Method for measuring heat consuming user heating load of vertical single tube cocurrent type system and heating metering distributing system of vertical single tube cocurrent type system
A technology for heat supply and heat users, which is applied in the field of heat metering and distribution systems, can solve the problems of difficult heat metering transformation of building vertical single-pipe downstream systems, and achieve the effect of simple transformation, less disturbance to residents, and low transformation cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
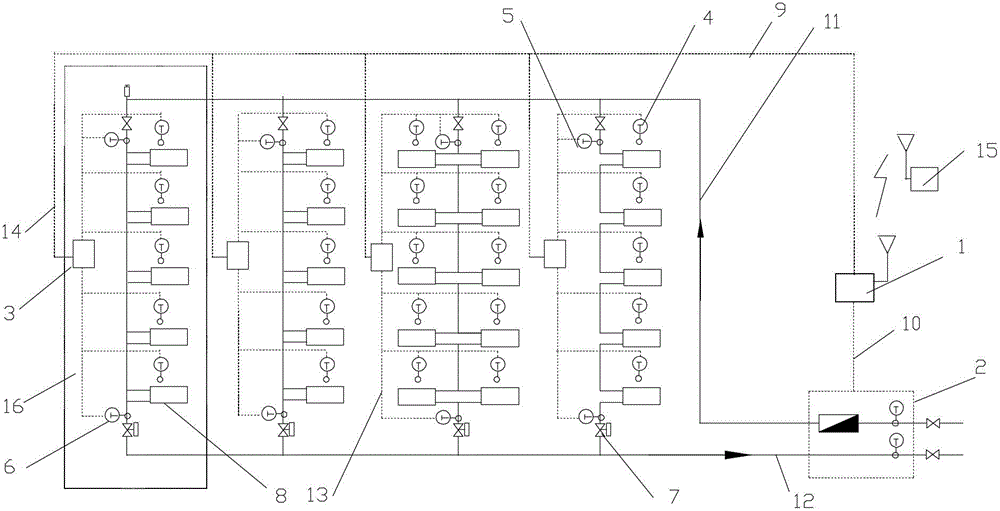
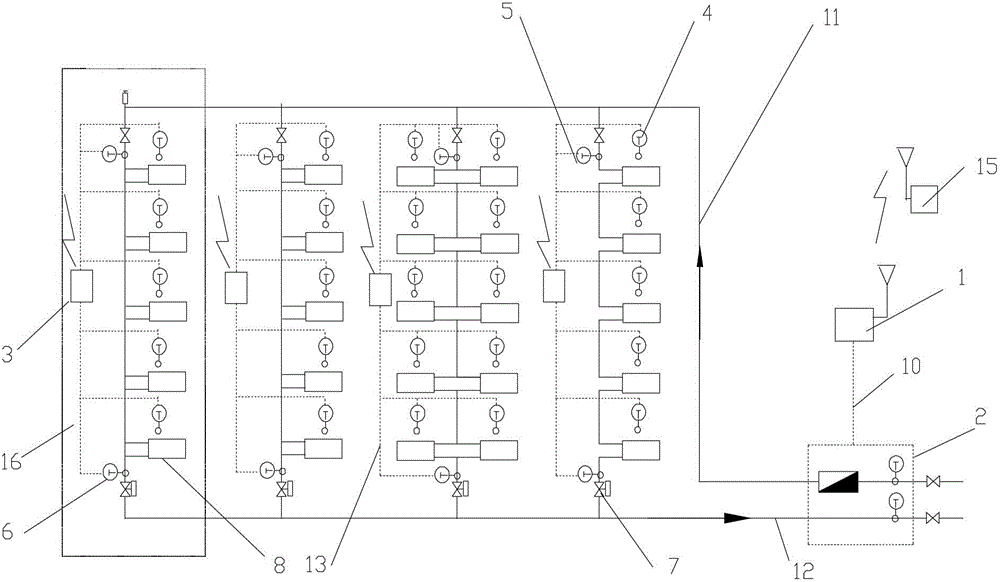
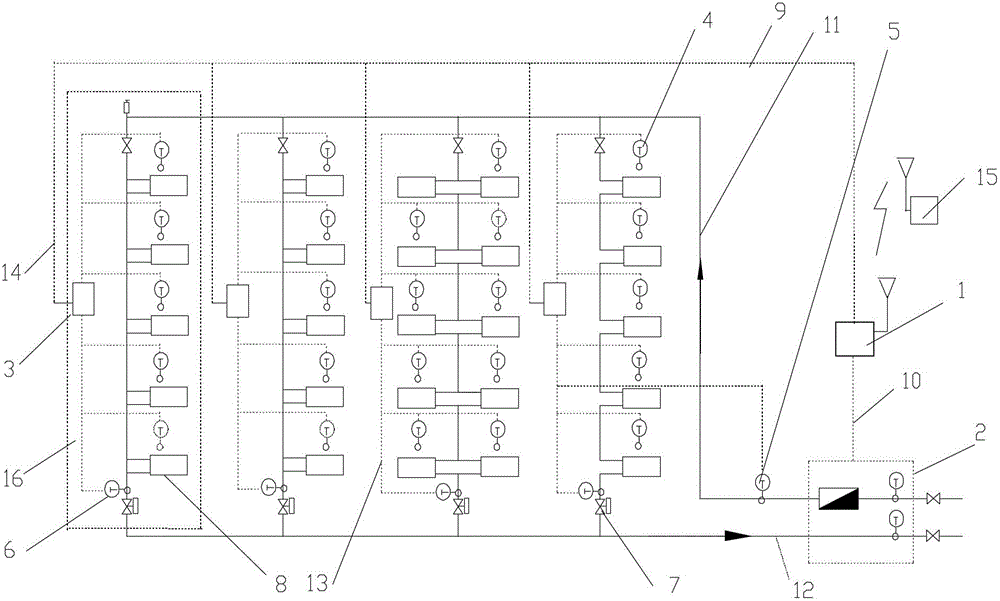
[0064] Specific implementation mode one: see Figure 5 To illustrate this embodiment, the specific calculation process of the method for measuring the heat supplied to users in a vertical single-pipe downstream system described in this embodiment is:
[0065] Step 1, collect the total heat supply of the building through the heat meter;
[0066] Step 2, collect the actual room temperature of each user in the building through the room temperature sensor installed in each household;
[0067] Step 3, collect the water supply temperature of the standpipe through the water supply temperature sensor arranged at the uppermost end of each standpipe of the heating system;
[0068] Step 4: Collect the return water temperature of the standpipe through the return water temperature sensor at the bottom of each standpipe in the heating system;
