Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
A manufacturing method, semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as increased parasitic capacitance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
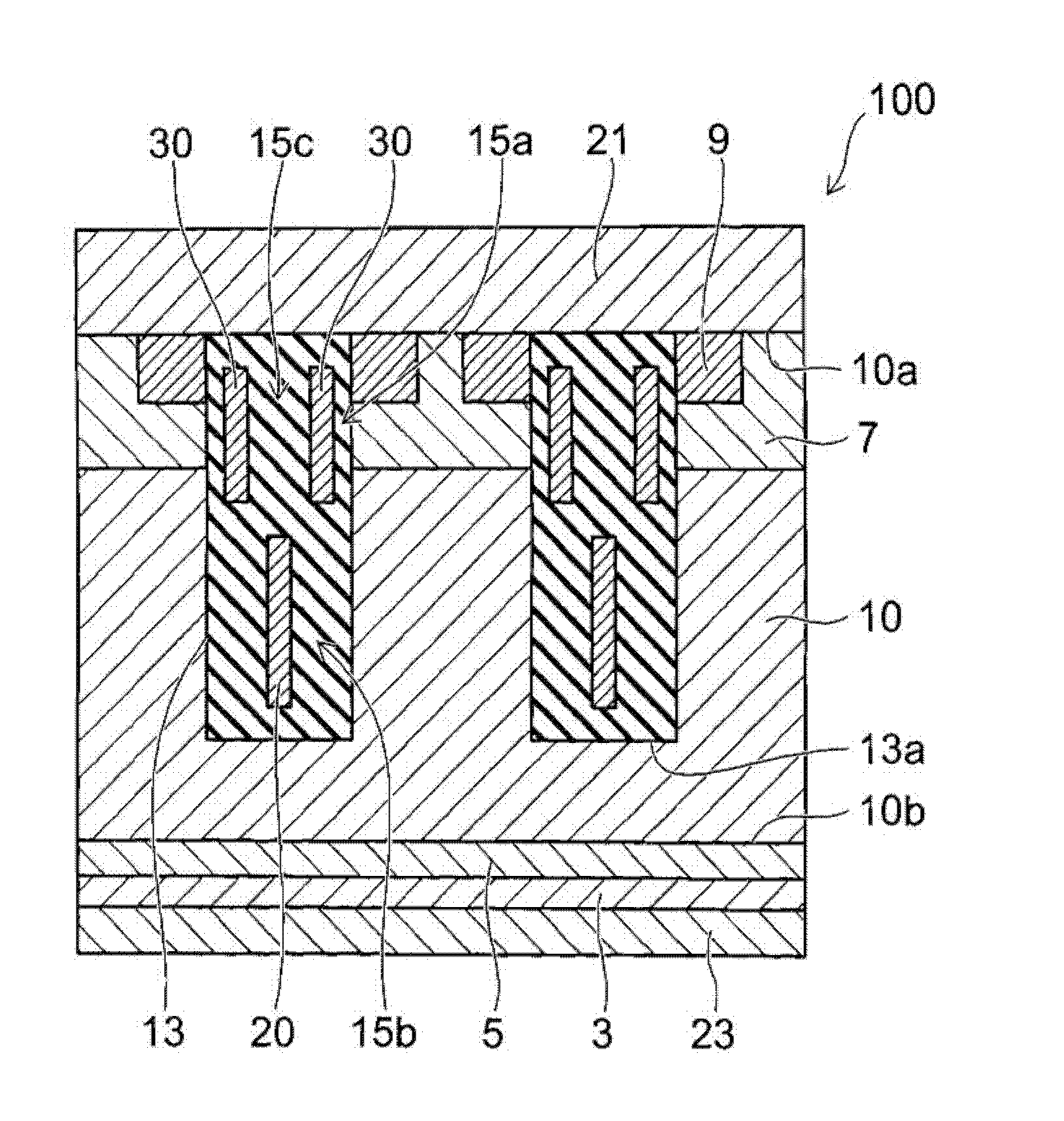
[0020] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing the cross-sectional structure of the semiconductor device 100 according to this embodiment. The semiconductor device 100 illustrated here is a power MOSFET having a trench gate structure.
[0021] The semiconductor device 100 has, for example: an n-type drain layer 5 provided on an n-type silicon substrate 3; and a drift layer 10 which is an n-type semiconductor layer. Furthermore, a p-type base region 7 as a first semiconductor region is provided on the surface of the n-type drift layer on the first main surface 10 a side. Furthermore, an n-type source region 9 as a second semiconductor region is provided on the surface of the p-type base region 7 .
[0022] A source electrode 21 as a first main electrode is provided on the first main surface 10 a side of the n-type drift layer 10 . Source electrode 21 is electrically connected to p-type base region 7 and n-type source region 9 .
