a user defined function engine retrieving data elements stored in the binary large objects. The registry includes data element classifications. The database table includes relational information of the data elements, the data element classifications and pointers to the binary large objects, and the relational database engine creates and updates the binary large objects based on the database table and the registry.
Owner:IBM CORP
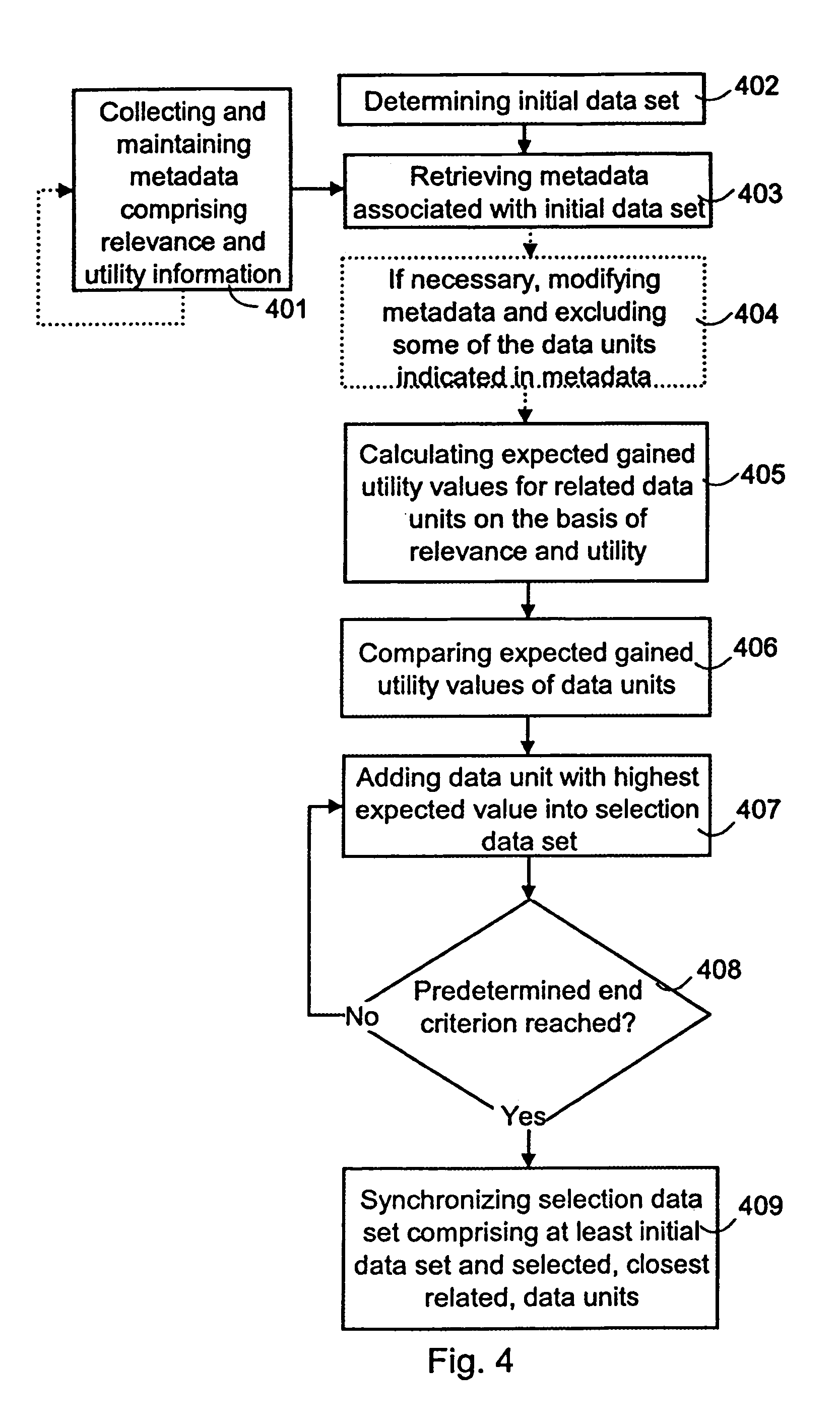
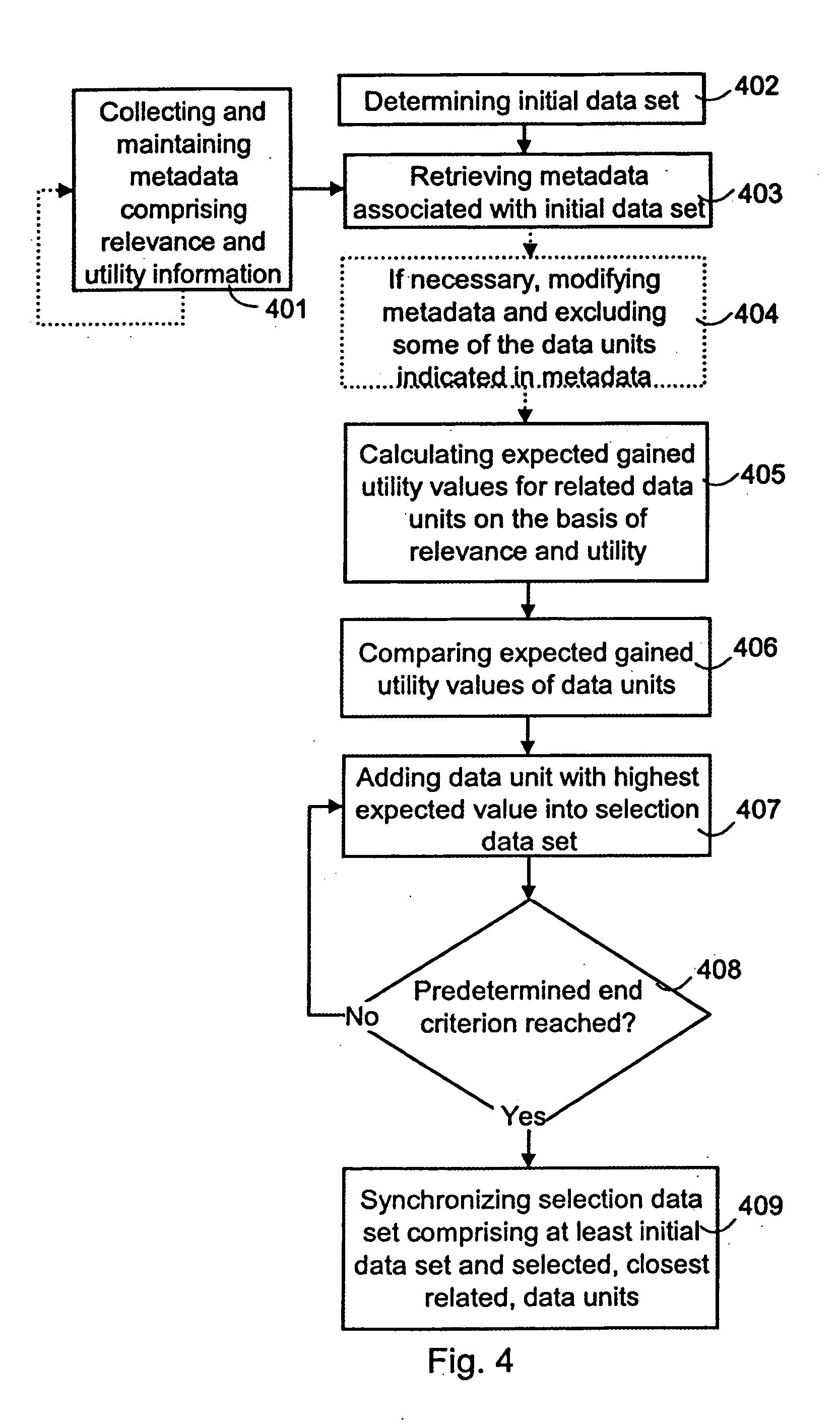
Selecting data for synchronization
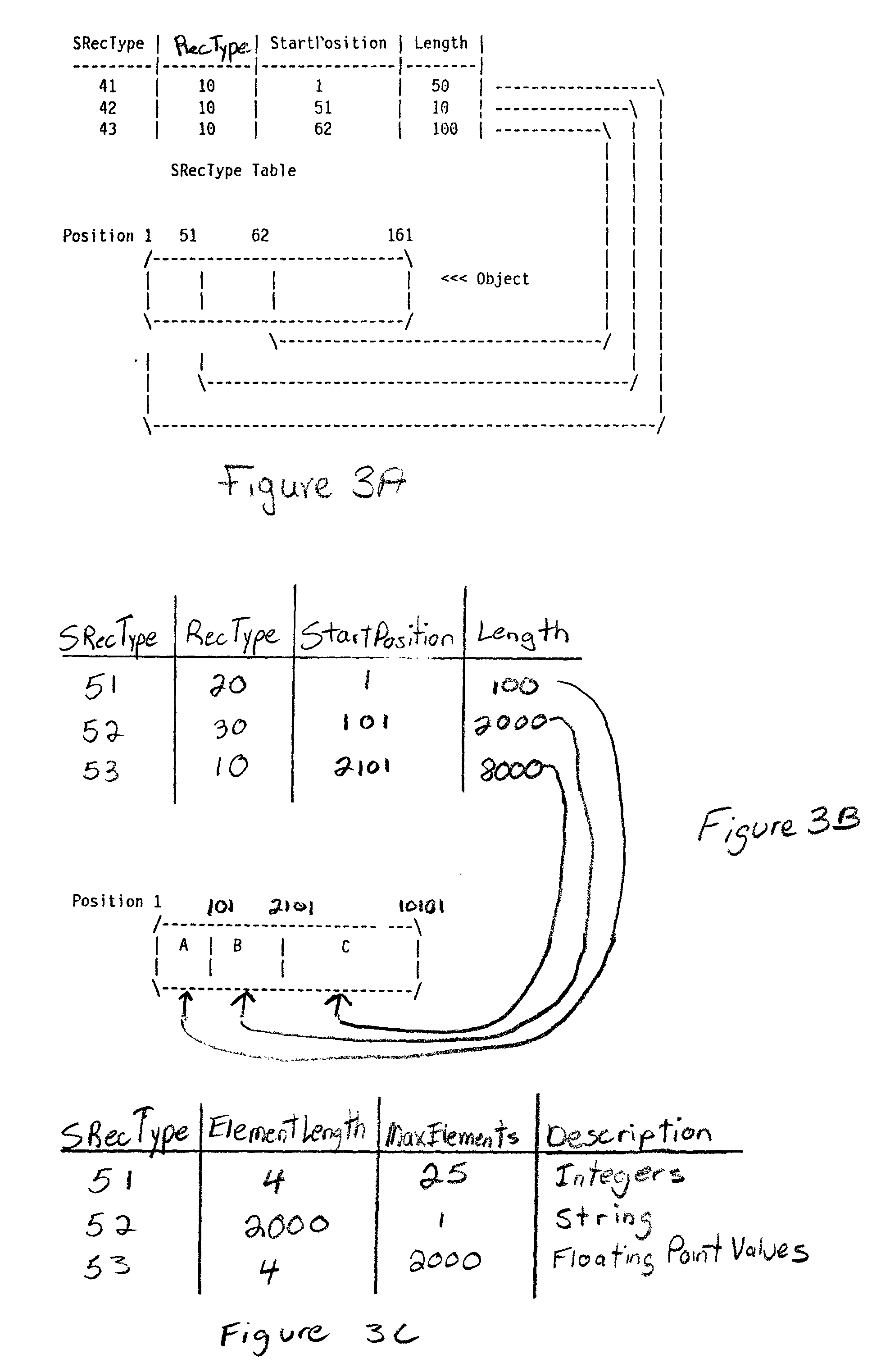
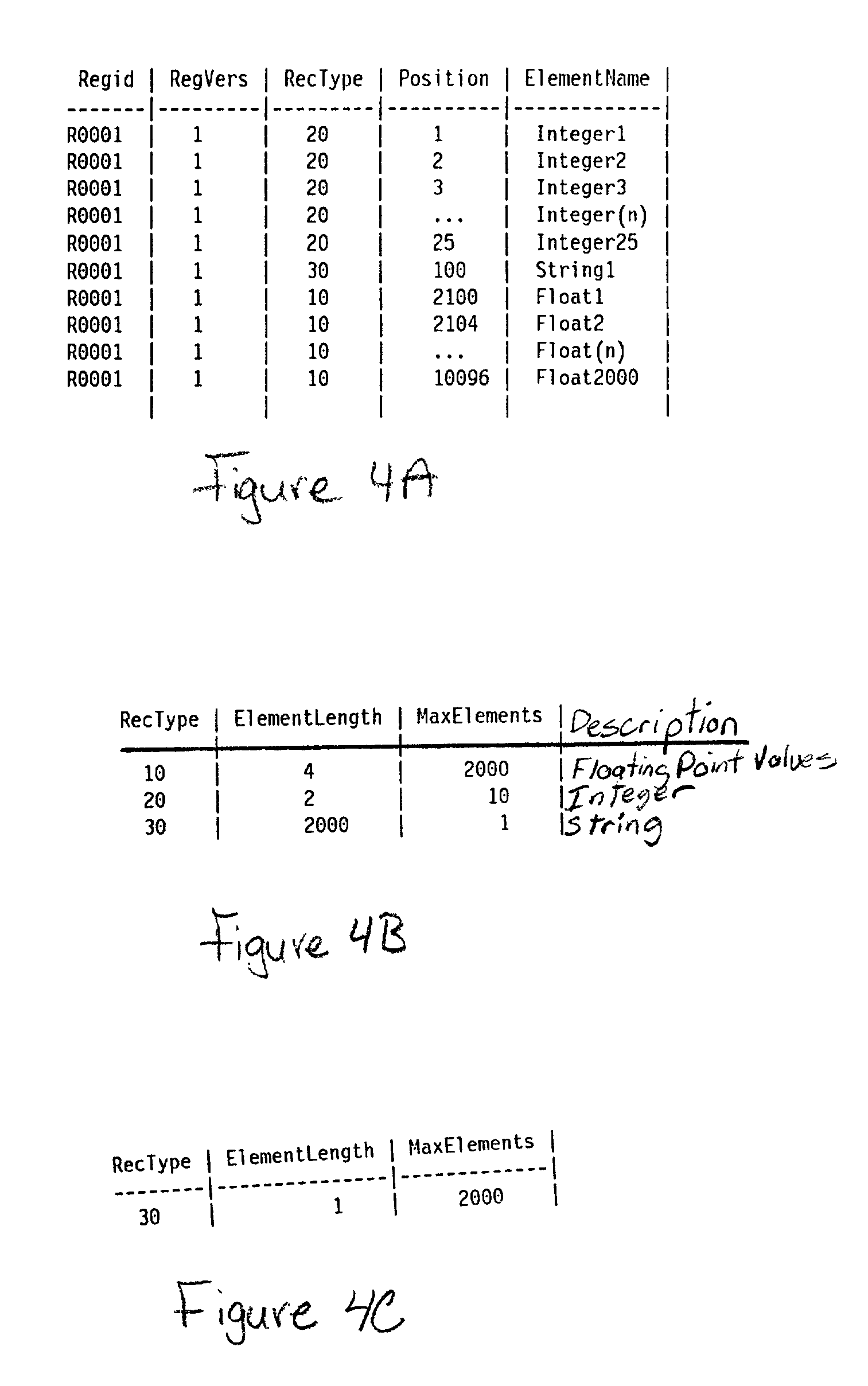
