Wireless sensor reader
A wireless sensor and reader technology, used in sensors, inertial sensors, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as limited battery life, large power, and large additional circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
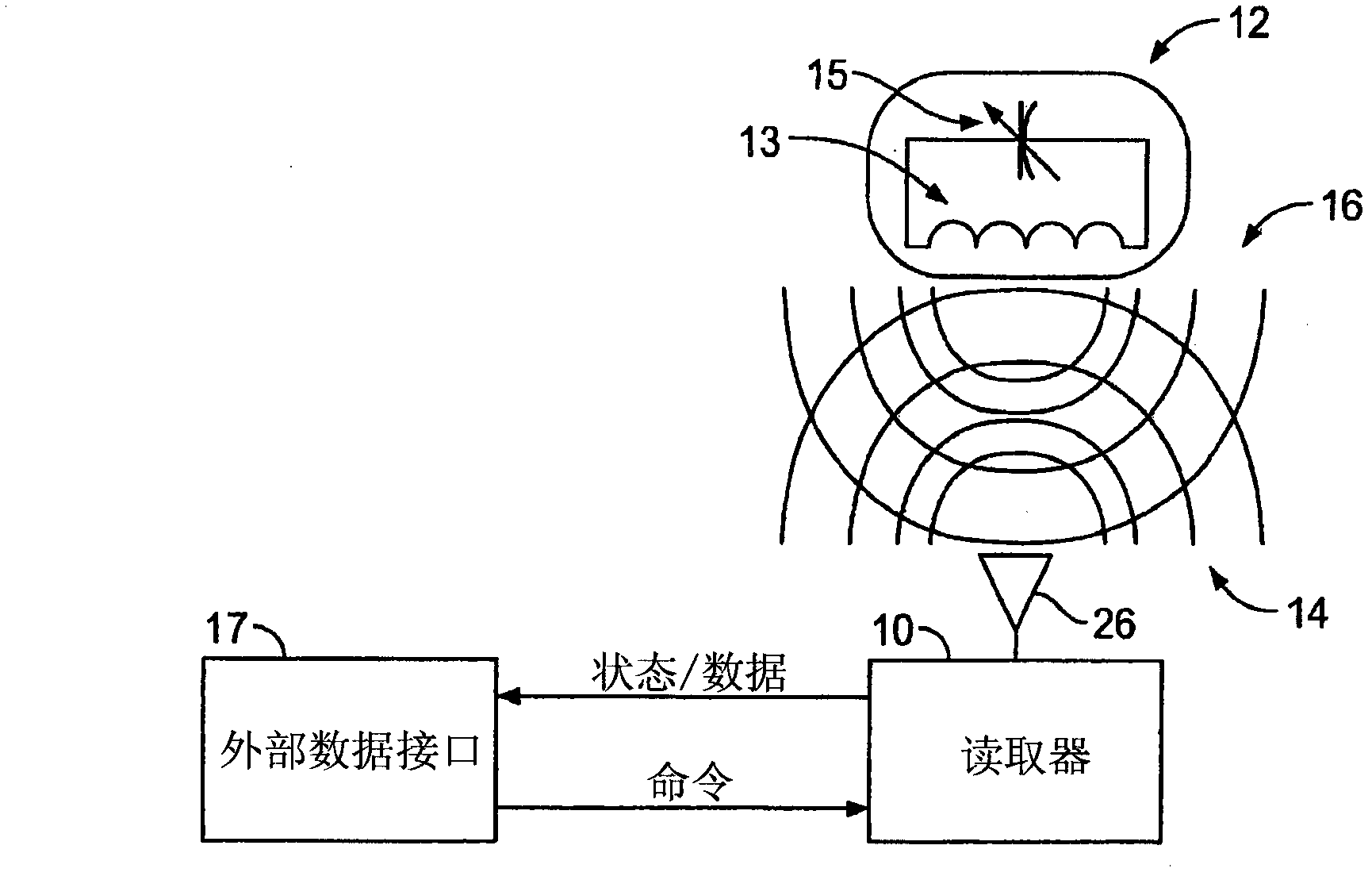
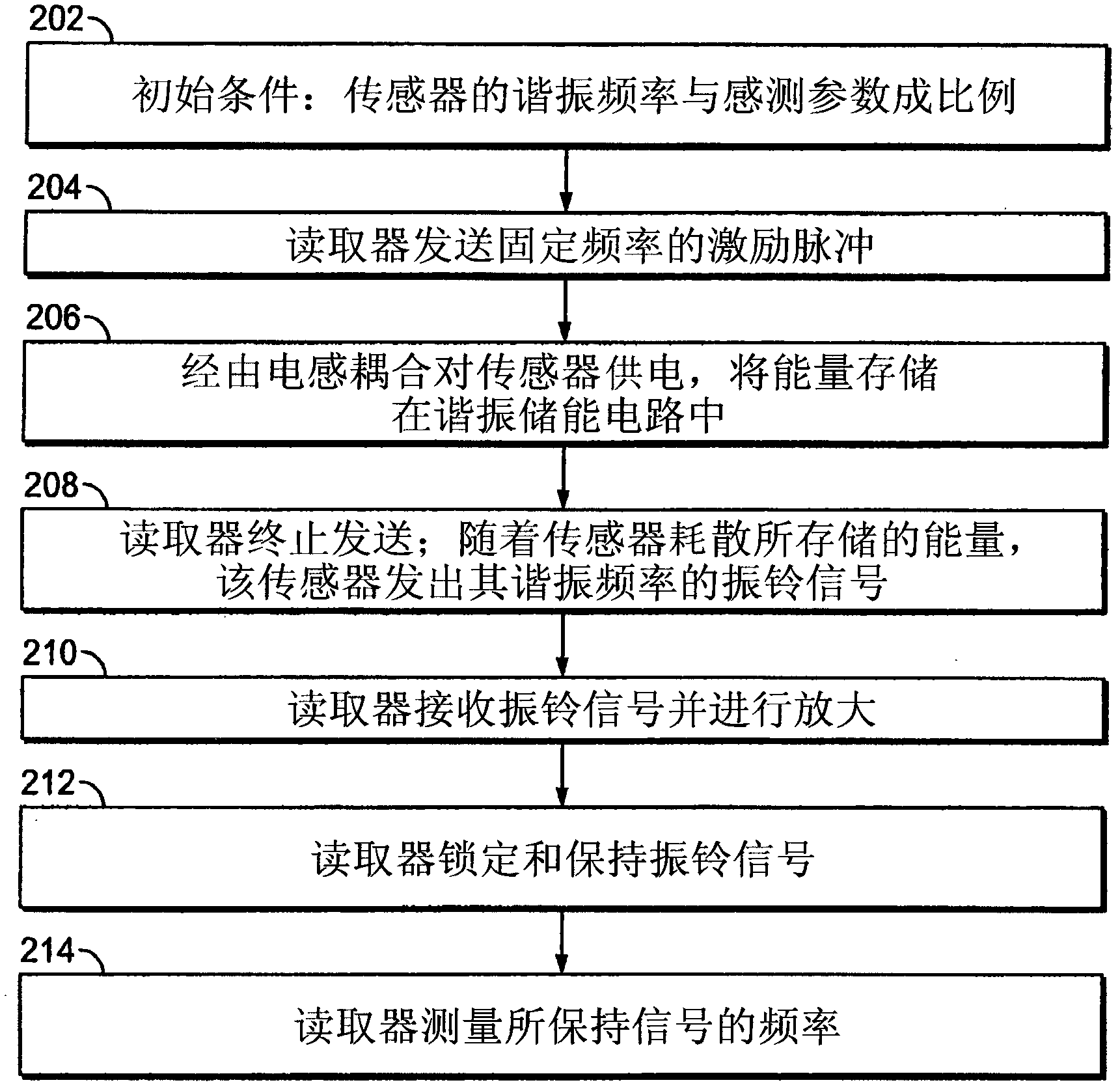
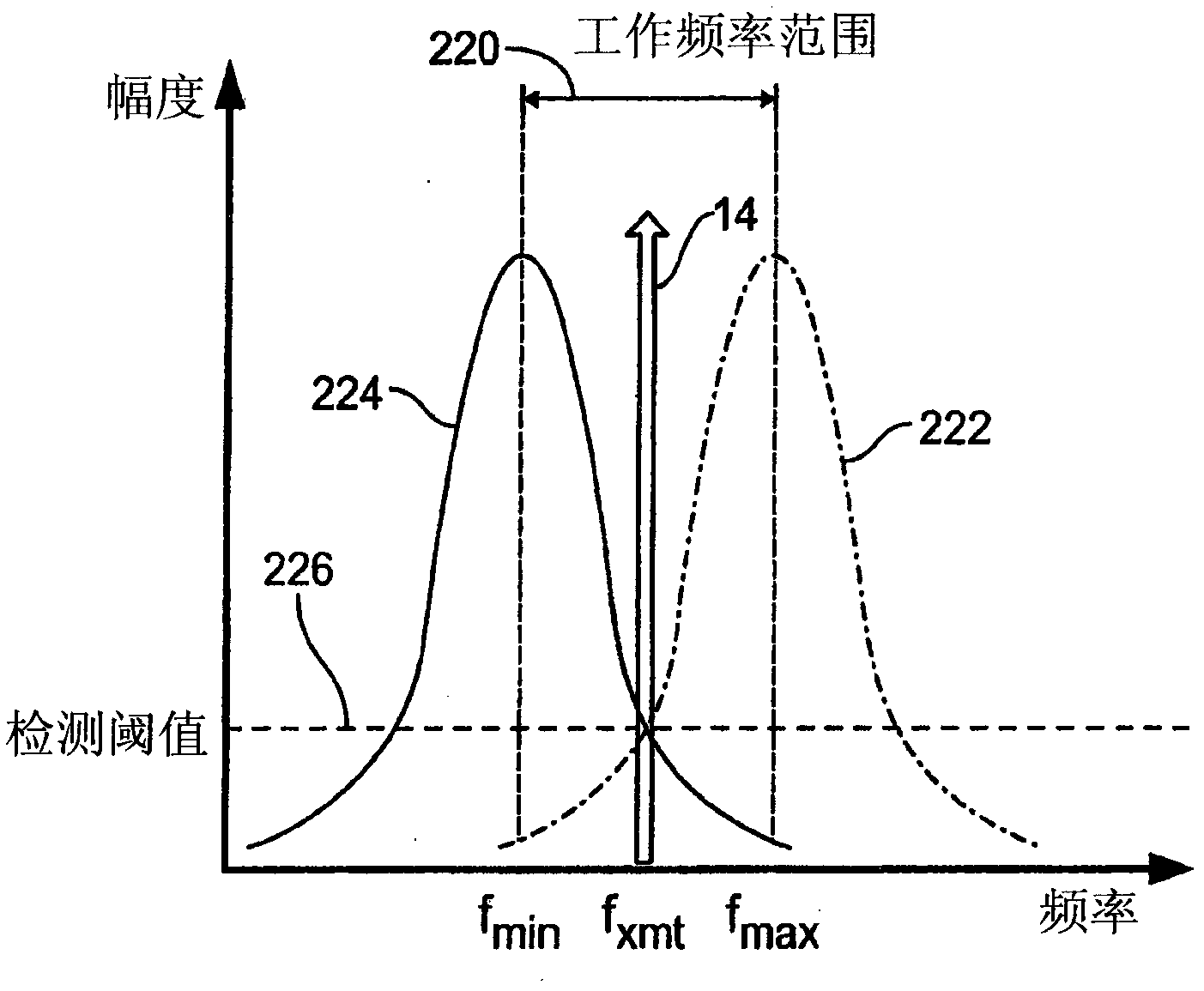
[0033] A passive wireless sensor system is provided wherein the passive wireless sensor system includes a reader 10 in remote communication with a sensor 12 . Reader 10 is capable of energizing sensor 12 by sending a signal, such as a radio frequency ("RF") pulse, at a frequency equal to or close to the resonant frequency of sensor 12 (see figure 1 ). The sensor 12 may emit a ringing signal for a short period of time in response to an excitation pulse from the reader 10 .
[0034] The sensor 12 may be a passive device that itself contains no power source and is capable of emitting a ringing signal 16 in response to an excitation signal 14 at or near the resonant frequency of the sensor 12 . Sensor 12 may be configured to sense a particular parameter. For example, sensor 12 may include a fixed inductor 13 and a capacitor 15 that varies based on a sensed parameter. Changing capacitance or inductance causes the resonant frequency of sensor 12 to change. However, it should be ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com