Low-complexity dynamic asynchronous BP decoding method
A low-complexity and dynamic technology, applied in the field of LDPC code decoding, can solve the problems of high complexity, slow convergence, iteration times, and burden, and achieve the effect of improving decoding performance and faster algorithm convergence.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
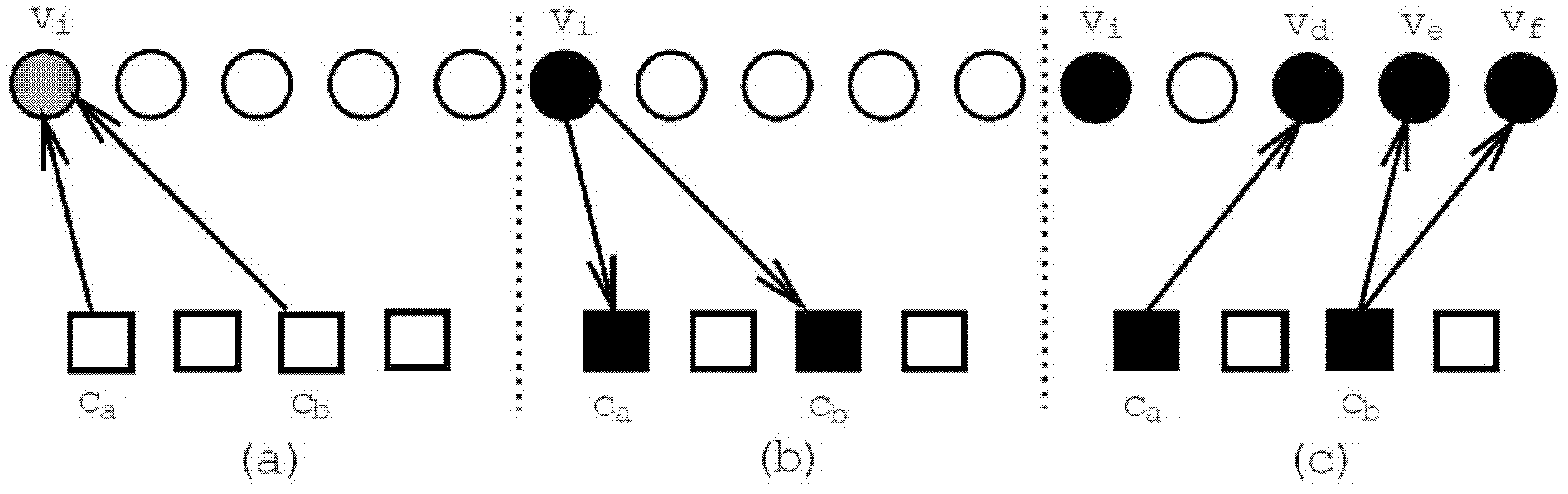
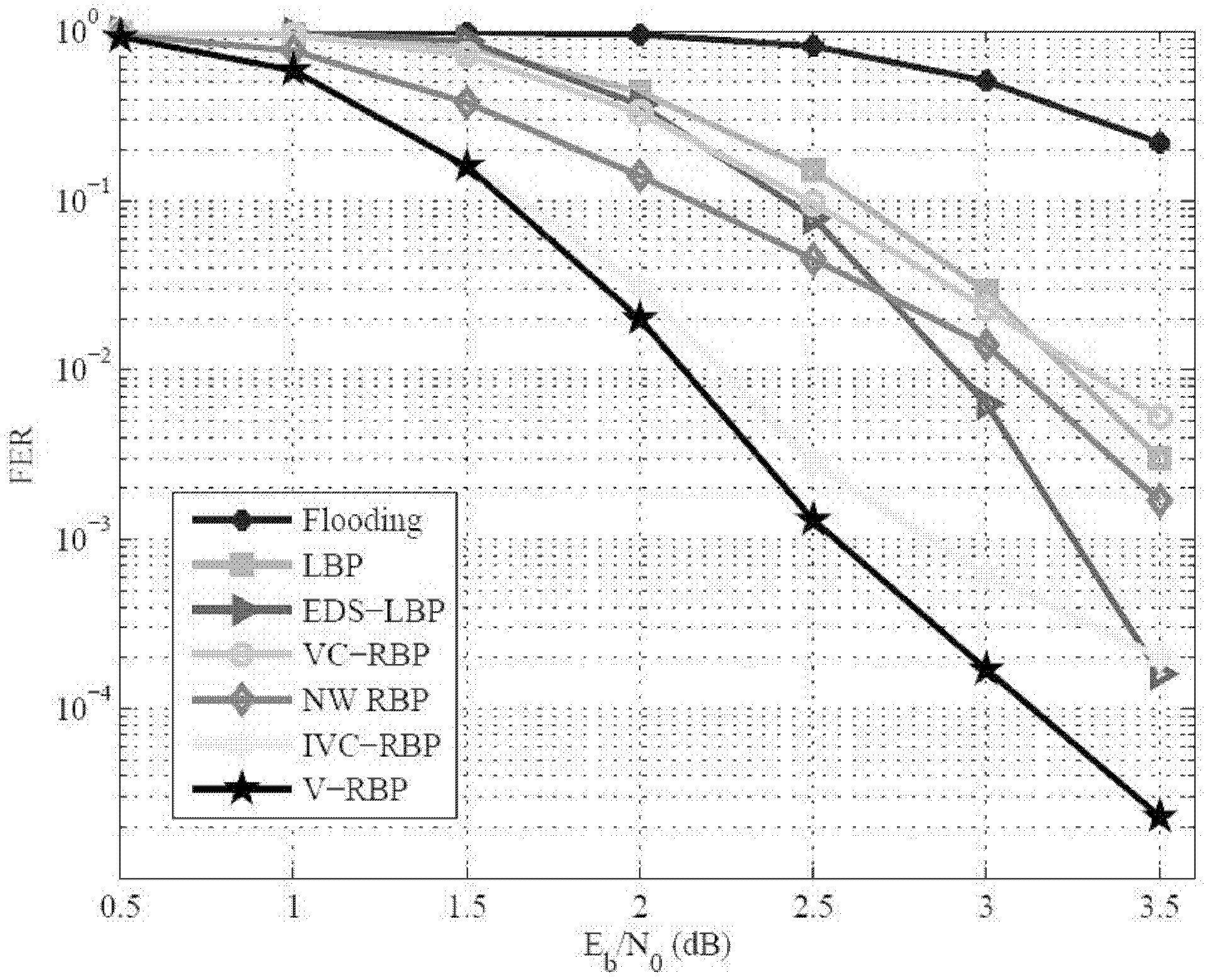
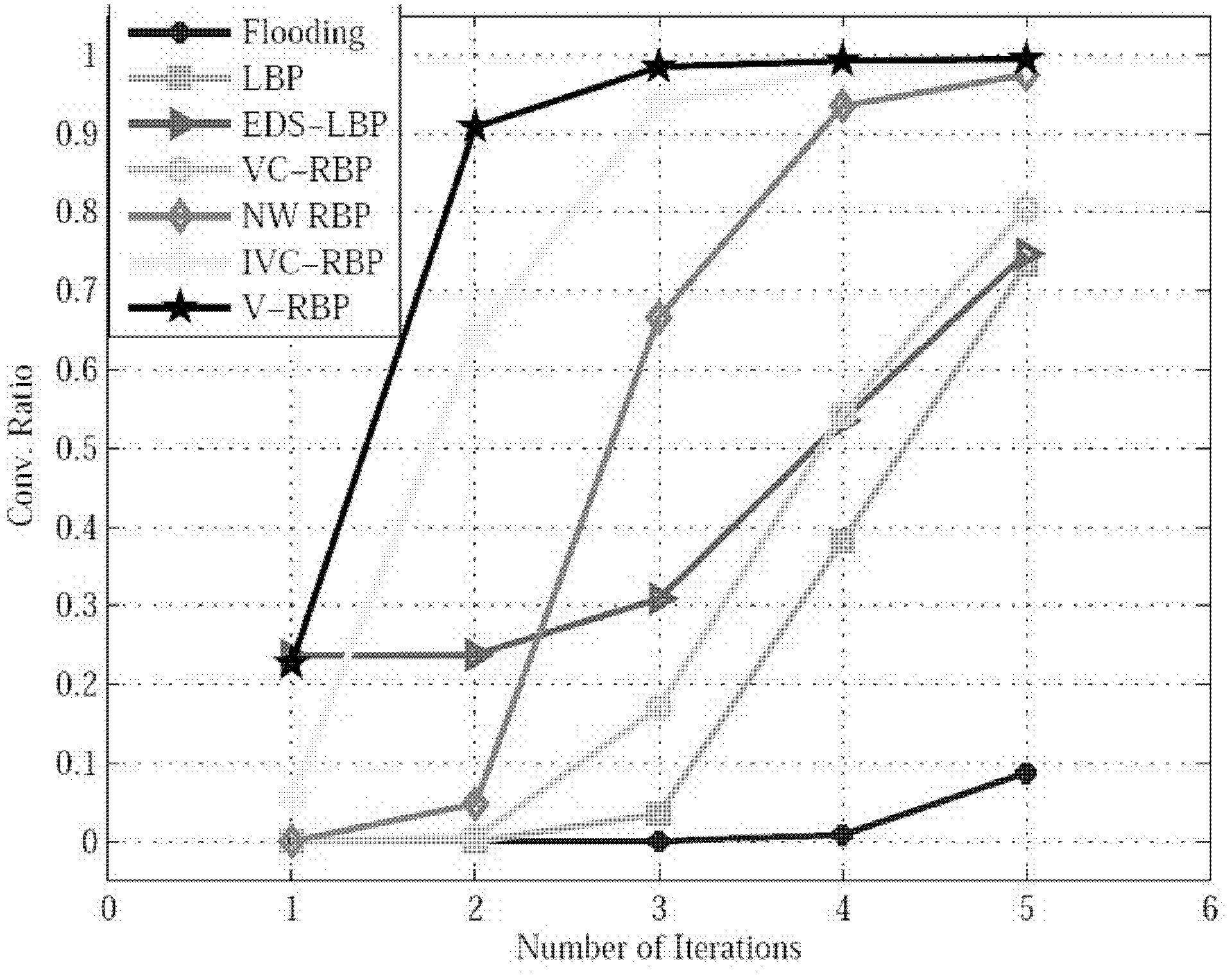
[0044] The present invention is aimed at a low-complexity dynamic asynchronous BP decoding method (V-RBP) for LDPC codes. The dynamic asynchronous message update strategy in the method includes a positioning method that utilizes the maximum fluctuation of the variable node likelihood A form of message passing for message computation from test nodes to variable nodes.
[0045] Let N(v i ) represents the node v with the variable i All connected check nodes, N(v i )\c j It means to remove the check node c j Outside with the variable node v i All connected check nodes; N(c i ) represents and check node (check equation) c i All connected variable nodes, N(c i )\v j Then it means to remove the variable node v j In addition to check node c i All connected variable nodes. The message function of the interconnected variable nodes and check nodes can be defined as where m means all messages. Prior probability of the channel (p v (0),p v (1) represent the probability ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com