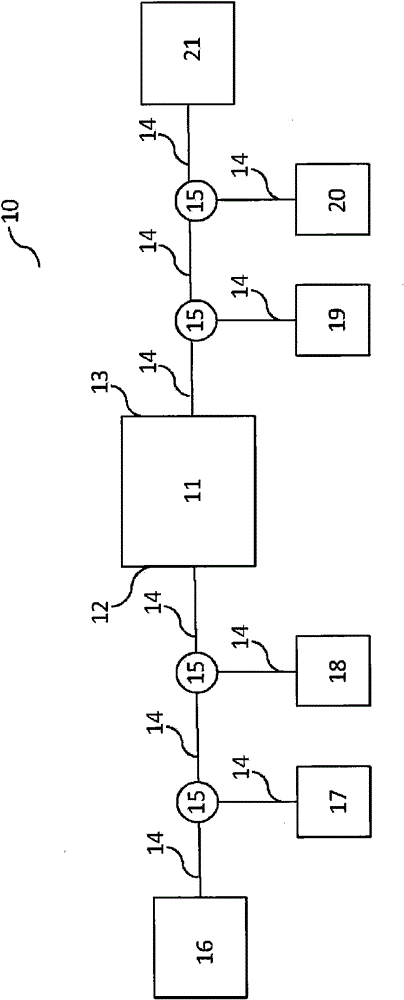
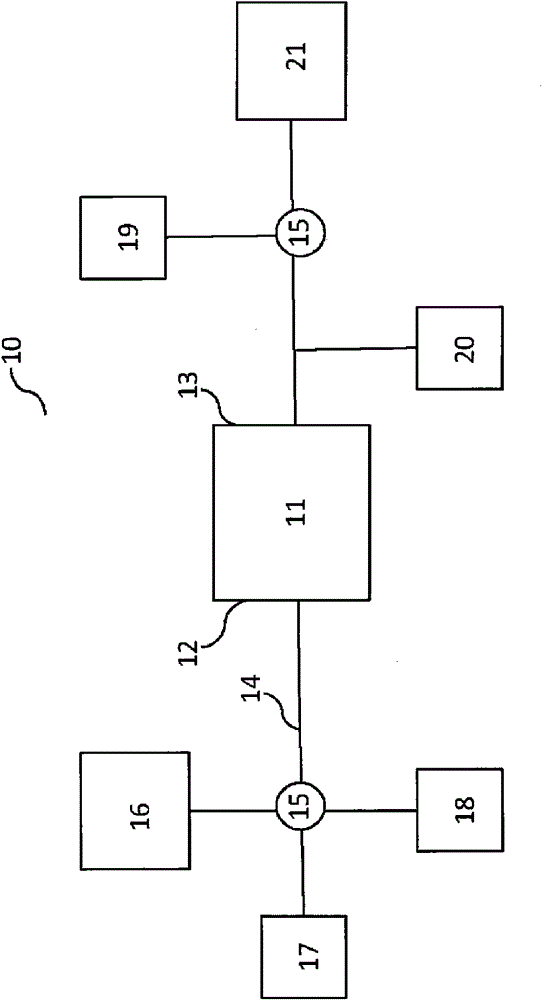
Device and method for biological sample purification and enrichment
A sample and injection port technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, biochemical cleaning devices, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to reduce the need for repeated sampling and to quickly diagnose information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Example 1 Flush of bladder contaminated with red blood cells
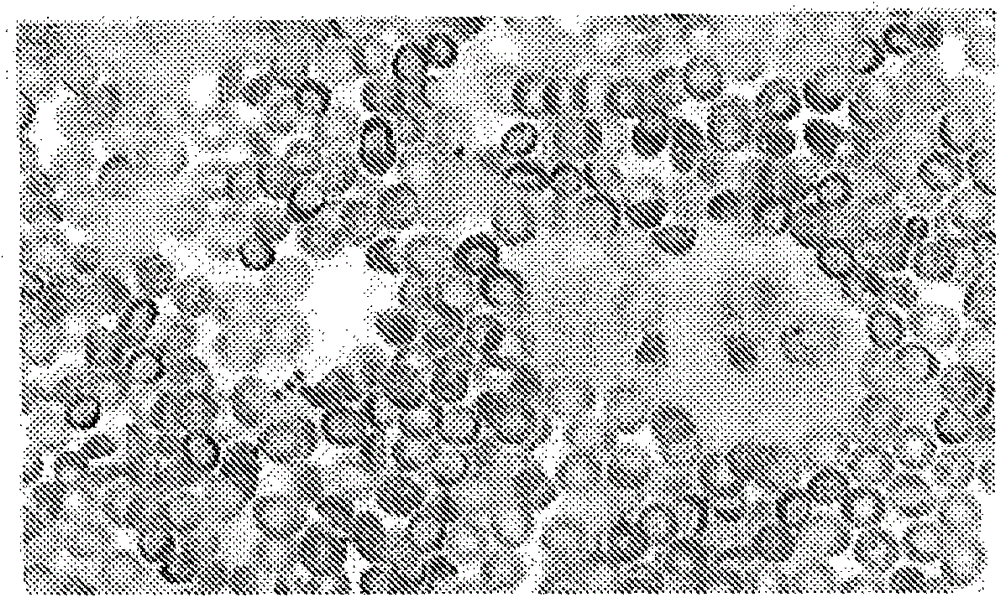
[0075] Perform bladder flushes on living organisms to collect flushes that may contain suspended cells and contaminants. Preliminary microscopic analysis of stained droplets of the sample confirmed the presence of a large number of red blood cells and a small number of possible target cells, see image 3 . The remaining sample was added to the injection port of the device of the present invention and filtered.
[0076] The processing time is about 10 minutes. The device reaches a maximum pressure of 140mm H when it first draws the sample through the filter 2 O. Material captured in the first aspiration reservoir was placed on slides and stained. Purified and enriched target cells are easily visualized in their native state by microscopy, see Figure 4 .
[0077] For comparison, a second suction reservoir was used. The material captured in the second aspiration reservoir was placed on a slide and stai...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Example 2 Ascites fluid contaminated by epithelial cells
[0079] Ascites fluid samples were obtained. Stained droplets of this fluid, viewed under a microscope, show a large number of epithelial cells and a small number of possible target cells, see Figure 5 . The remaining 10ml of sample was loaded into a 200ml inlet tube and filtered using the device of the present invention.
[0080] The process ends in approximately 10 minutes, during which time a maximum pressure of 140 mm H is reached on the first draw of the sample through the filter 2 O. Material captured in the first aspiration reservoir was placed on slides and stained. Purified and enriched target cells are easily visualized in their native state by microscopy, see Figure 6 .
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3 Secondary purification and enrichment
[0082] Samples containing cells, including peripheral blood cells, are provided. The cells are chemically lysed according to known techniques. The cellular content is loaded into the inlet tube of the device according to the invention.
[0083] The first process is performed by using a filter whose pores are able to allow the free passage of most subcellular components but retain the largest: the nucleus. After this operation of the system, the nuclei are retained for subsequent use and the remaining components collected in the second suction reservoir are removed. The system is again ready for use and the components previously collected in the second aspiration reservoir are loaded into the injection port.
[0084] The second process is performed using a filter with pores that allow the free passage of most of the cellular components but retains the large mitochondria from this fraction. After this procedure, the nu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com