Biological thermochemistry method for safety evaluation and screening of cigarette auxiliary material
A technology for safety evaluation and auxiliary materials, applied in the field of cigarette harm reduction effect and safety, which can solve the problems of long cycle, high cost and low efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
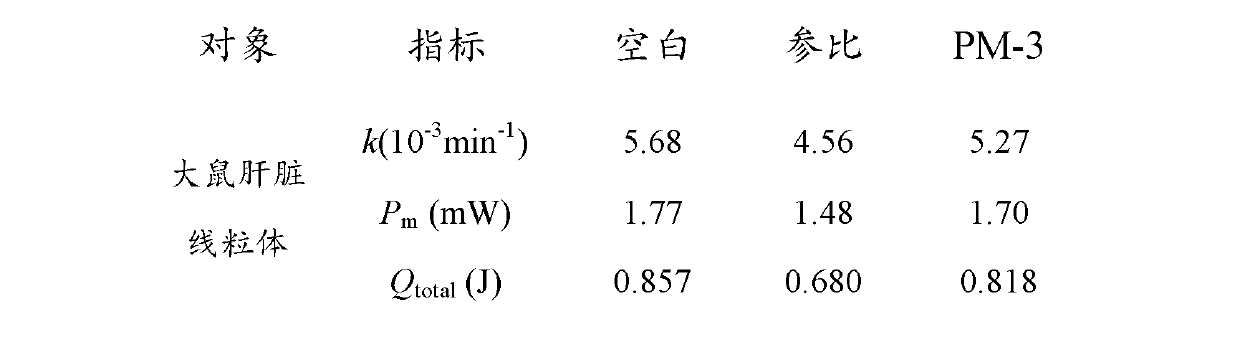
[0034] The preliminary identification of the biological effect of a new type of titanium dioxide-doped fullerene harm reduction material for cigarettes is designated as CB02. This new type of fullerene material has a very good purification effect on harmful components in flue gas. Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans were used as models to study organisms, and their metabolic processes were monitored in real time by TAM3 microcalorimeter. We collected the mainstream smoke of the cigarette after adding this material, and compared it with the smoke of the same kind of cigarette without adding this material. Put the Cambridge filters that have captured mainstream smoke into numbered wide-mouth conical flasks, add a certain amount of 10ml of distilled water to soak and shake for 30min. After filtration, accurately take out 100 μl of the filtrate corresponding to the number from each Erlenmeyer flask and add it to 5 ml of culture medium that has been inocu...
Embodiment 2
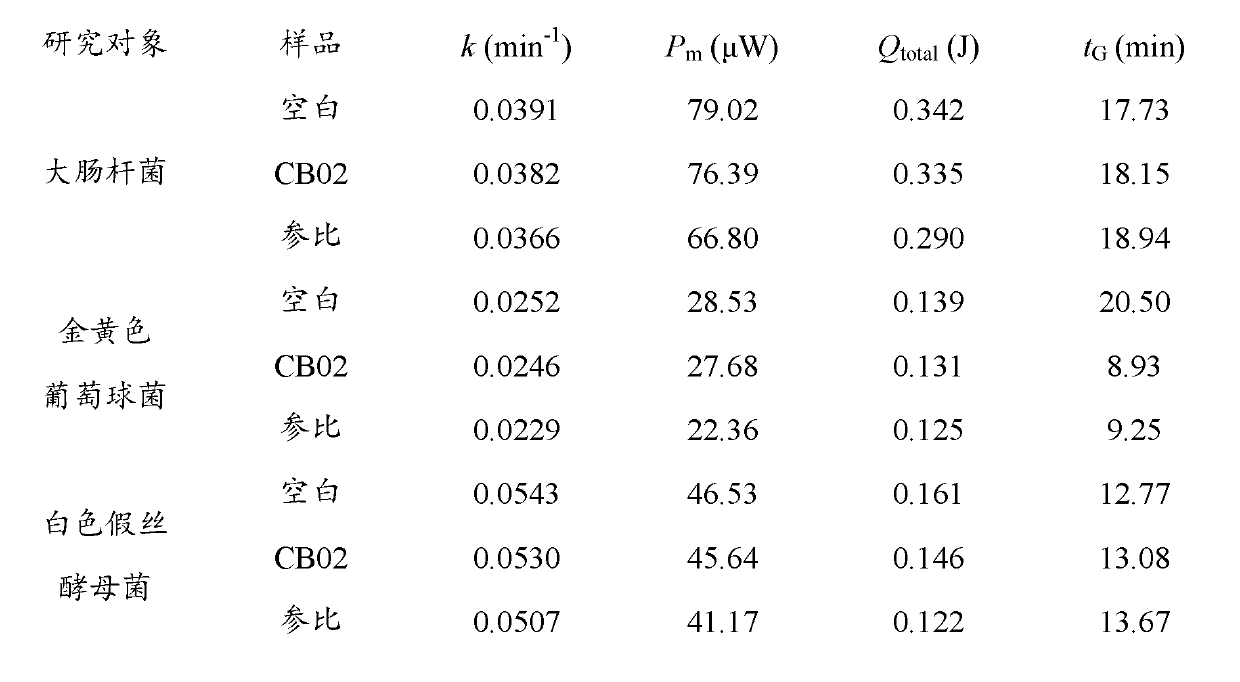
[0038] The filter effects of four new functional carbon nanotube composite filters for cigarettes were analyzed. The first two are mostly walled carbon nanotubes, with diameters of 5 nm and 10 nm, respectively; the latter two are single-walled carbon nanotubes, with diameters of 2 nm and 1 nm, respectively. Theoretically, these four