[0023] On the other hand, a drain electro...
no. 2 approach
[0048] Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram showing the cross-sectional structure of the semiconductor device 300 according to the second embodiment. The semiconductor device 300 is a Schottky barrier diode (SBD) having a trench gate structure, and the Schottky barrier diode (SBD) includes a gate electrode 61 and a field electrode 62 as a second control electrode.
[0049] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the semiconductor device 300 has: an n-type drift layer 10; an anode electrode 41 is a first main electrode arranged on the first main surface 10a side of the n-type drift layer 10; a cathode electrode 43 is arranged on a second main surface 10b side of the second main electrode. A Schottky junction is formed between the anode electrode 41 and the n-type drift layer 10 .
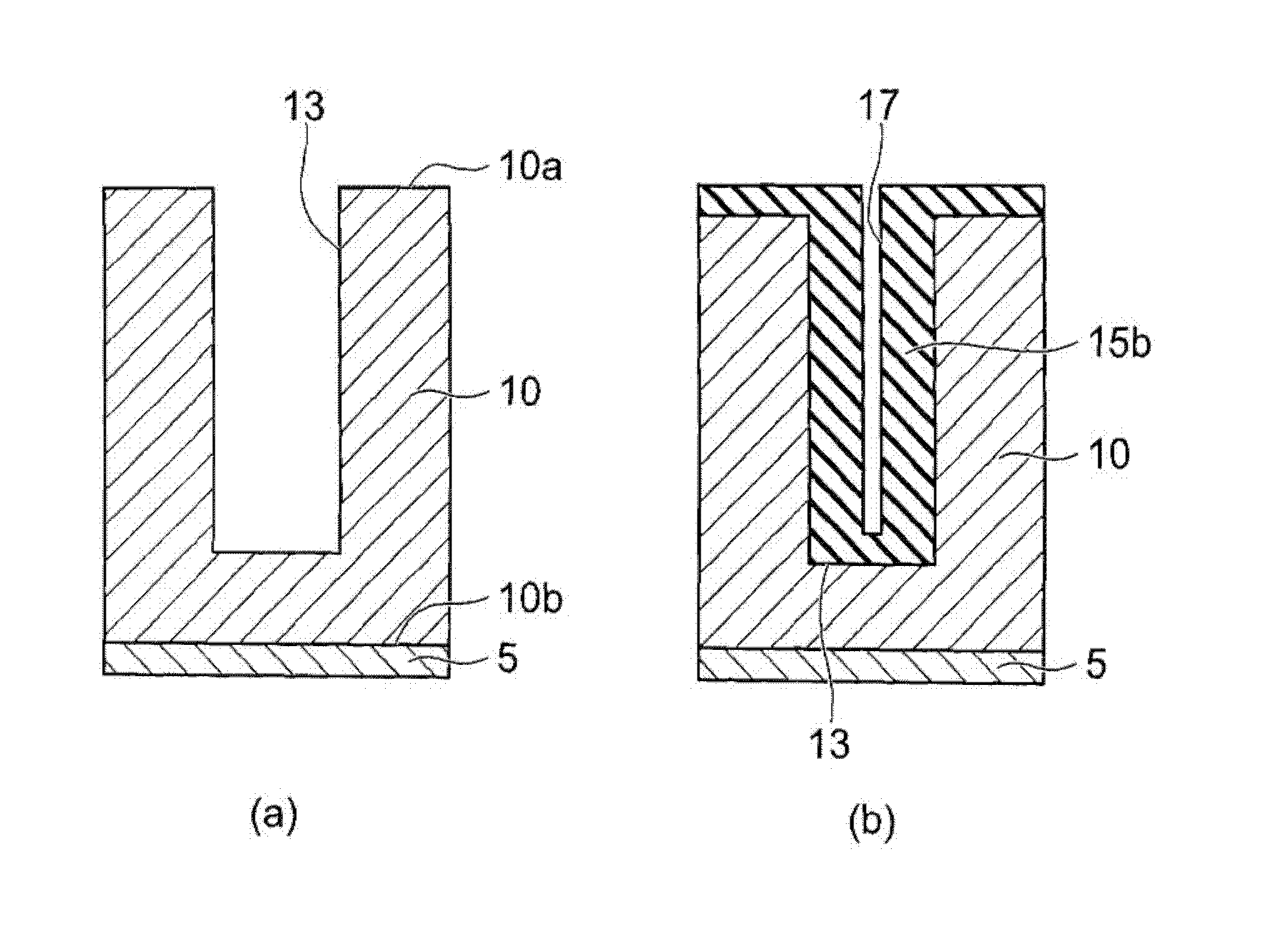
[0050] Further, trench 13 is formed in the direction from the first main surface 10 a side of n-type drift layer 10 toward the second main surface 10 b. Two gate electrodes 61 and a field electrode 62 are pro...
no. 3 approach
[0053] Figure 9 It is a schematic diagram showing a cross-sectional structure of a semiconductor device 400 according to the third embodiment. The semiconductor device 400 is an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor: Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) having a trench gate structure, and has a p-type collector layer 45 and a collector electrode 53 on the second main surface 40b side of the n-type base layer 40. this, with figure 1 The illustrated semiconductor device 100 is different.
