Fault monitoring and forecasting method of direct current (DC)-direct current (DC) power source system
A DC-DC and power system technology, applied in the field of DC-DC power system fault monitoring and prediction, can solve problems such as the difficulty of constructing fault trees, easy omissions in analysis, and inability to clearly analyze fault mechanisms, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
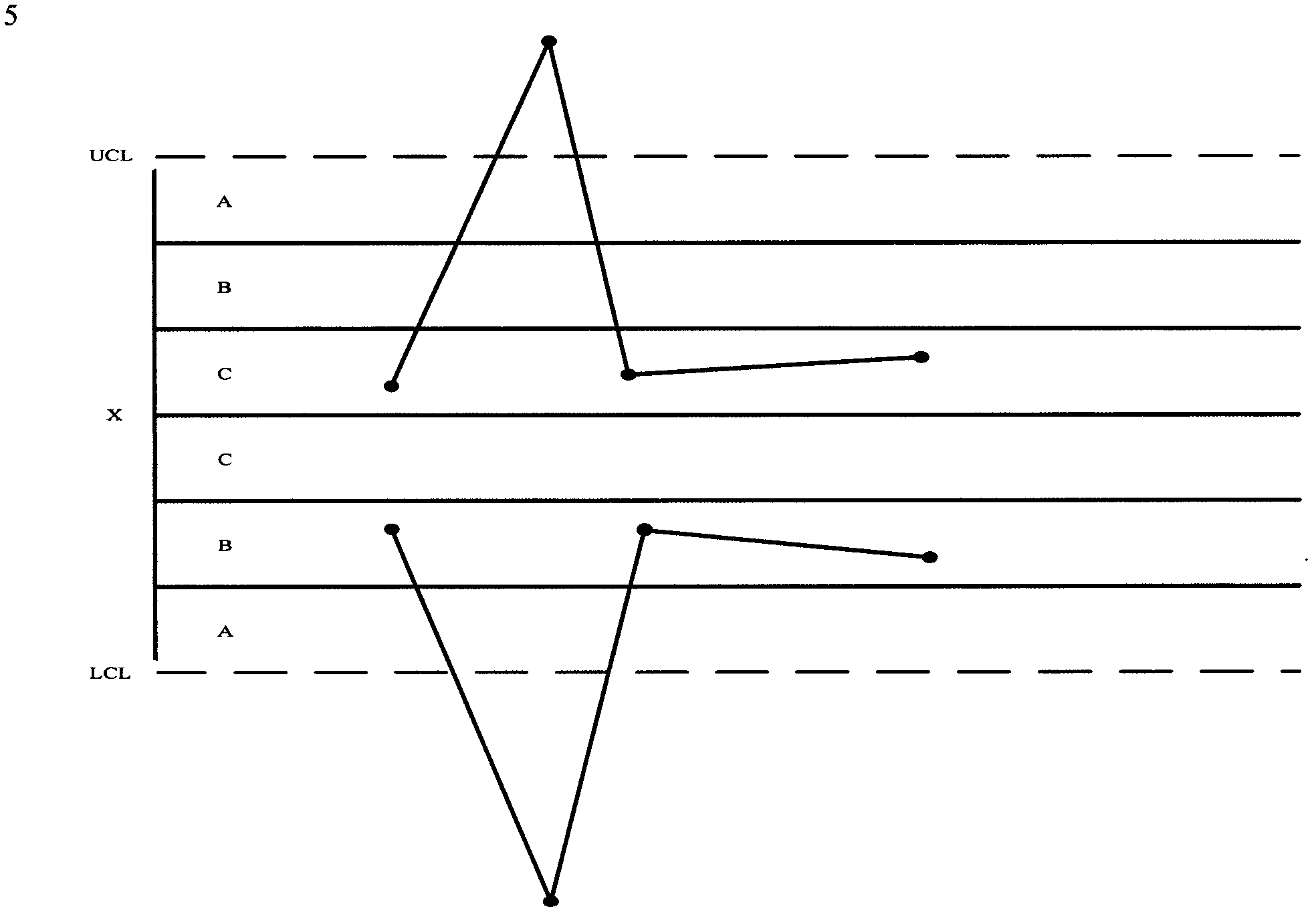
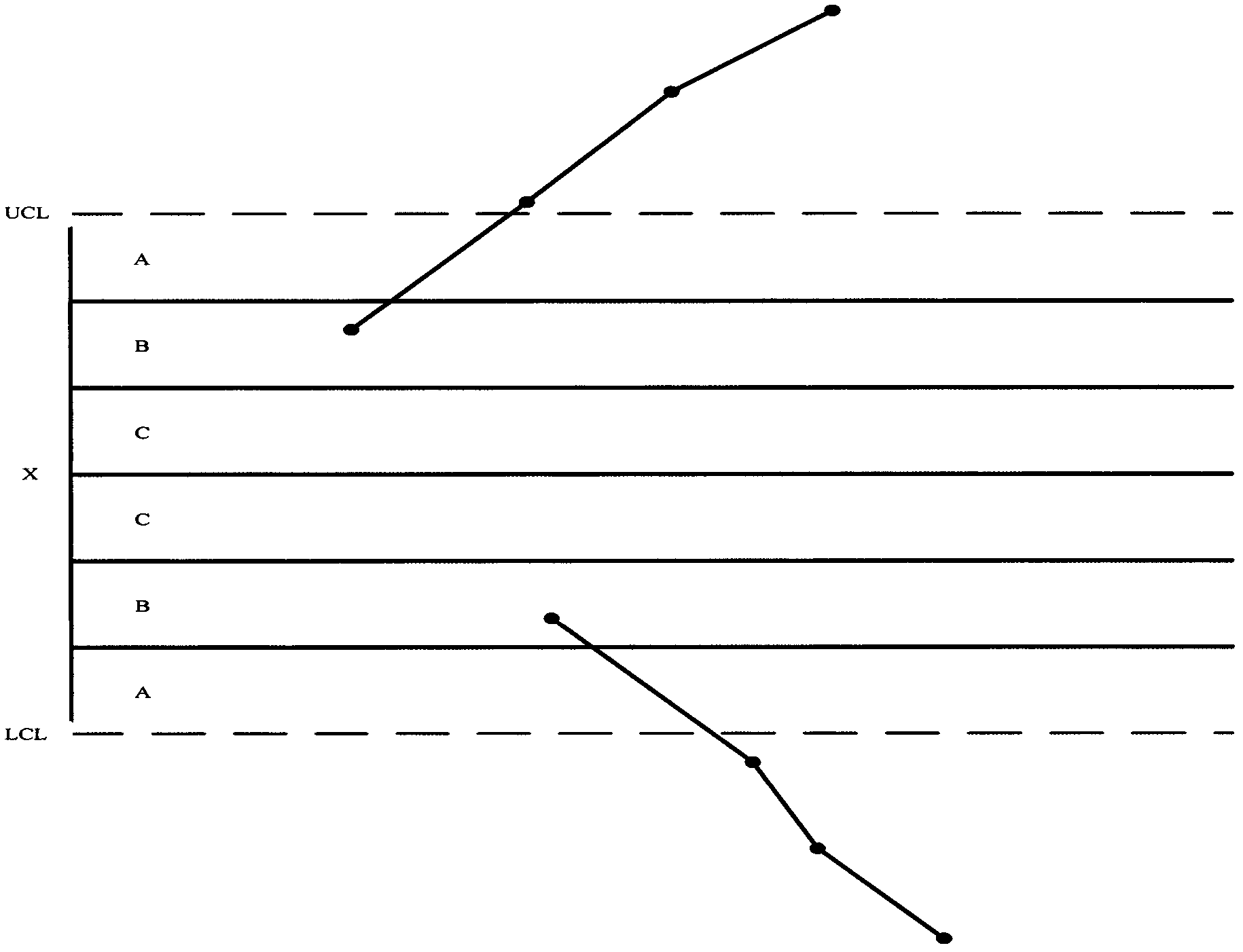
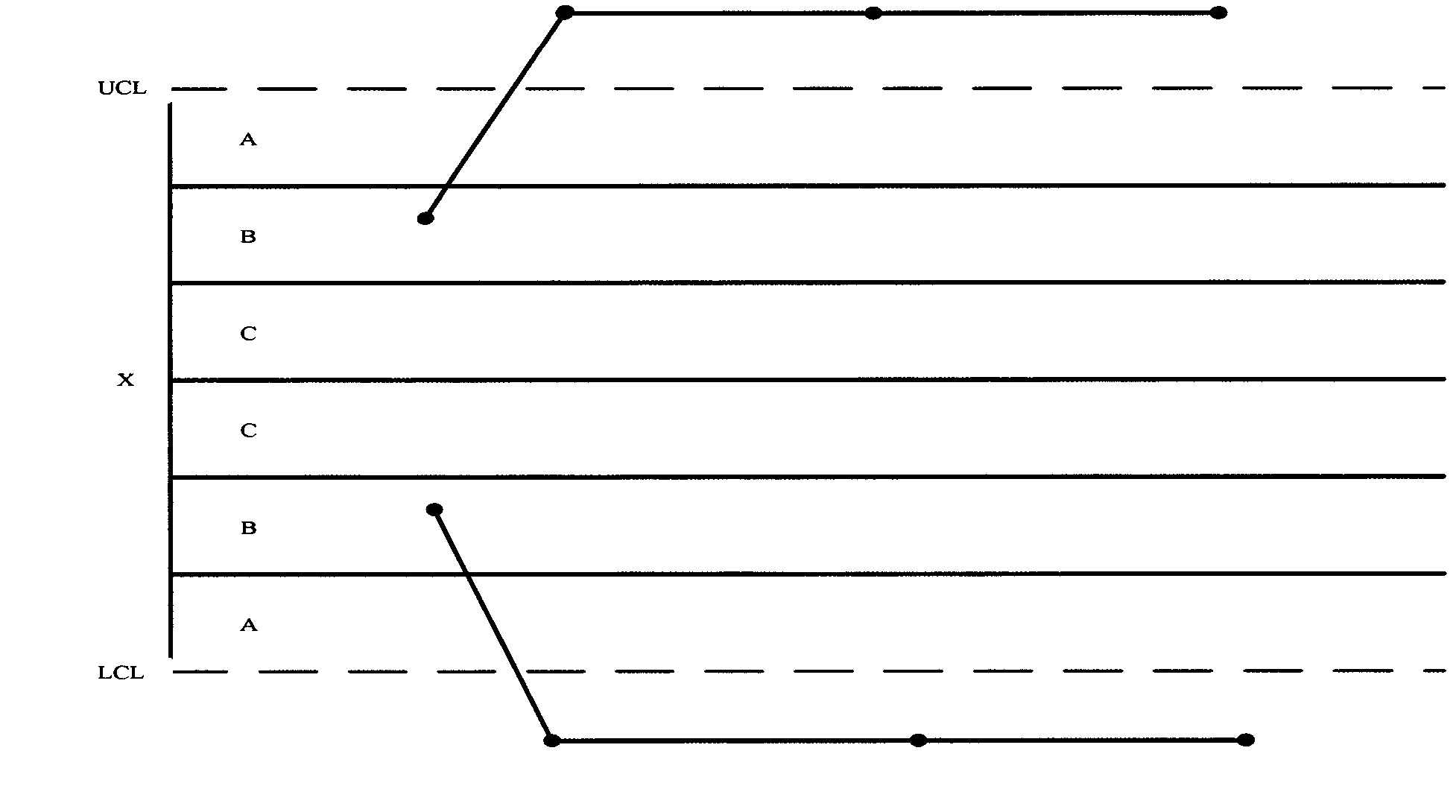
[0026] Figure 1 to Figure 9 Among them, X is the standard output of the DC-DC power supply system, UCL and LCL are the upper control boundary and lower control boundary for judging whether to cross the ±3σ boundary, respectively, and the range of A area is between -3σ and -2σ or between +2σ and +3σ , the range of area B is between -2σ and -1σ or between 1σ and 2σ, and the range of area C is between -1σ and 0 or between 0 and +1σ. When the DC-DC power system is running in a steady state, the ±1σ, ±2σ and ±3σ boundaries can be calculated according to the ±1%, ±5% and ±10% of its output voltage, respectively, and the DC-DC power system faults The monitoring and forecasting provide a basis for judgment.
[0027] figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 It is a specific implementation manner of monitoring a fault in a DC-DC power supply system during operation.
[0028] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com