filters have different degrees of adsorption and selectivity effects on smoke, and they are numbered 1#, 2#, 3# and 4# respectively. Using microcalorimetry technology can quickly and accurately compare the filtering capabilities of these four filters and evaluate their filtering capabilities. Screening and excluding filters with obviously poor effects does not require evaluation of pilot tests or industrial applications, which saves a lot of money and time. The same brand of shredded tobacco was used in the experiment, and the cigarette of this brand was used as the reference cigarette. Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus plantarum, Bacillus ...
Embodiment 3
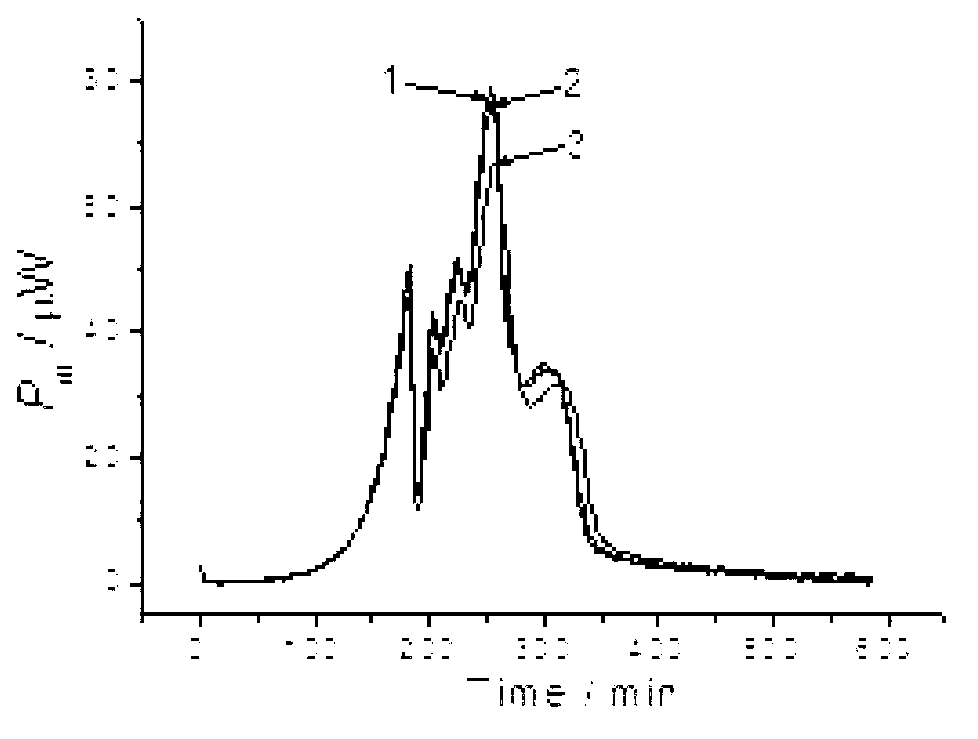
[0042] For improving the burning effect and slowing down the burning speed of the two new types of cigarette paper, they are numbered 1# and 2# respectively. These two kinds of cigarette papers were respectively added with 2 different flame retardants - 1# was added with aluminum hydroxide (1%), and 2# was added with magnesium hydroxide (1%). The two flame retardants can slow down the burning speed of the cigarette paper, make the burning process more complete, reduce the release of harmful substances, and are easy to prepare and low in cost. Before carrying out large-scale industrial testing, we first use microcalorimetry to conduct a preliminary assessment of the harm reduction effect. Taking Bacillus thuringiensis as a model to study organisms, TAM 3 microcalorimeter was used to monitor the influence of smoke components after burning two kinds of cigarette papers on Bacillus thuringiensis. The microcalorimetry experiment obtained various physical and chemical indicators re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com