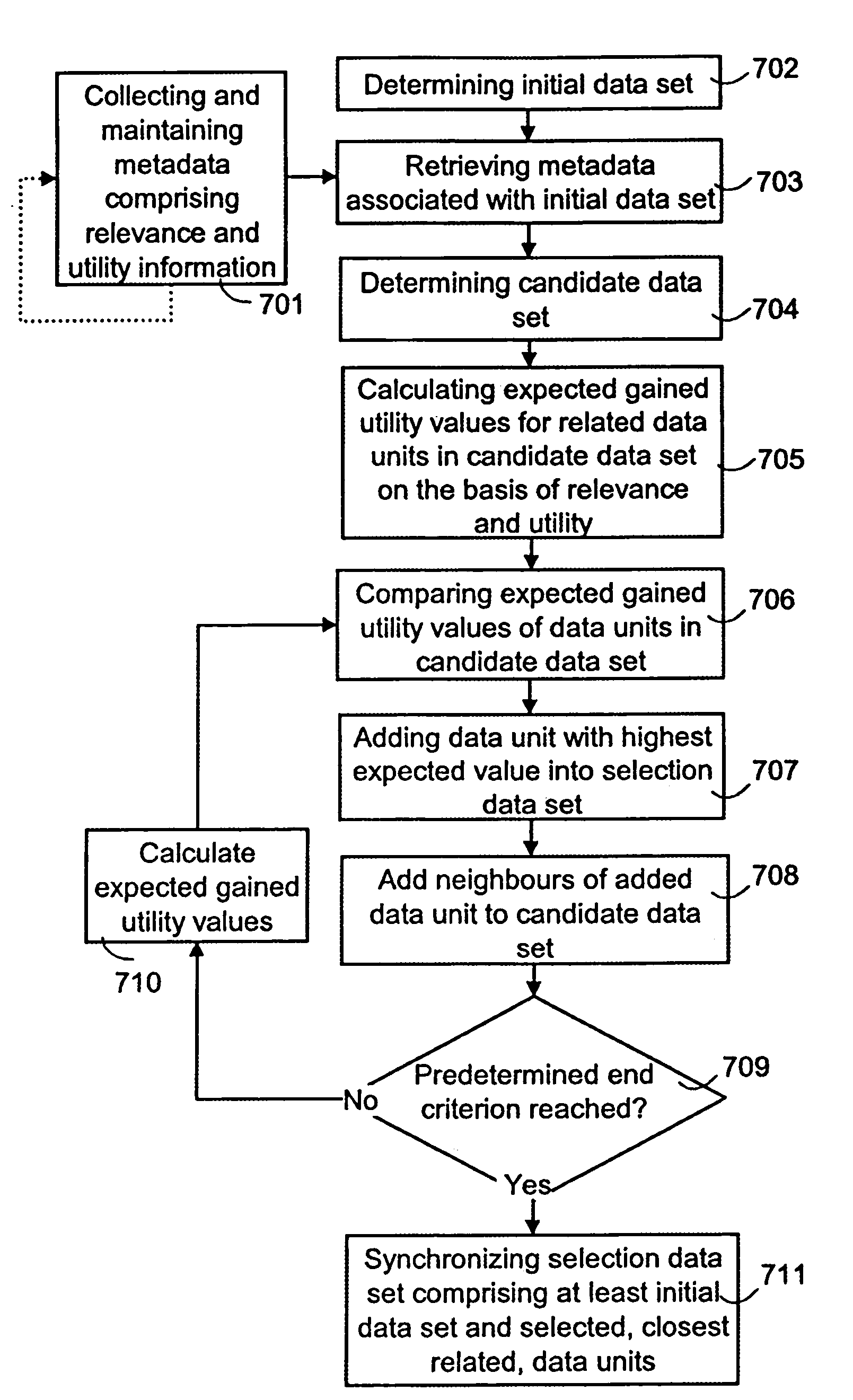
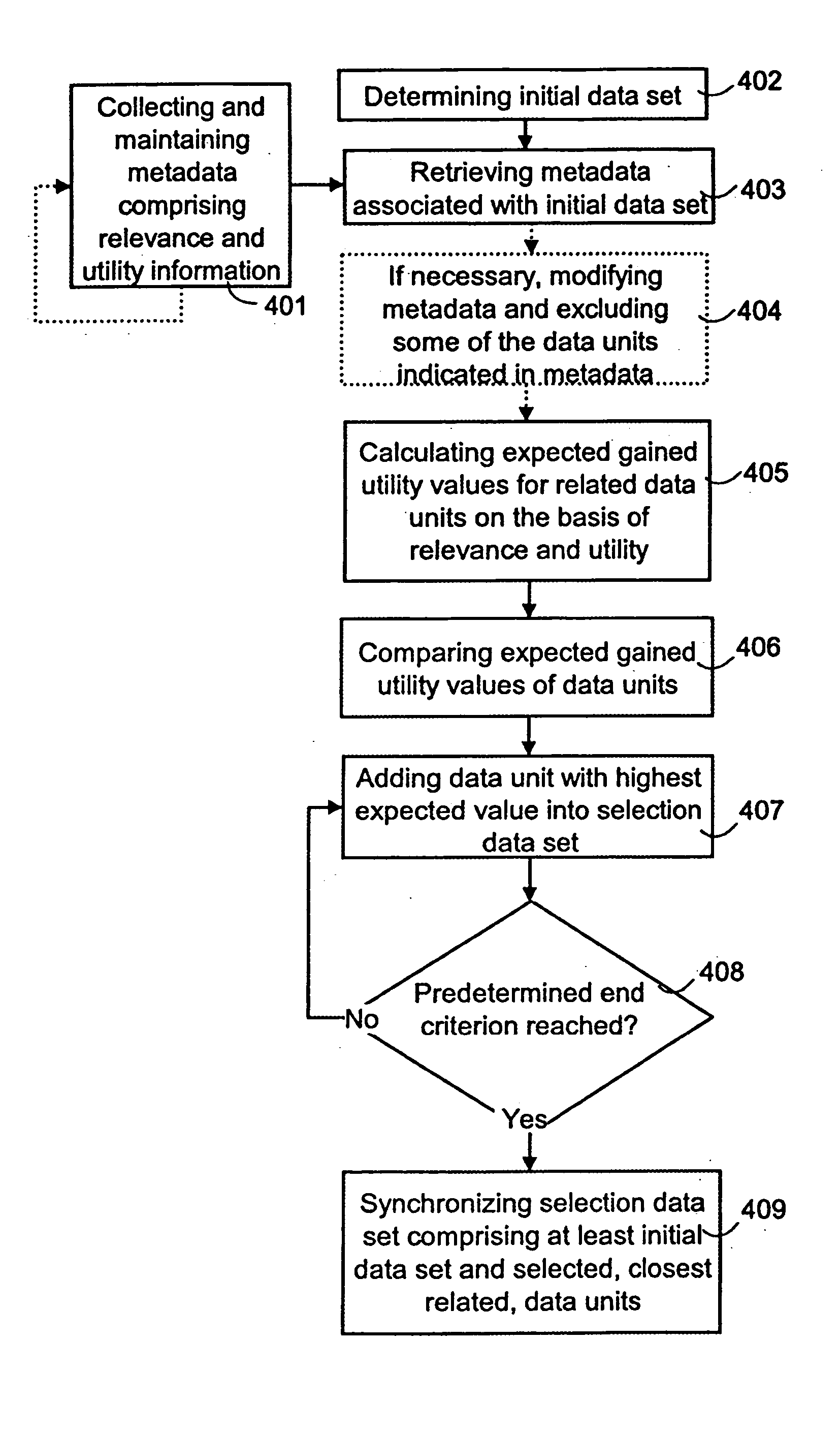
InactiveUS7483925B2Guaranteed normal transmissionLimited resourceDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsData setData system
A method for selecting a data set to be synchronized from databases of a data system, in which system metadata illustrating the relationships between data units of the data system are stored for the selection of the data set to be synchronized. The metadata comprises at least information on the relevance between the data units. When a first data set is to be synchronized, metadata associated with at