Index cache tree
An indexing and memory technology, applied in the field of memory mapping, can solve the problem of no longer storing data, and achieve the effect of reducing the average time and increasing the number of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] System Overview
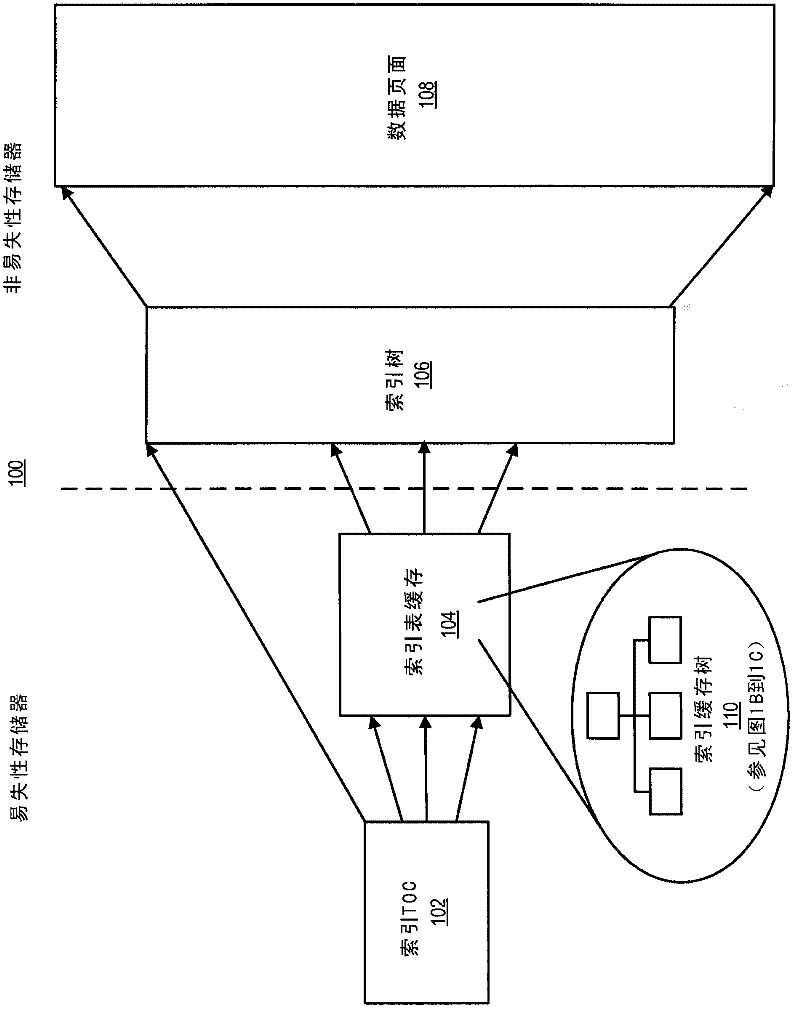
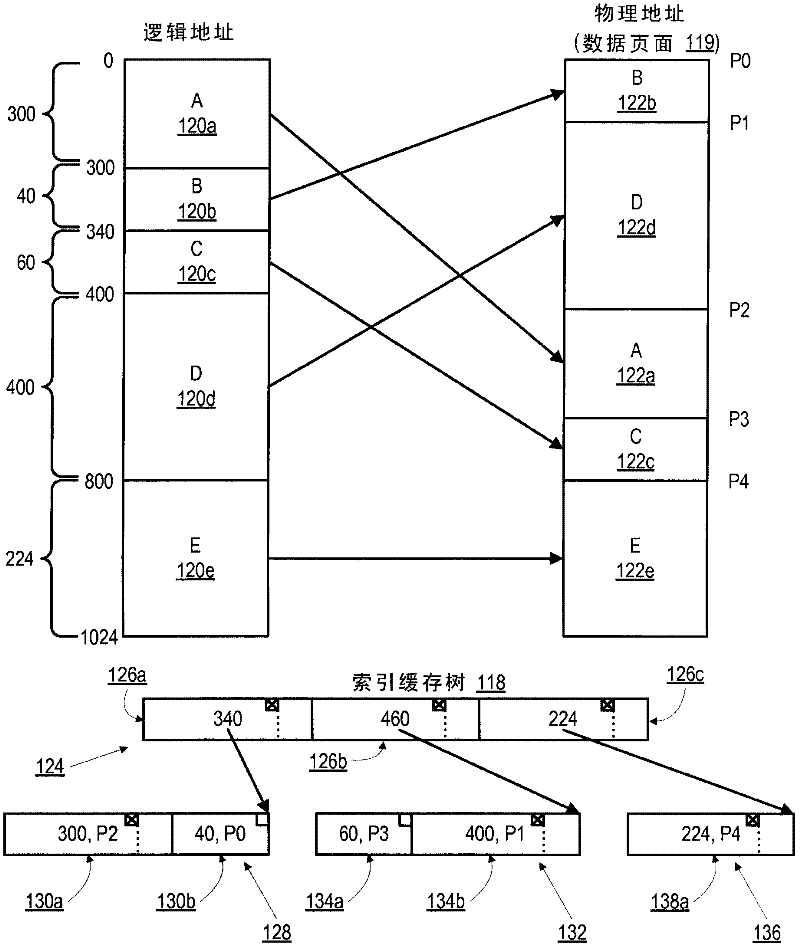
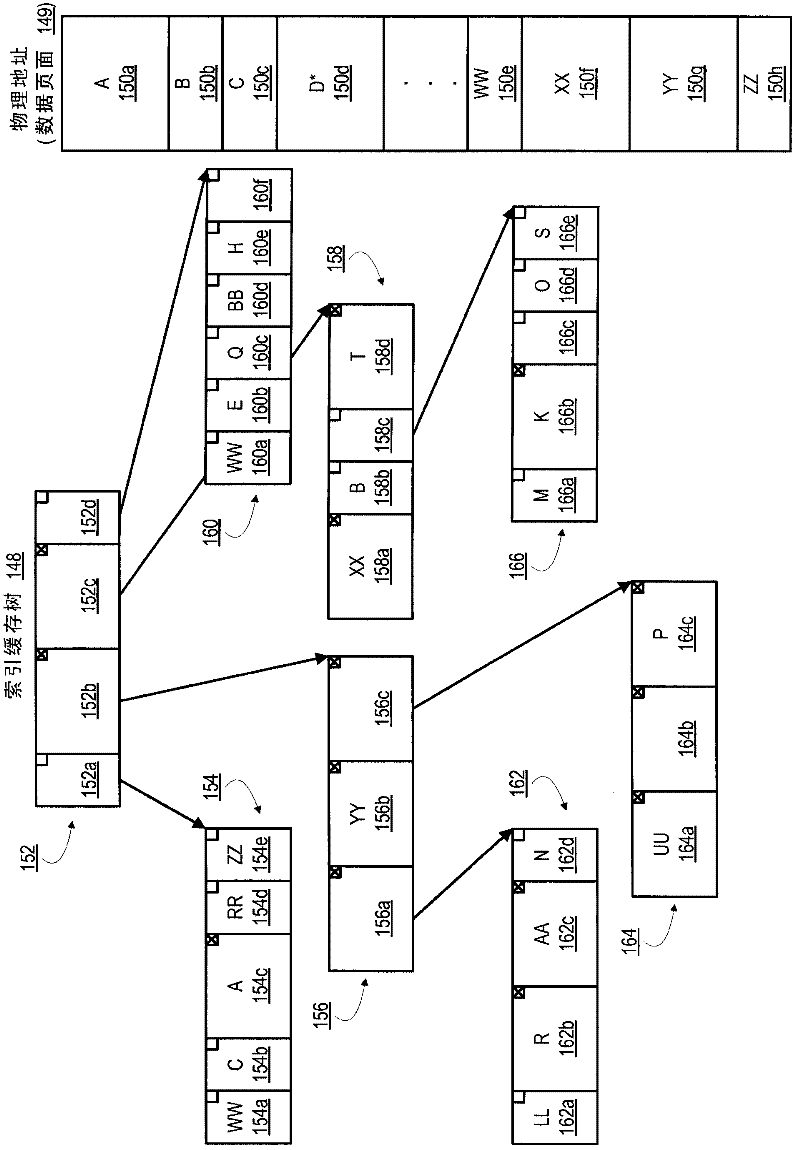
[0017] Figure 1A is a block diagram illustrating an example memory mapping architecture 100 for mapping logical sectors into physical pages using lookup tables and index cache trees. In some implementations, the look-up table 102 in volatile memory (eg, RAM) holds the location (eg, physical address) of the look-up table 106 in non-volatile memory (eg, flash memory). Lookup table 106 holds the physical addresses of data pages 108 . In some implementations, a cache 104 in non-volatile memory holds the physical addresses of recently written, read or accessed logical sectors to allow faster readout. In the example shown, lookup table 102 is also referred to as index TOC 102 , lookup table 106 is also referred to as index table 106 or index page, and cache 104 is also referred to as index table cache 104 .
[0018] In architecture 100, index TOC 102 and index table cache 104 enable at least a portion of index table 106 to be stored in non-volatile memor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com