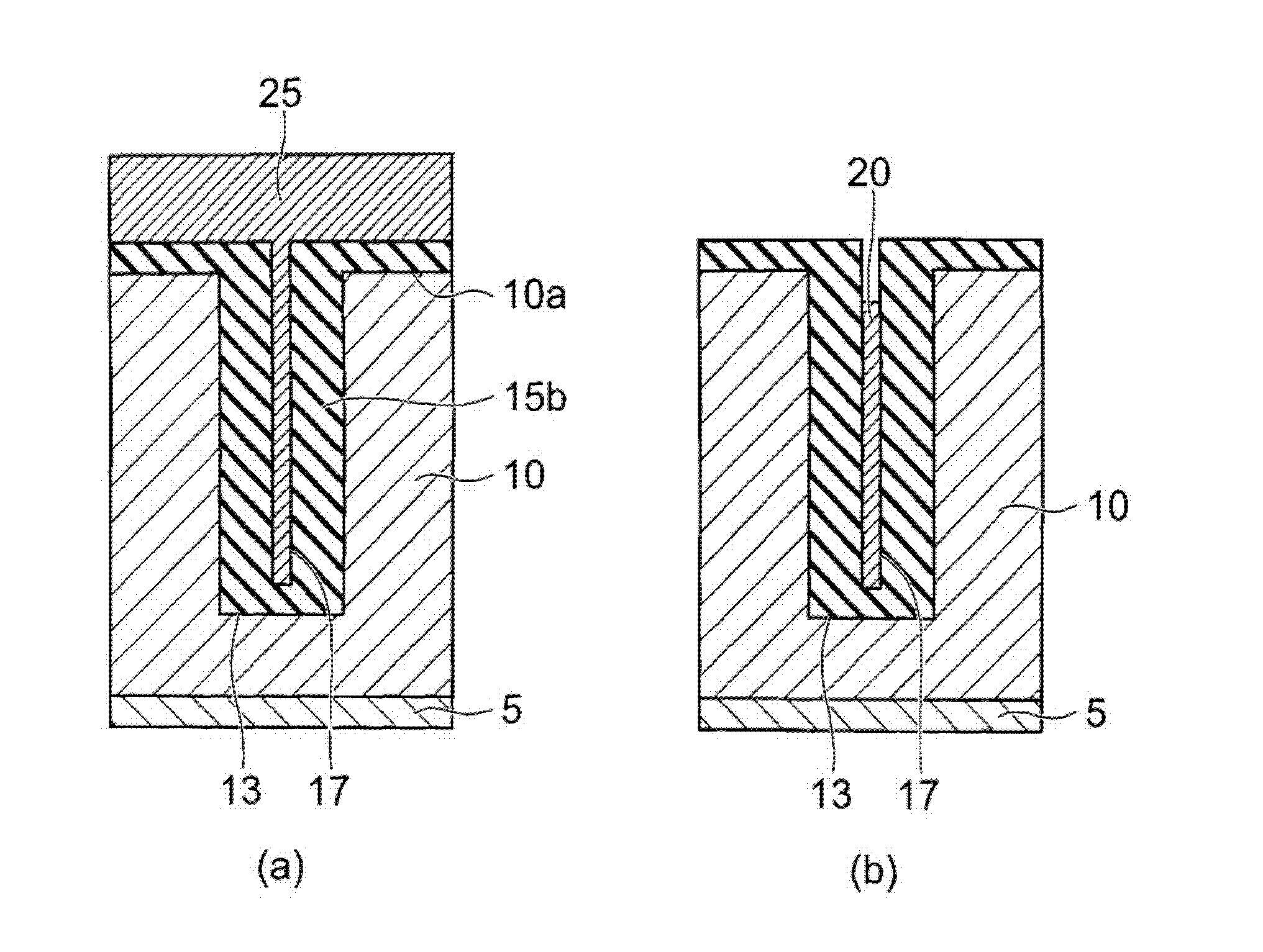
[0054] In the semiconductor device 400, a trench gate structure including a field electrode 20, a p-type base region 47 and an n-type emitter region 49, and an emitter electrode 51. Thereafter, the n-type silicon substrate 3 is removed on the side of the second main surface 40b, and the p-type current collecting layer 45 is provided by, for example, ion-implanting p-type impurities. Then, a collector electrode 53 connected to the p-type collector layer is provided.
[0055] Such as Fig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com