least one initial data unit of the first data set is retrieved. Next, a second data set, which according to at least one metadata element comprises a data unit of maximum relevance to the initial data unit, is selected for synchronization.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
Metadata-related mappings in a system
InactiveUS20050203920A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData elementFunctional expression
A method and system comprising a processor and storage coupled to the processor are provided. The storage contains elements of metadata belonging to a plurality of schemas. Mappings between the elements of metadata that comprise functional expressions executable by the processor relate the elements of metadata. Methods for validating and updating the mappings when one of the plurality of schemas change are also provided.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
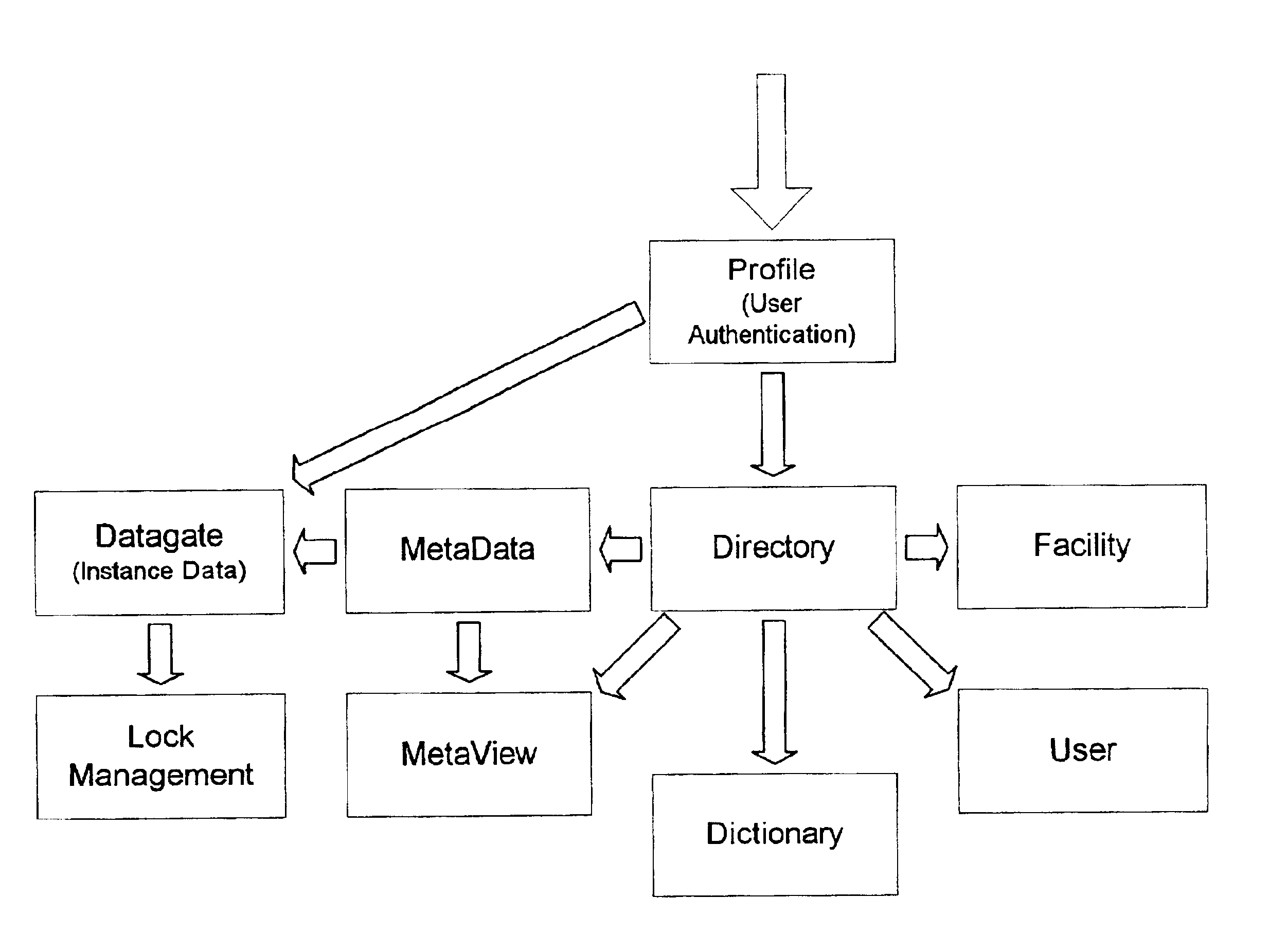
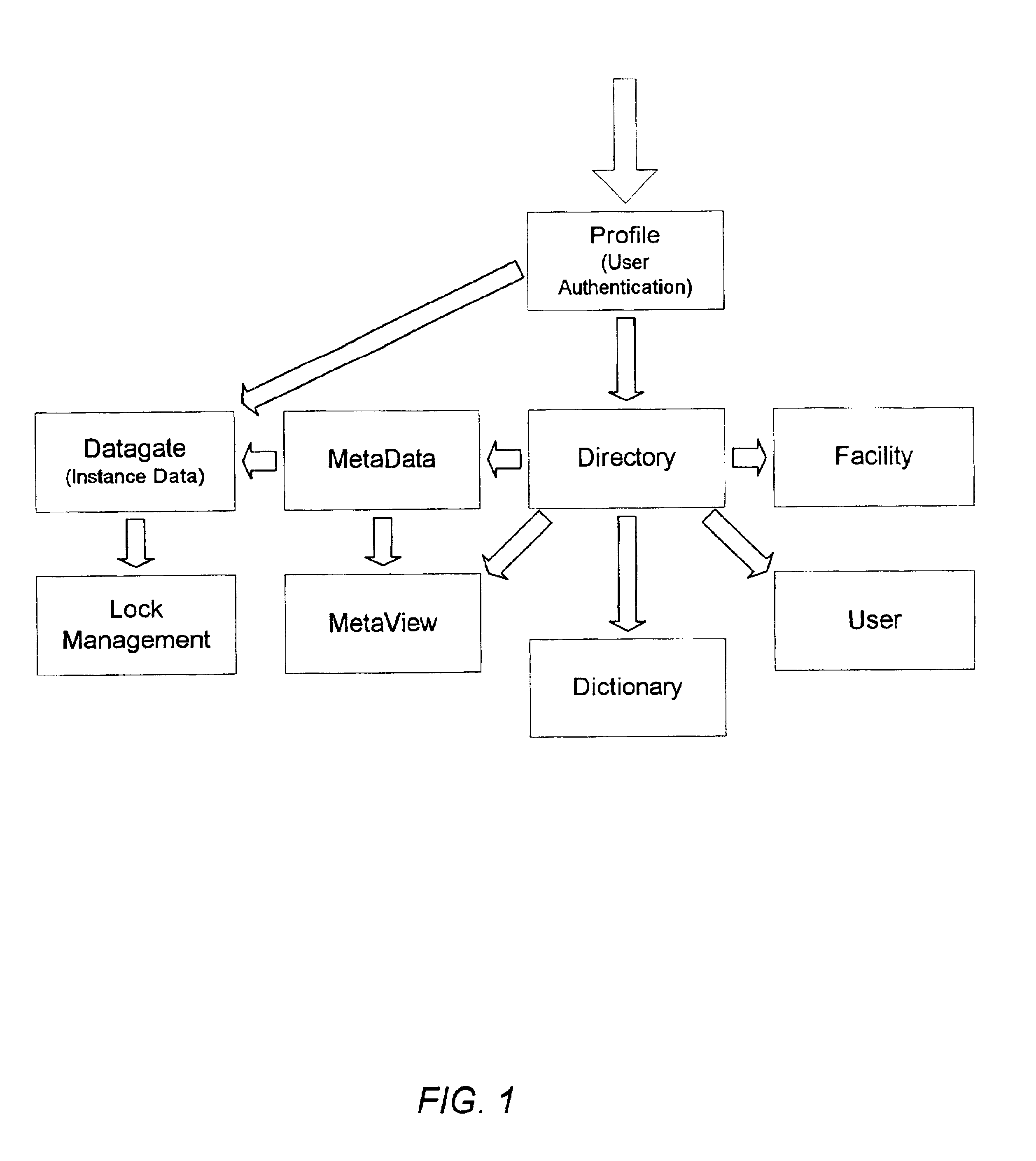
Method for adaptive data management
InactiveUS7693917B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsAdaptive managementRelational database
A method for managing a back-end information storage infrastructure and a flexible development environment for data storage using a computer system. The method includes managing system resources including a relational database. Meta data models are created to model processes and to define meta data elements and their relationships by using trees and graphs. The method manages access to the data by authenticating users through several levels of authentication describing user rights, while providing management of multi-user access and concurrency. The method includes running the processes that generate instance data, storing the instance data following the meta data model, and transforming the instance data into physical views.
