Method for extracting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
A methicillin, staphylococcus-resistant technology, applied in DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology and other directions, can solve the problems of complex process, limited sensitivity, containing harmful chemicals, etc., and achieve the effect of simple preparation process and high detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0025] Example 1
[0026] 1) Configuration of lysate:
[0027] Weigh Tris (tris(hydroxymethylaminomethane, molecular weight 121.14)), Na2-EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid sodium salt, molecular weight 336.21), chelex100 (weak cation chelating resin), lysozyme, lysozyme (lysostaphin) and proteinase K are dissolved in an appropriate amount of sterile water, then an appropriate volume of Triton x-100 solution is added, the pH value is adjusted to 8.0 with HCL (or NaOH), and the volume is made constant with sterile water.
[0028] The final concentration of the solution is as follows (pH8.0): 20mM (ie mmol / L) Tris (tris(hydroxymethylaminomethane)); 2 mM Na2-EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid sodium salt); 1.0%(v / v) Triton x-100; 20mg / ml lysozyme; 0.10g / ml chelex100 (weak cation chelating resin); 100ug / ml lysostaphin; 2mg / ml proteinase K; the rest is sterile water;
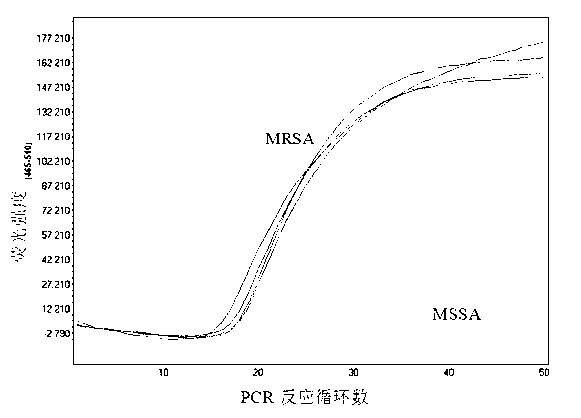
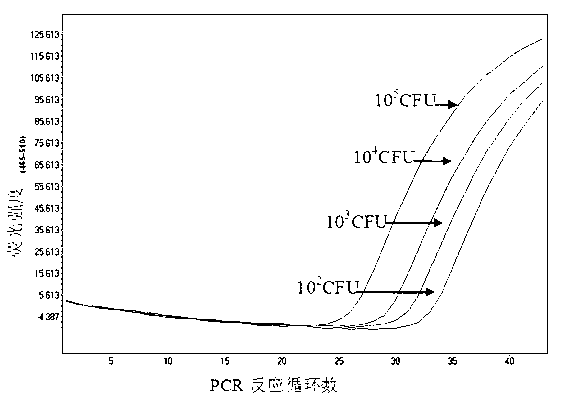
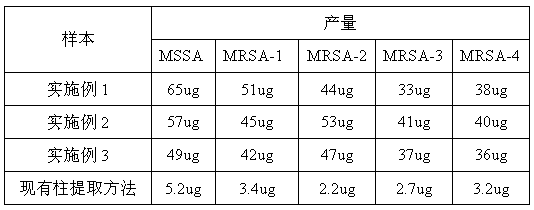
[0029] 2) 5 clinically isolated Staphylococcus aureus strains, including 1 strain of MSSA and 4 strains of MRSA, we...
Example Embodiment
[0031] Example 2
[0032] The configuration of the lysis solution in this embodiment is as follows:
[0033] Weigh Tris (tris(hydroxymethylaminomethane, molecular weight 121.14)), Na2-EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid sodium salt, molecular weight 336.21), chelex100 (weak cation chelating resin), lysozyme, lysozyme (lysostaphin) and proteinase K are dissolved in an appropriate amount of sterile water, then an appropriate volume of Triton x-100 solution is added, the pH value is adjusted to 8.0 with HCL (or NaOH), and the volume is made constant with sterile water.
[0034] The final concentration of the solution is as follows (pH8.0): 20mM (ie mmol / L) Tris (tris(hydroxymethylaminomethane)); 2 mM Na2-EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid sodium salt); 1.0%(v / v) Triton x-100; 20mg / ml lysozyme; 0.05g / ml chelex100 (weak cation chelating resin); 90ug / ml lysostaphin; 2mg / ml proteinase K; the rest is sterile water.
[0035] Then take 5 strains of clinically isolated Staphylococcus aureu...
Example Embodiment
[0036] Example 3
[0037] The configuration of the lysis solution in this embodiment is as follows:
[0038] Weigh Tris (tris(hydroxymethylaminomethane, molecular weight 121.14)), Na2-EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid sodium salt, molecular weight 336.21), chelex100 (weak cation chelating resin), lysozyme, lysozyme (lysostaphin) and proteinase K are dissolved in an appropriate amount of sterile water, then an appropriate volume of Triton x-100 solution is added, the pH value is adjusted to 8.0 with HCL (or NaOH), and the volume is made constant with sterile water.
[0039] The final concentration of the solution is as follows (pH 8.0): 20mM (ie mmol / L) Tris (tris(hydroxymethylaminomethane)); 2 mM Na2-EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid sodium salt); 1.0%(v / v) Triton x-100; 20mg / ml lysozyme; 0.15g / ml chelex100 (weak cation chelating resin); 100ug / ml lysostaphin; 1.8mg / ml proteinase K; the rest is sterile water .
[0040] Then take 5 strains of clinically isolated Staphylococcus...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap