Topographical map high-fidelity reducing method utilizing rotating TIN (triangulated irregular network) overlay analysis
A topographic map, high-fidelity technology, applied in graphics and image conversion, image data processing, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of improving distortion problems, saving sampling points, and large coverage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
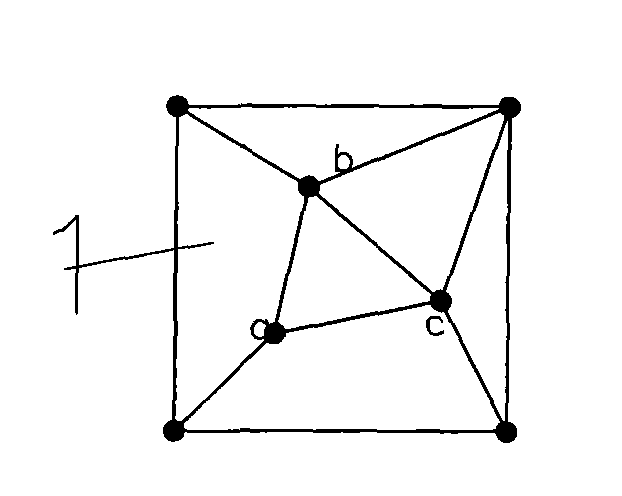
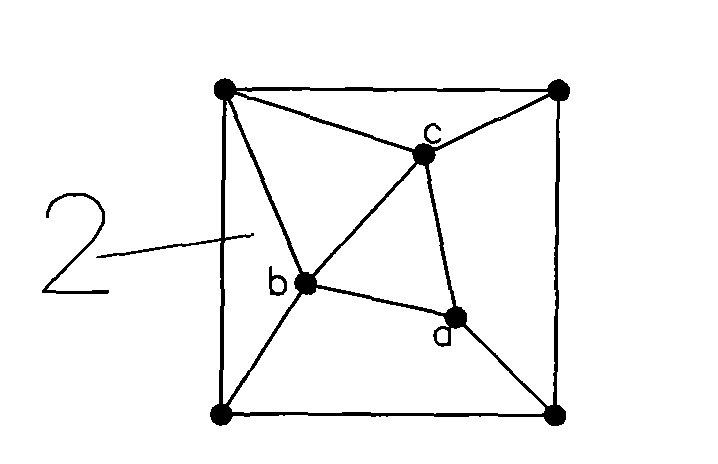
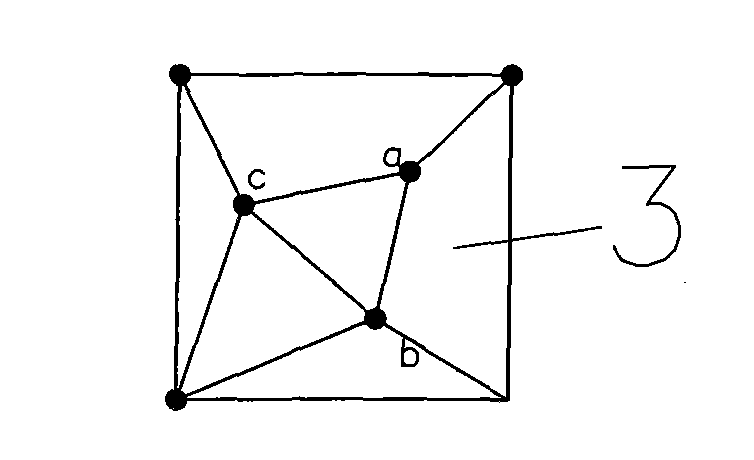
[0007] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 7 This embodiment will be specifically described. The present embodiment comprises the following steps: 1. In the present embodiment, 10m (measured on a drawing scale) is used as the side length of the basic square of the rotating TIN network. 2. Arrange one sampling point at each of the four vertices of the basic square, and distribute 3 sampling points in the basic square, a total of 7 sampling points, and the distance between any two of the 3 sampling points scattered in the square Between 0.20 and 0.85 times the side length of the basic square. The vertices of the basic square and the internal sampling points are connected by triangles to ensure that the length of the connection between any two adjacent sampling points is between 0.20 and 0.85 times the side length of the basic square, which has good interlacing and dispersion. All interior angles of all triangles in the basic square s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0008] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that step A is also included between step 4 and step 5, scaling the length or width of the supporting unit to make it a rectangle, and the positions of all sampling points inside Adjust as stated. Other steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0009]Specific embodiment three; see schematic diagram 8 to schematic diagram 13, the difference between this embodiment and embodiment one is: in step two, the three surveying and mapping points dispersedly arranged in the basic square are respectively, a (6, 6), b(15, 24), c(24, 15); other steps are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com