Method and apparatus for testing transdermal medicaments
A technology of drugs, therapeutic drugs, applied in the direction of measuring devices, testing pharmaceutical preparations, separation methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
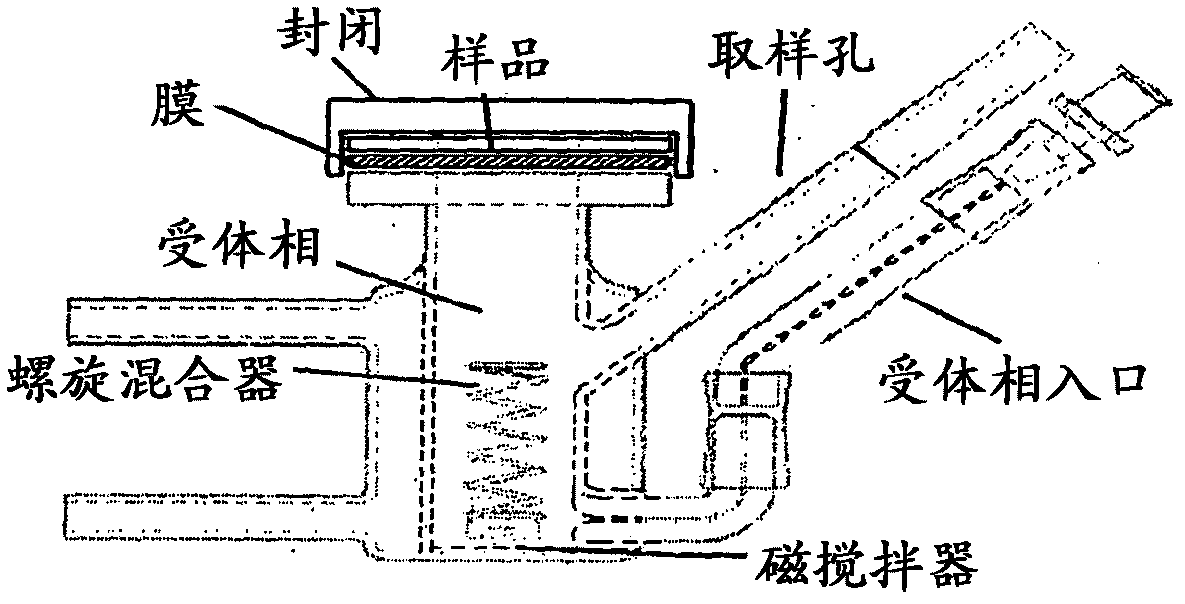
[0077] Membrane Permeation Detection of Troxerutin 5% Gel
[0078] The test formulation contained 5% troxerutin as active ingredient. In the assay, a 0.9% by weight sodium chloride solution was used as the acceptor phase. The flow rate of the acceptor phase was 1 ml / min. The membrane celophane used in the assay was 10 cm wide by 10 cm long. The temperature of the cell was 34°C. The pool is exposed to natural daylight. In the first (I) test, no artificial air flow was applied. In the second test group (II), the linear air velocity was 2 m / sec. The concentration of the active ingredient was determined online by UV spectroscopy at a wavelength of 349 nm.
[0079] The membrane along with the device was allowed to stabilize for 60 minutes. Thereafter, within 2-3 seconds, an amount of approximately 300 mg of the test formulation as measured by analytical precision was transferred uniformly to the membrane. Thereafter the flow of the acceptor phase is restarted and the concen...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Comparative Membrane Permeation Assay of Piroxicam-Containing Creams Using Cellophane and Human Skin Membranes
[0085] The test formulation contained 1% piroxicam as an active ingredient. In the assay, the acceptor phase contained a 0.9% by weight sodium chloride solution. The flow rate of the acceptor phase was 0.3 ml / min. Cellophane membranes were used during the first test series (I) and human skin membranes during the second test series (II). The temperature of the cell was maintained at 34°C. During the two test series, the pools were exposed to natural daylight. No air flow was applied.
[0086] The membrane was allowed to stabilize for 60 minutes.
[0087] After a stabilization period, 300-400 mg of the test formulation as measured by analytical precision was uniformly applied to the membrane within 2-3 seconds. Flow of the acceptor phase was restarted and effluent fractions were collected for each 30 minute period. The piroxicam and methylparaben concent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com