Owner:INTELLIGENT MEDICAL OBJECTS
Enterprise-level transaction analysis and reporting
InactiveUS20070239476A1Digital data processing detailsOffice automationMetadata elementEnterprise level
Systems and methods are provided for enterprise-level analysis and reporting of transaction information. According to one embodiment, a method is provided by way of an enterprise-level analysis and reporting software application to enable a non-technical user on a Personal Computer (or other Network Appliance) to drag and drop metadata elements (e.g., XBRL elements / objects or generic data keys) onto a productivity tool, such as a spreadsheet (e.g., Microsoft Excel), and interactively update the spreadsheet with aggregated information from originating transactions. According to one embodiment of the present invention, transactions are dynamically accumulated into time-sensitive balances (or buckets) and then aggregated into cube(s) before the spreadsheet is refreshed. The user can then drill back through aggregated information to original transaction information.
Owner:CERTENT
Metadata, models, visualization and control
InactiveUS7272786B1More informativeEasy to trackDigital data information retrievalBiological modelsData processing systemDocumentation
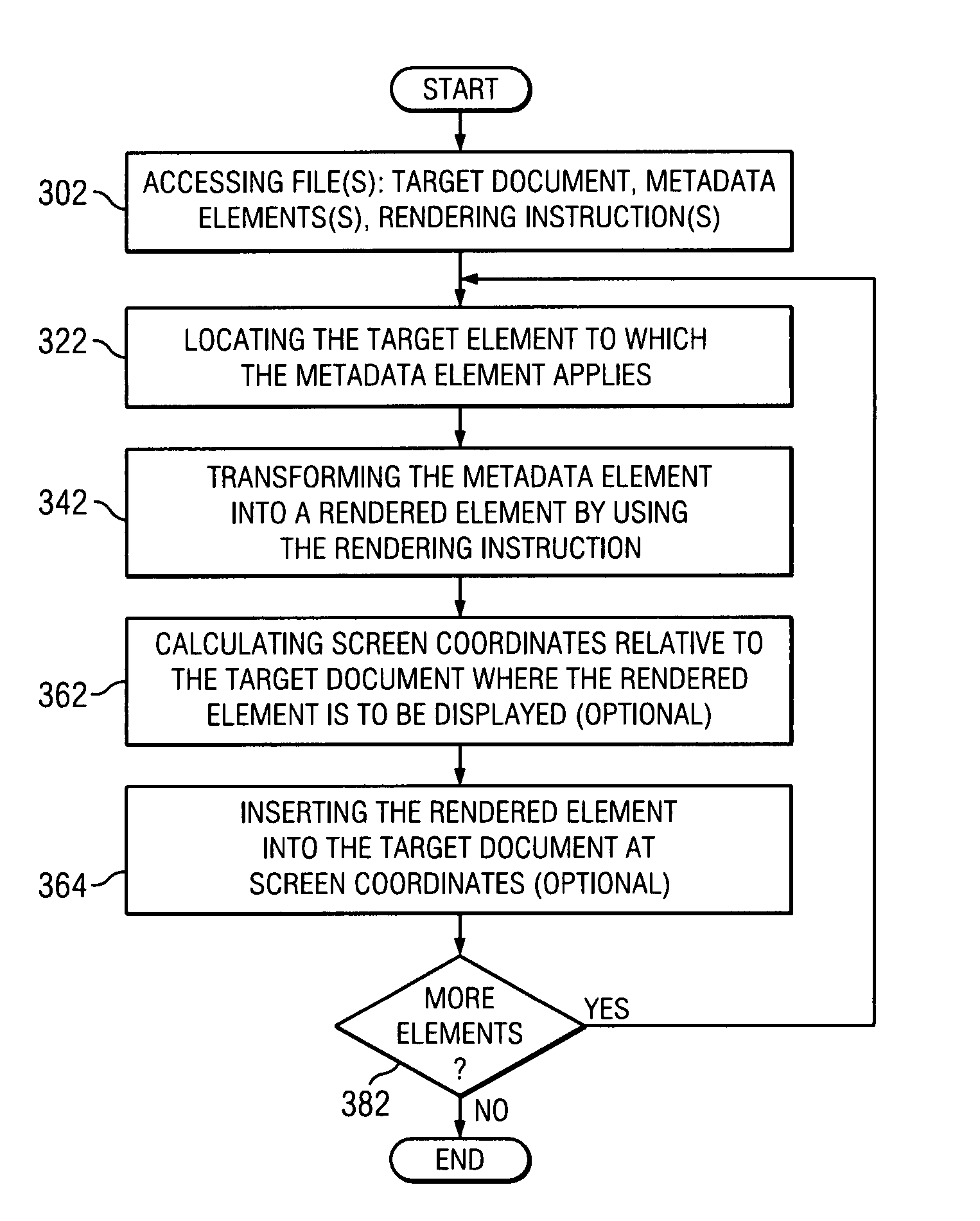
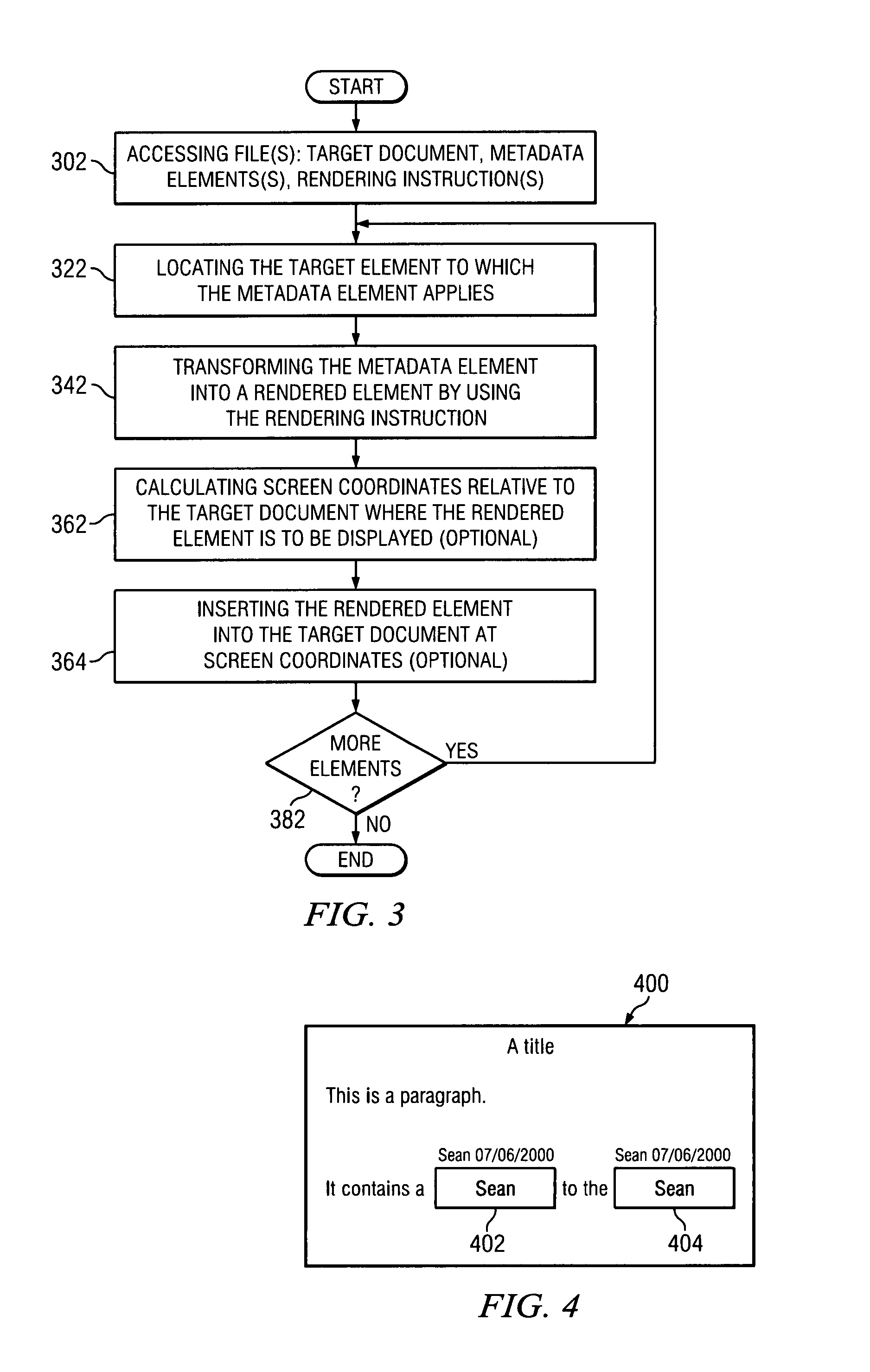
A method or data processing system readable medium can be used for modifying a target document. The data processing system medium or method may use metadata and rendering instructions to modify a target document to make the target document more user-friendly, more informative, or easier to track statistics related to the target document. In modifying the document, the rendering instructions render the metadata elements that can be used in the target document. In some embodiments, different sets of metadata and rendering instructions may be used with the same target document.
Owner:OPEN TEXT SA ULC
Selectively updating a dynamic manifest file
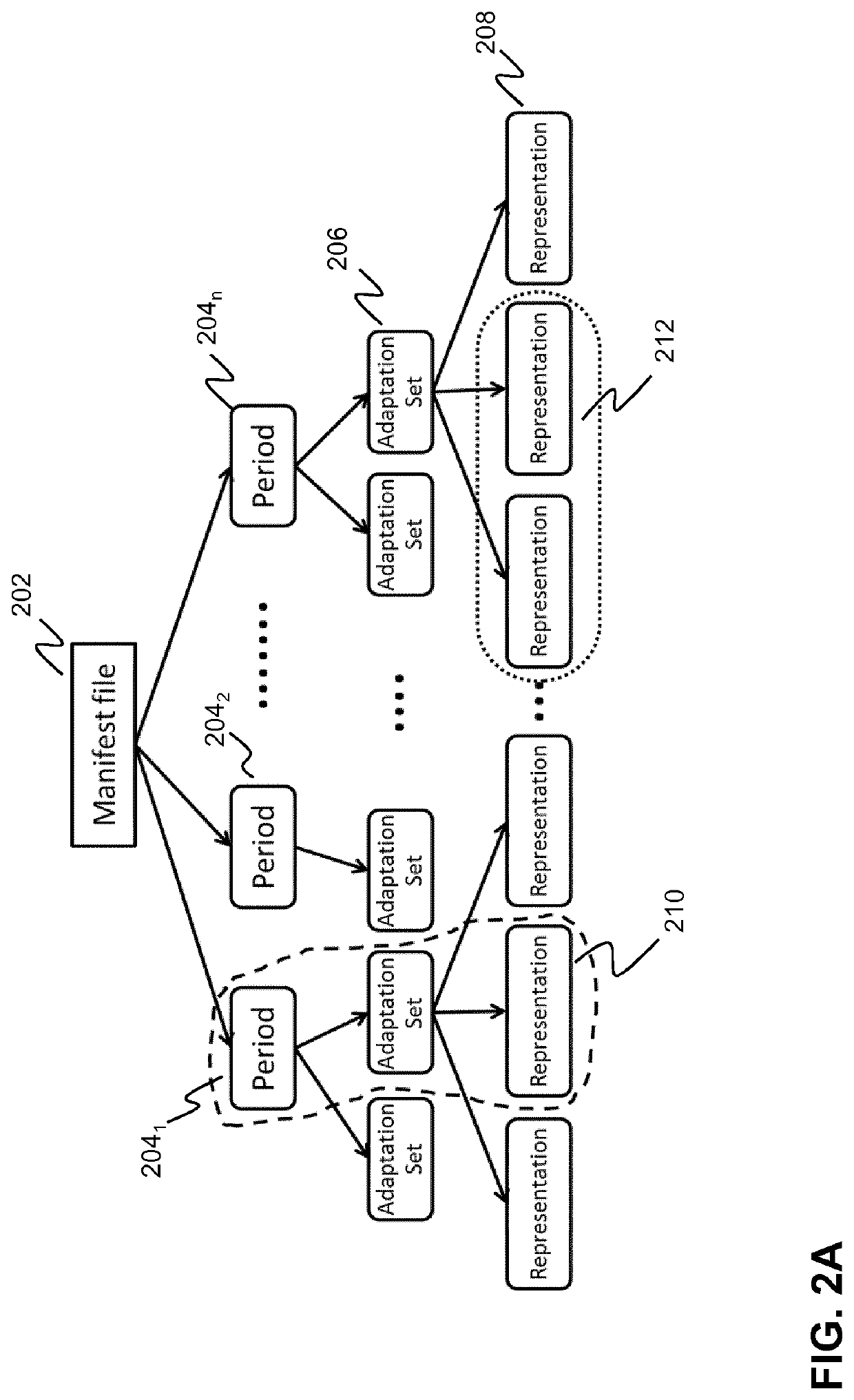
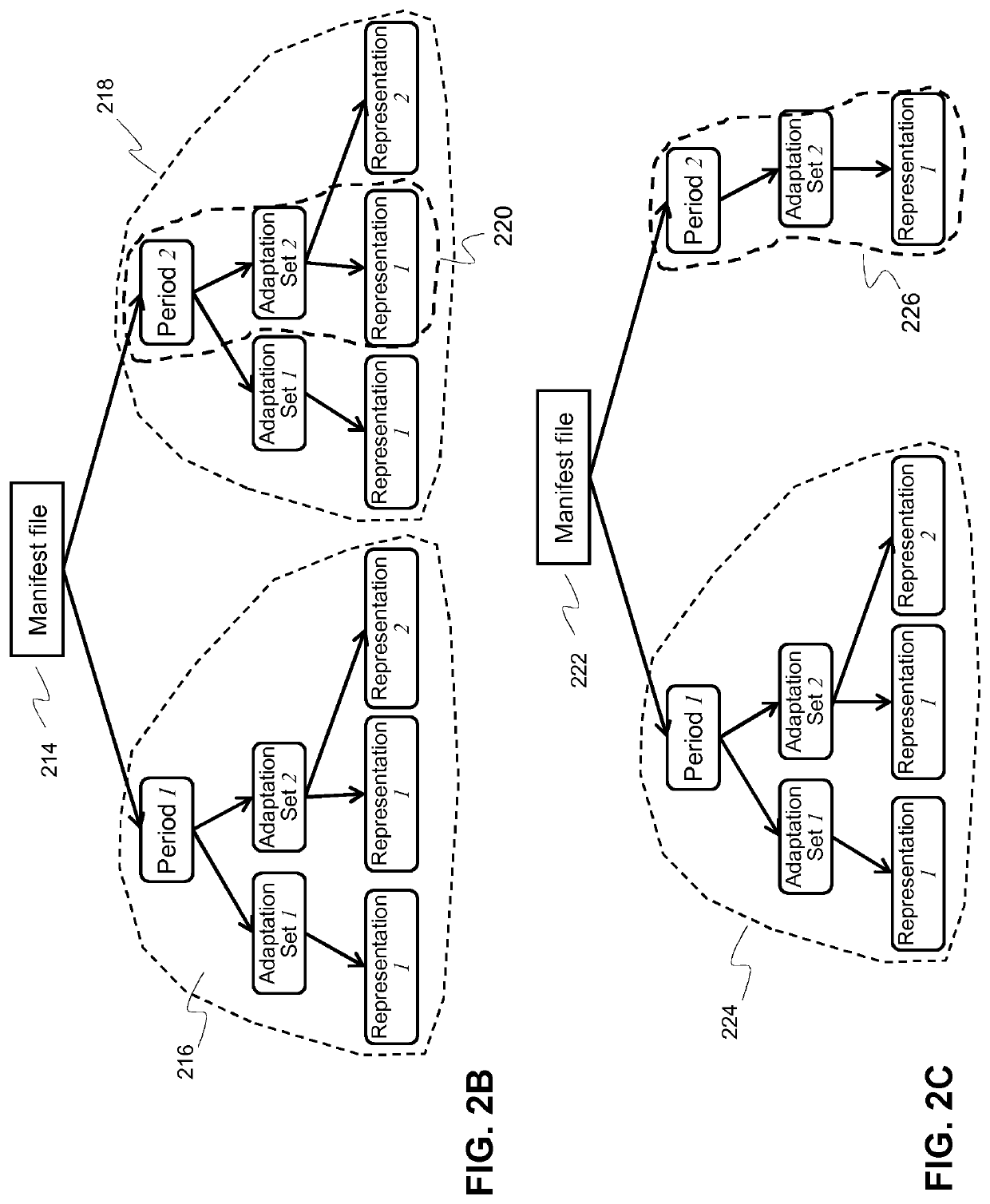
InactiveUS20190342356A1Amount of information needsReduce dataTransmissionSelective content distributionManifest fileUniform resource locator
A method for selectively updating a dynamic manifest file is described, wherein the method may comprise: selecting one or more metadata elements of a manifest file used by a client, the one or more selected metadata elements being associated with a subset of representations of the set of representations defined in the manifest file; transmitting a request message identifying the selected one or more metadata, and, optionally, said manifest file identifier, to a network node, the request message being configured to trigger the network node to generate a response message on the basis of the information in the request message; and, receiving the response message from the network node, wherein the response message comprises: location information, preferably an URL or a part thereof, for retrieving a selectively updated version of the dynamic manifest file used by the client, wherein the selectively updated version only comprises new segment identifiers associated with the one or more selected metadata elements; or, wherein the response message comprises: update information, preferably a patch, configured to selectively update the dynamic manifest file used by the client apparatus, wherein the update information only comprises new segment identifiers associated with the one or more selected metadata elements.
Owner:KONINK KPN NV +1
Selecting data for synchronization
ActiveUS20050203971A1Improve usabilityLimited resourceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData setData system
A method for selecting a data set to be synchronized from databases of a data system, in which system metadata illustrating the relationships between data units of the data system are stored for the selection of the data set to be synchronized. The metadata comprises at least information on the relevance between the data units. When a first data set is to be synchronized, metadata associated with at least one initial data unit of the first data set is retrieved. Next, a second data set, which according to at least one metadata element comprises a data unit of maximum relevance to the initial data unit, is selected for synchronization.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
3D layering of map metadata
ActiveCN102359791AInstruments for road network navigationVehicle position indicationParallaxView based
Techniques and tools are described for rendering views of a map in which map metadata elements are layered in 3D space through which a viewer navigates. Layering of metadata elements such as text labels in 3D space facilitates parallax and smooth motion effects for zoom-in, zoom-out and scrolling operations during map navigation. A computing device can determine a viewer position that is associated with a view altitude in 3D space, then render for display a map view based upon the viewer position and metadata elements layered at different metadata altitudes in 3D space. For example, the computing device places text labels in 3D space above features associated with the respective labels, at the metadata altitudes indicated for the respective labels. The computing device creates a map view from points of the placed labels and points of a surface layer of the map that are visible from the viewer position.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com