[0069] Step 5, by adjusting the opening of the flow controller arranged on each standpipe, the heating system is adjusted to balance, and the flow...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0077] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the method for measuring the heat supply of heat users in the vertical single-pipe downstream system described in Embodiment 1 is that the calculation of the heat supply of each standpipe in the step 8 The method is:
[0078] For a building with m risers, where m is a natural number greater than 1, the characteristic coefficient a of riser i calculated according to step 7 i The value is calculated according to the formula (5), i is the serial number of the riser, and i is any natural number less than or equal to m,
[0079] Q ij =a i x ij (5)
[0080] In the formula:
[0081] Q ij Indicates the heat supply of standpipe i under working condition j, the unit is KJ;
[0082] a i Indicates the characteristic coefficient a value of riser i;
[0083] x ij Indicates the unit heat dissipation of the radiator on the riser i under the j working condition, which is determined according to the temperature d...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0085] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the method for measuring the heat supply of heat users in the vertical single-pipe downstream system described in Embodiment 1 is that the method for calculating the flow rate of each standpipe in the above step 9 is as follows: :
[0086] According to the water supply temperature, return water temperature and heat supply of standpipe i obtained in step 3, step 4 and step 8 in working condition j, the flow rate of standpipe is calculated according to formula (6),
[0087] G ij = Q ij c ( t ijg - t ijh ) - - - ( 6 )
[0088] In ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com