Dynamic bidirectional-stretch in-situ online-observation cell biomechanics loading device
A biaxial stretching and biomechanical technology, applied in biochemical cleaning devices, enzymology/microbiology devices, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of inability to realize online observation of dynamic loading of adherent cells.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
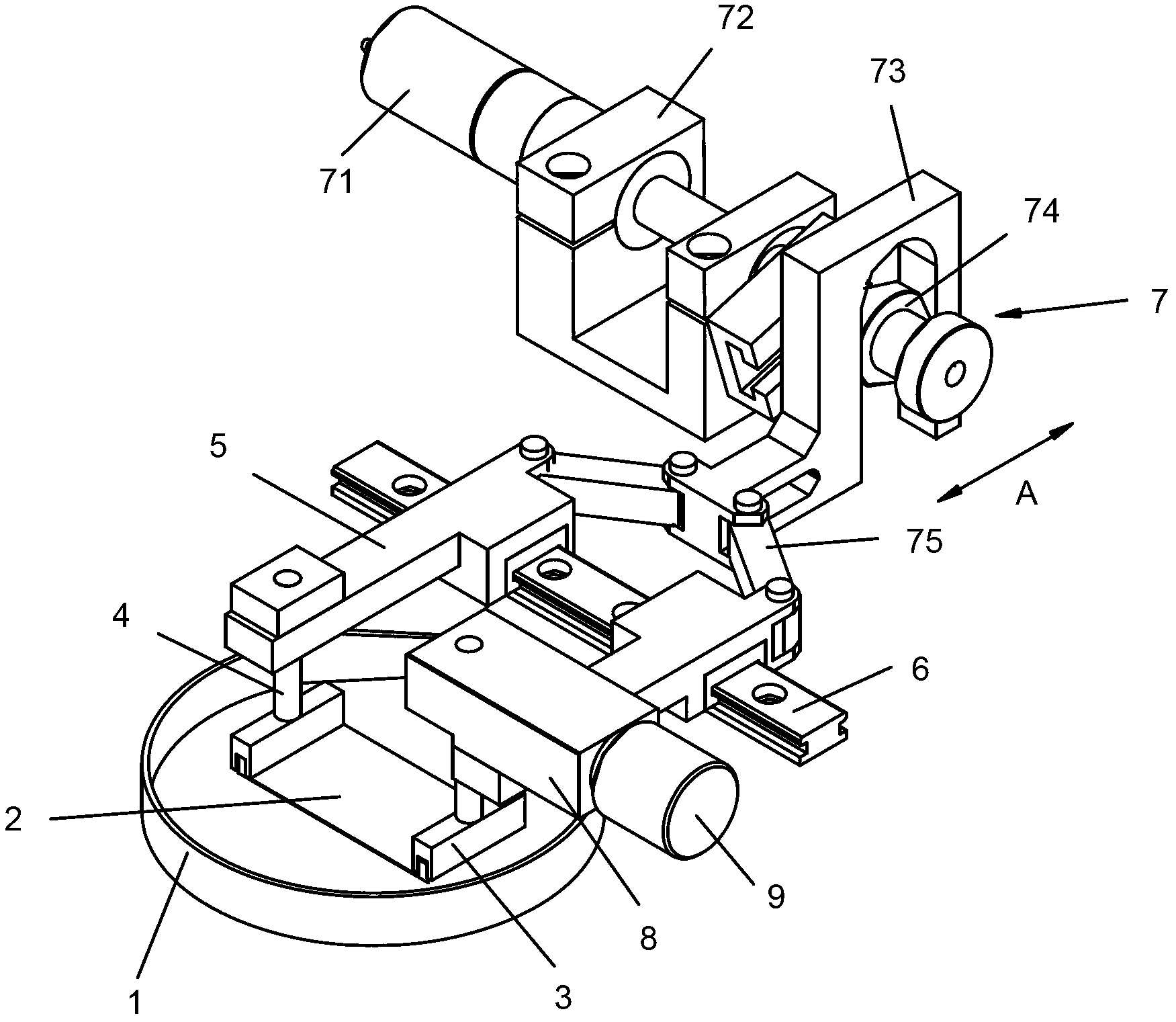
[0015] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention includes: a base film 2 , a fixing clip 3 , a displacement support arm 4 and a driving part 7 . Adherent cells grown on basement membrane 2 for observation. There are two fixing clips 3, which respectively clamp the two sides of the basement membrane 2. There are also two displacement support arms 4, which are arranged corresponding to the fixing clips 3, and are used to respectively support the fixing clips 3, and the fixing clips 3 are movably arranged on the guide rail 6. The driving part 7 is used to drive the displacement support arm 4 to move symmetrically and oppositely on the guide rail 6, so as to bidirectionally stretch the base film 2 .
[0016] Such as figure 1 As shown, in the embodiment of the present invention, the drive portion 7 includes: a drive motor 71, a varicose arm 75, a deflection wheel chute 73, a deflection wheel 74 and a motor bracket 72; the drive motor 71 is arranged on the motor bracket 3,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com